Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > History for GCSE/IGCSE > How Did Hitler Consolidate His Power in 1933–34?
How Did Hitler Consolidate His Power in 1933–34? | History for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Hitler's Path to Dictatorship - Timeline & Summary
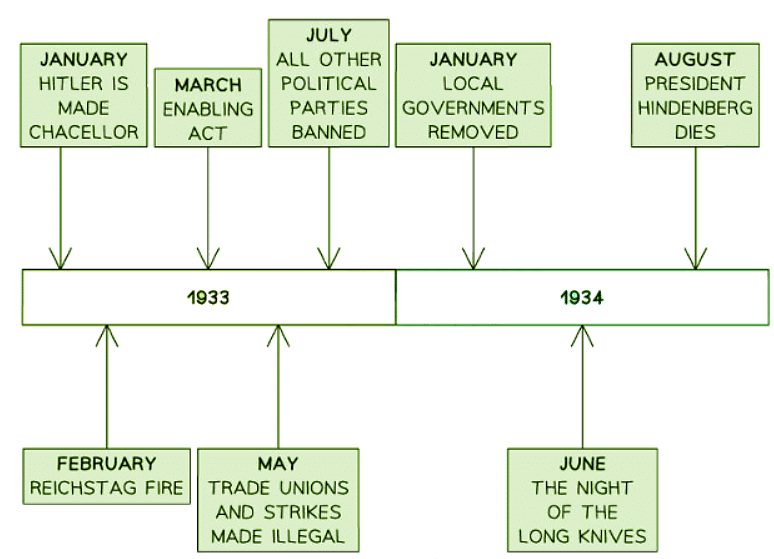
- Hitler’s appointment as chancellor on 30th January 1933 marked the initial step in his ascent to total control over Germany.
- The Reichstag Fire provided the Nazi Party with the legal pretext to limit and suppress the power of the KPD.
- After achieving a two-thirds majority in the March 1933 election, Hitler passed the Enabling Act, transforming Germany into a one-party state. This law silenced opposition, banned trade unions, and placed local governments under pro-Nazi leaders.
- With external opposition significantly reduced, Hitler focused on dissent within the Nazi Party. Ernst Röhm, head of the SA, had distanced himself from Hitler, and the SA was growing increasingly restless due to unemployment, similar to the Freikorps before the Kapp Putsch of 1920. During the Night of the Long Knives, Hitler purged leading members of the SA.
- The death of President Hindenburg in August 1934 enabled Hitler to become Führer, marking the end of the Weimar Republic and the beginning of Nazi Germany.
The Reichstag Fire
- Upon assuming Chancellorship on January 30, 1933, Hitler faced a divided Germany:
- The Nazi Party's control was limited to one-third of the Reichstag.
- President Hindenburg wielded significant power.
- The Weimar Constitution restricted the Chancellor's authority.
- A pivotal incident occurred on February 27, 1933, when the Reichstag building was engulfed in flames.
- Dutch Communist Marinus van der Lubbe was apprehended at the scene and later executed.
- The blaze led to the arrest of approximately 4,000 Communists.
- Exploiting the crisis, Hitler urged Hindenburg to enact the Reichstag Fire Decree.
- Blaming the Communist Party (KPD), Hitler used the decree to suppress political opponents.
- Subsequently, Hitler's regime resorted to violence and intimidation against dissenters.
Question for How Did Hitler Consolidate His Power in 1933–34?Try yourself: What event provided the Nazi Party with the legal pretext to limit and suppress the power of the KPD?View Solution
The Election of 1933
- In March 1933, crucial Reichstag elections were conducted by the government.
- The infamous Reichstag Fire incident granted Hitler power over the radio, a pivotal tool for propaganda.
- Hitler utilized the SA and SS forces to instill fear and suppress his adversaries.
Election Results Importance:
- The election outcomes carried significant weight as the Nazis secured close to 44% of the votes.
- However, this fell short of the essential two-thirds majority required to alter the constitution.
- Subsequently, Hitler maneuvered a coalition with the Nationalists and the Centre Party by employing a mix of promises and threats.
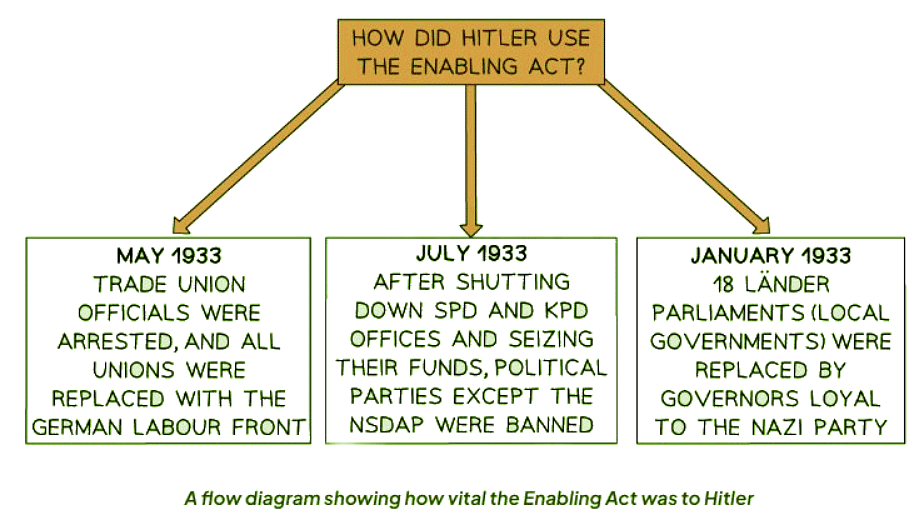
The Enabling Act
- The Enabling Act, passed on 24th March 1933 with a significant majority, granted the Nazi Party extensive powers.
- The Communist Party's 81 members were absent during the vote, while the Social Democratic Party (SPD) was the sole opposition.
- The SA, under Nazi influence, exerted intimidation tactics on Reichstag members before the vote.
- Chancellor Hitler gained the authority to introduce new laws, which could be approved by his cabinet without Reichstag's consent.
- These laws had the supremacy to override the Weimar Constitution, essentially undermining democratic principles.
- Initially valid for four years, the Enabling Act was later renewed in 1937, solidifying authoritarian control.
- Subsequently, parties within the Reichstag lost the ability to contest or impede new legislations, leading to the demise of democratic governance in Germany.
Removing Public Opposition
- Hitler's regime implemented the Enabling Act, providing him with unparalleled legislative control, enabling the Nazi Party to pass laws without Reichstag's consent. This measure effectively sidelined any opposition, consolidating power in Hitler's hands.
- For instance, Hitler leveraged the Enabling Act to quash dissenting voices within the public sphere. By curtailing freedom of speech and assembly, Hitler ensured that only the Nazi Party's narrative prevailed, stifling any opposition.
The Night of the Long Knives
- The Enabling Act empowered Hitler to eliminate opposition to the Nazi Party from outside forces.
- Internal dissent, especially from SA leader Ernst Röhm, troubled Hitler due to Röhm's suspected homosexuality conflicting with Nazi ideology. Röhm, commanding three million SA members, a majority unemployed, advocated merging the SA with the military and pushing for a "second revolution" focused on the working class, diverging from Hitler's pro-rich stance, resembling Communist tactics. Tensions escalated as Röhm's SA clashed with the SS, led by Himmler and Heydrich.
- Faced with a potential threat of martial law from Hindenburg over the unruly SA, Hitler orchestrated a meeting on June 30, 1934, in Bad Wiessee, resulting in Röhm's arrest and subsequent execution, along with 400 SA members. Other opponents like von Schleicher, Gregor Strasser, and von Kahr met similar fates. The Nazi Party falsely alleged that Röhm plotted against Hitler, justifying his demise as serving the national interest.
Question for How Did Hitler Consolidate His Power in 1933–34?Try yourself: What was the significance of the Election of 1933 for Hitler and the Nazi Party?View Solution
The Death of Hindenburg
- Paul von Hindenburg served as the President of Germany starting from 1925 until his demise.
- On the 2nd of August 1934, at the age of 86, Hindenburg passed away due to lung cancer.
- Following Hindenburg's death, Hitler merged the roles of president and chancellor, establishing himself as the Führer.
- An overwhelming 90% of the populace supported Hitler's consolidation of power as the Führer.
- Hitler mandated that all soldiers pledge an oath of allegiance to him, solidifying his authority.
- This significant turn of events marked the conclusion of the Weimar Republic era and the inception of Hitler's Nazi Germany regime.
The document How Did Hitler Consolidate His Power in 1933–34? | History for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course History for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
81 videos|86 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on How Did Hitler Consolidate His Power in 1933–34? - History for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. How did Hitler consolidate his power in 1933-34? |  |
Ans. Hitler consolidated his power in 1933-34 through events such as the Reichstag Fire, the Election of 1933, the Enabling Act, the removal of public opposition, the Night of the Long Knives, and the death of Hindenburg.
| 2. What role did the Reichstag Fire play in Hitler's path to dictatorship? |  |
Ans. The Reichstag Fire, which occurred in February 1933, was used by Hitler as a pretext to push through the Reichstag Fire Decree, which suspended civil liberties and allowed for the arrest of political opponents. This event helped Hitler consolidate his power by weakening the opposition.
| 3. How did Hitler use the Enabling Act to strengthen his dictatorship? |  |
Ans. The Enabling Act, passed in March 1933, gave Hitler the authority to enact laws without the consent of the Reichstag. This allowed him to bypass democratic processes and consolidate his power by making him essentially a dictator.
| 4. What was the significance of the Night of the Long Knives in Hitler's consolidation of power? |  |
Ans. The Night of the Long Knives, which took place in June 1934, was a purge of the SA (Sturmabteilung) leadership and other political opponents. This event eliminated internal opposition to Hitler within the Nazi Party and helped solidify his control over Germany.
| 5. How did the death of Hindenburg contribute to Hitler's rise to dictatorship? |  |
Ans. The death of President Hindenburg in August 1934 allowed Hitler to merge the positions of Chancellor and President, making him the sole leader of Germany. This consolidation of power further solidified Hitler's dictatorship.
Related Searches


















