Graphical Representation of Data | General Aptitude for GATE - Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Bar graphs and Histograms |

|
| Bar Graph |

|
| Comparing two sets of data |

|
| Significance of a Bar Graph |

|
| Histograms |

|
| Frequency Polygons |

|
Bar graphs and Histograms
- The science of collecting and analyzing data in large quantities, especially for inferring proportions in a whole form is known as Statistics. The word ‘statistics’ itself refers to numbers that are used to describe the relationships of data. Therefore, we can say that the field of applied mathematics that deals with data collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation is called statistics.
- A Bar graph or a Histogram is the diagrammatic representation of data in statistics. In bar graphs or histograms, the use of graphs, charts, and tabular data makes it very easy to understand the concept and relationships among data.
Bar Graph
The pictorial representation of data in groups, either in horizontal or vertical bars where the length of the bar represents the value of the data present on axis. They (bar graphs) are usually used to display or impart the information belonging to ‘categorical data’ i.e; data that fit in some category.
Reading a Bar Graph and comparing two sets of data
In order to read a Bar graph, we need to ask questions to ourselves looking at the displayed graph. Let’s understand reading a Bar graph through a very basic example,
Different types of fruits liked by People,
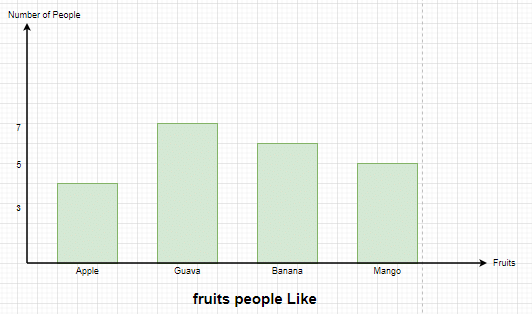
What does the X-axis and Y-axis on the graph are representing?
The X-axis represents the different types of fruits like apple, guava. while Y-axis represents the Number of people.
What is the Common base for the Bars?
The bars are showing a common base of category of fruits.
What is the scale used on the Y-axis?
The scale used is normal, i.e; 1 Unit = 1 person
Overall, what kind of information the bar graph displaying?
The bar graph is displaying the number of People liking different types of fruits.
Looking at the bar Graph, can one answer, how many people like Mango?
Yes, By observing the length of the bar, one can tell that there are 5 people who like Mango.
Comparing two sets of data
Noticing the graph, explain the fruit liked by most people and the fruit liked by least people?
The data displayed on the graph is easily comparable, it can be concluded that the most liked fruit is Guava and the least liked fruit is Apple.
How many more people like Guava than Mango?
There are 7 people who like guava and 5 who like Mango. Thus, we can say that there are 2 more people liking guava.
It can be concluded the following just by looking at the graph:
- 4 People like Apples.
- 7 People like guava.
- 6 People like banana.
- 5 People like Mango.
Properties of Bar Graph
- All Bars have a common base.
- The length of each bar corresponds to its respective data mentioned on the axis (Y-axis for Vertical Graph, X-axis for Horizontal Graph).
- Each bar displayed has the same width.
- The distance between consecutive bars is the same
Significance of a Bar Graph
It is always easier and more comfortable to visually understand something than to look at the large table of Numerical data. Bar graphs are extensively used in presentations and reports. It is very prominently used as it summarizes data and displays it in a frequency distribution.Sample Problems on Bar Graph
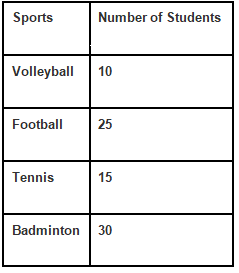
Question 1: Draw the Bar Graph for the following table,
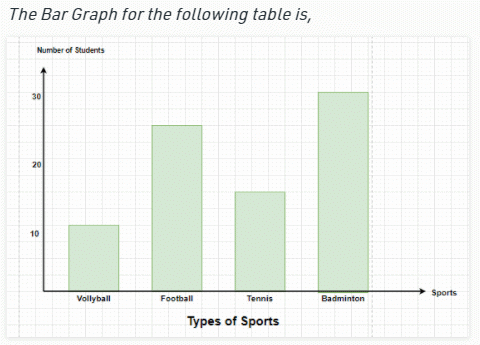
Solution:
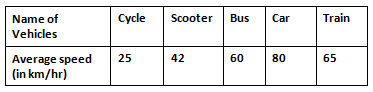
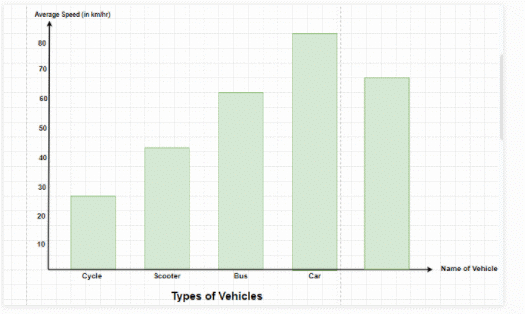
Question 2: The average speed of some vehicles is shown below, Represent it through a bar graph.
Solution:
The average speed mentioned in the table is the frequency which decides the length of each bar graph, therefore, if the graph is vertical, the Average speed will be shown on the y-axis and the types of vehicles will be shown on the x-axis.
Histograms
Histograms are the graphical display of data with the help of bars, the heights of the bars may vary due to different data. The similarity of a Histogram resembles a bar chart, but histogram groups numbers into different ranges. The length of each bar tells how many fall into each range, and it can be decided which ranges are to be used.
Construction and interpretation of Histogram
- First, mark the class intervals on X-axis and frequencies on Y-axis.
- Make sure that the scale of both axes is the same.
- The class Intervals shall always be exclusive.
- Create bars with class intervals on the x-axis and corresponding frequencies on the y-axis.
- The length of each bar reflects the Frequency when intervals are equal.
- The area of each bar is the same as its respective frequency when intervals are unequal.
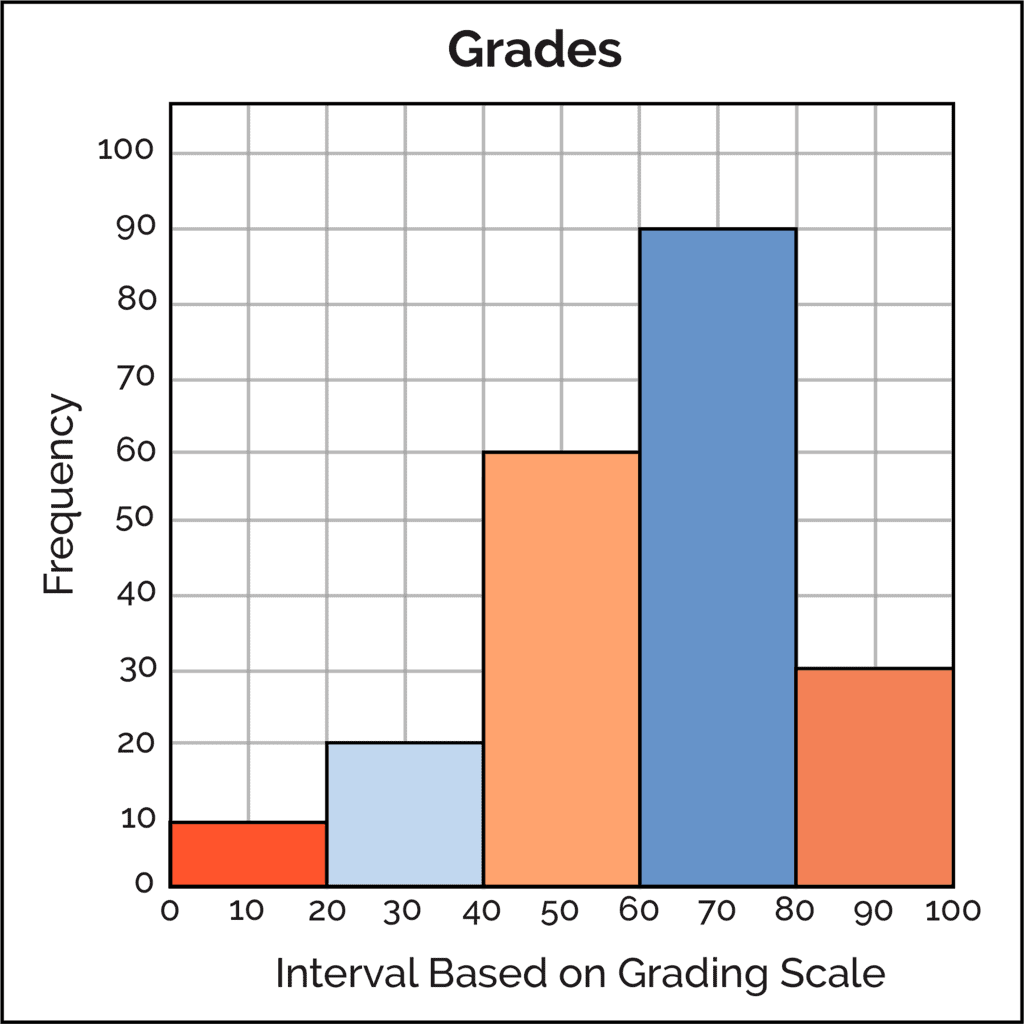 A Histogram
A Histogram
Difference Between Histograms and Bar graph
- Bar graph is a one-dimensional figure while Histogram is a two-dimensional figure.
- In Bar graphs, the length of the bars shows the frequency, but the width has no special significance but in Histograms, the frequency is shown by the area of the bar.
- In bar graphs, the bars are separated from each other with equal spaces, while in Histograms, the bars are always touching each other.
Sample Problems on Histogram
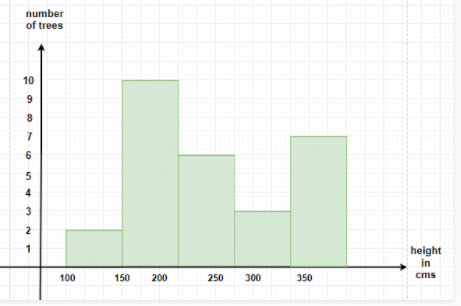
Question 1: In a Park, there are 28 trees of different heights, the heights can be measured in centimeters and the range of the trees lie between 100-350 cms. Draw the Histogram for the following data,
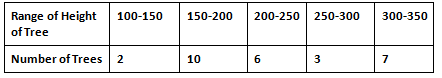
Solution:
Since the height of the trees are lying between 100-350, we shall start by marking the heights on x-axis in groups of 50cm each and the number of trees will be mentioned on y-axis.
Therefore, if a tree has a height of 230 cm, it will lie in the rectangle 200-250.
Question 2: In the below-given table, the number of machines working in a factory for their fixed amount of time is shown. Draw the Histogram for the following data.
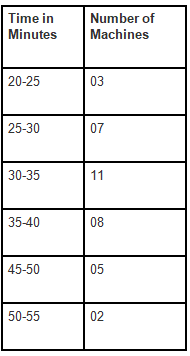
Solution:
The Histogram for the table mentioned above will have class intervals of 5 minutes on x-axis and the number of machines used should be on y-axis.
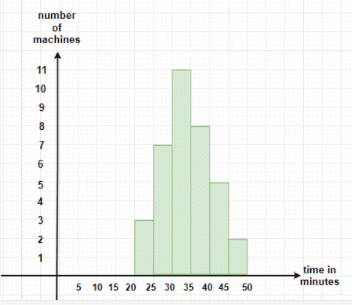
Frequency Polygons
A frequency polygon is almost identical to a histogram, which is used to compare sets of data or to display a cumulative frequency distribution. It uses a line graph to represent quantitative data.
Statistics deals with the collection of data and information for a particular purpose. The tabulation of each run for each ball in cricket gives the statistics of the game. Tables, graphs, pie-charts, bar graphs, histograms, polygons etc. are used to represent statistical data pictorially.
Frequency polygons are a visually substantial method of representing quantitative data and its frequencies. Let us discuss how to represent a frequency polygon.
Steps to Draw Frequency Polygon
To draw frequency polygons, first we need to draw histogram and then follow the below steps:
- Step 1- Choose the class interval and mark the values on the horizontal axes
- Step 2- Mark the mid value of each interval on the horizontal axes.
- Step 3- Mark the frequency of the class on the vertical axes.
- Step 4- Corresponding to the frequency of each class interval, mark a point at the height in the middle of the class interval
- Step 5- Connect these points using the line segment.
- Step 6- The obtained representation is a frequency polygon.
Let us consider an example to understand this in a better way.
Example 1: In a batch of 400 students, the height of students is given in the following table. Represent it through a frequency polygon.
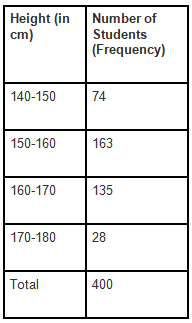
Solution: Following steps are to be followed to construct a histogram from the given data:
- The heights are represented on the horizontal axes on a suitable scale as shown.
- The number of students is represented on the vertical axes on a suitable scale as shown.
- Now rectangular bars of widths equal to the class- size and the length of the bars corresponding to a frequency of the class interval is drawn.
ABCDEF represents the given data graphically in form of frequency polygon as:
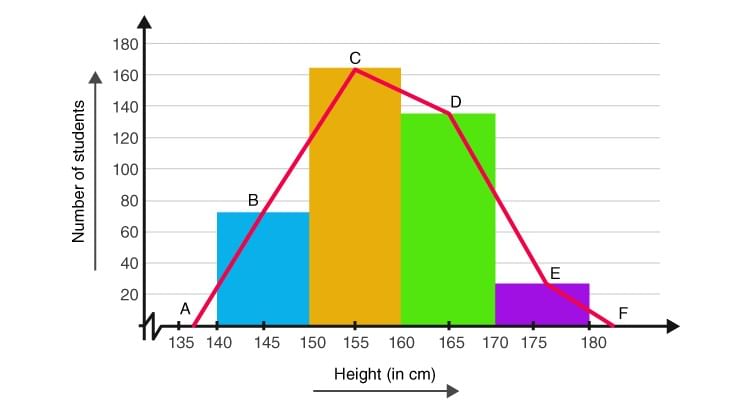
Frequency polygons can also be drawn independently without drawing histograms. For this, the midpoints of the class intervals known as class marks are used to plot the points.
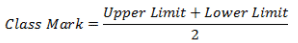
|
193 videos|169 docs|152 tests
|
FAQs on Graphical Representation of Data - General Aptitude for GATE - Mechanical Engineering
| 1. What is the difference between a bar graph and a histogram? |  |
| 2. How can a bar graph be used to compare two sets of data? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of using a bar graph? |  |
| 4. How are histograms different from bar graphs? |  |
| 5. What is the purpose of a frequency polygon in graphical representation of data? |  |
















