Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > History for GCSE/IGCSE > How Did Young People React to the Nazi Regime?
How Did Young People React to the Nazi Regime? | History for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Education and Youth in Nazi Germany - Summary |

|
| Nazi Beliefs Towards the Young |

|
| The Hitler Youth and the League of German Maidens |

|
| The Impact of Youth Groups |

|
| Education in Nazi Germany |

|
Education and Youth in Nazi Germany - Summary
- Hitler and the Nazi Party implemented numerous changes that profoundly impacted Germany's youth. Their policies targeted the establishment of youth groups and children's education, aiming to indoctrinate young people with radical Nazi ideology.
- By 1933, boys and girls in Germany were permitted to join only one of the available Nazi youth groups. Male teenagers were encouraged to join the Hitler Youth, emphasizing physical and military training. Hitler envisioned creating a future army to safeguard Nazi Germany. Teenage girls were urged to join the League of German Maidens, focusing on skills such as cooking and needlework. While physical activities were included, the emphasis was on preparing them to be capable mothers and produce healthy offspring.
- Education in schools was also tailored to promote Nazi beliefs. The curriculum included lessons on eugenics, with a strong focus on physical education, particularly for boys. Girls learned about the importance of marrying "pure" German men. The educational system was tightly controlled, and all teachers were expected to join the Nazi Teachers' League.
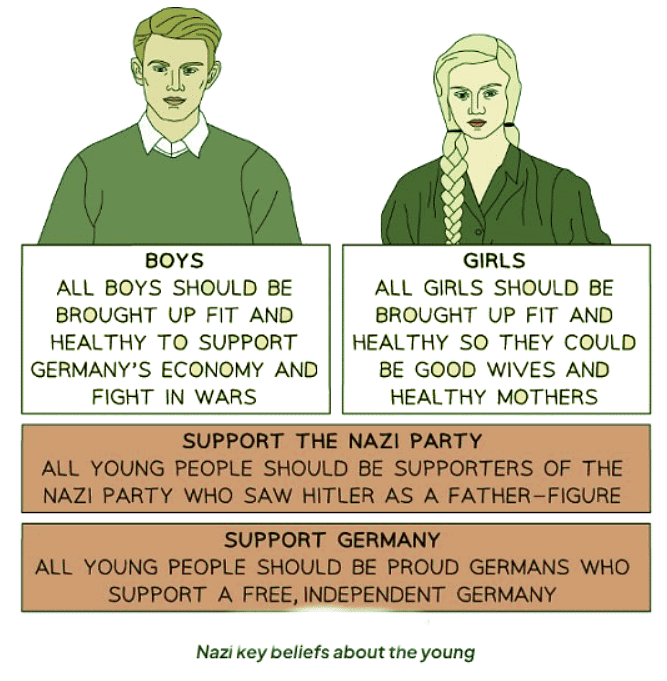
Nazi Beliefs Towards the Young
- Hitler and the Nazis aimed to establish a Third Reich enduring for a millennium.
- Hitler acknowledged that adults in Nazi Germany held diverse opinions of the Nazi Party, being harder to sway than the youth.
- Adults were more challenging to influence and change compared to the young.
- Control of the youth and future generations was crucial for ensuring continuous public support for the Nazi Party.
- The Nazis held specific beliefs regarding the young:
The Hitler Youth and the League of German Maidens
- The Nazis implemented various changes in the 1930s to increase the membership of the Nazi youth groups.

Types of Nazi Youth Groups
- Distinct youth organizations existed for boys and girls across different age groups.

The Hitler Youth
- Baldur von Schirach led the Hitler Youth organization.
- Boys who were 14 years old could become members of the Hitler Youth.
- Upon reaching 18 years of age, boys transitioned to becoming members of the Nazi Party and participated in either work or military service.
- The training within the Hitler Youth was segmented into four distinct areas:


The League of German Maidens
- The League of German Maidens, also known as the Bund Deutscher Mädel (BDM), functioned as the female counterpart to the Hitler Youth with a focus on domestic roles.
- Unlike the Hitler Youth, the BDM concentrated on preparing young girls for traditional roles as wives and mothers.

- The activities within both organizations revolved around the concept of the 'three Ks': Kinder (Children), Kirche (Church), and Küche (Cooking).
- In 1938, the Nazis established a subgroup of the League of German Maidens (BDM) known as the 'Faith and Beauty Society' to cater to girls aged 17-21.
- The primary concern of the Nazis was that BDM members might forget their teachings upon leaving the organization at 18 years old.
- The 'Faith and Beauty Society' functioned as a platform for young women to continue their education until they were eligible to join the National Socialist Women's League.
The Impact of Youth Groups
- By 1939, the membership in Nazi youth groups had reached nine million, but not all members found the experience enjoyable.
Education in Nazi Germany
- Children in Nazi Germany were not only expected to join a Nazi youth group but also attend school for education.
- Adolf Hitler understood that shaping children's education would enable him to cultivate a generation loyal to the Nazi ideology.
- In 1934, Bernhard Rust assumed the role of Education Minister and implemented significant reforms in the education system, impacting teachers and schools.
Teachers
- Teachers who were not loyal to the Nazi regime were dismissed.
- Rust dismissed over 180 teachers in Prussia.
- Teachers were required to swear an oath of loyalty to Hitler and join the Nazi Teachers' League.
- Membership of the Nazi Party was mandatory.
- Teachers had to attend political education courses that taught key Nazi ideologies.
- Responsibilities of Teachers:
- Teach students the Nazi salute.
- Begin and end each lesson with 'Heil Hitler'.
- Display posters, Nazi flags, and a picture of Hitler in each classroom.
Curriculum
- Education was strictly segregated by gender, with boys and girls receiving separate schooling.
- The Nazi regime controlled the curriculum to shape the beliefs of children.

- After 1935, the Nazis gained authority to approve all educational textbooks.
- Textbooks were mandated to include images of Hitler, promoting a cult of personality.
- "Mein Kampf" by Adolf Hitler became a compulsory read for students.
- Historical events like the First World War were manipulated to shift blame onto Jewish people and the so-called "November Criminals."
- Napolas were institutions intended for the most 'gifted' and racially pure children.
- These schools were administered by SS members who replaced conventional teachers.
- The curriculum emphasized physical training and sports, grooming students for roles in the SS or police services.
- By 1939, there were 16 Napolas schools in operation.
The document How Did Young People React to the Nazi Regime? | History for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course History for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
81 videos|86 docs|18 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Year 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches

















