How to Solve Form, Note, Table, Flow-chart & Summary Completion type of Questions | Listening for IELTS PDF Download
Diagrams & Flowcharts
This lesson includes examples of two IELTS Listening practice tests. One is a diagram labelling question, the other a flowchart question. Both types come up regularly in the Listening test so you need to know how to answer them.
The lesson includes:
- Sample questions
- Strategy & tips
- Practice question
- Answers
- Vocabulary tips
Diagram labelling
- In diagram labelling questions, you will be given a diagram of a process, an object, a structure or a machine and you must either fill in the missing labels or complete notes within the diagram.
- You could get almost any topic. Examples of diagrams from past papers have included a beehive, a soda can, a fire extinguisher, a Ferris wheel, a zip fastener, a solar heating system, an undersea turbine and soil layers.
- As long as you have a good strategy to follow, you’ll be able to answers questions on any subject. In fact, students generally find this one of the easiest question types to answer because the graphic and the existing labels give lots of clues as to what the missing words might be.
- Here’s a typical question to give you an idea of what to expect. I’ll be using this example to practice the strategy and tips I’m about to show you.
IELTS Listening Practice Tests – 1: Float Project
Flowchart Completion
- Flowchart Completion questions, on the other hand, show the steps of a process. The process will have a start and an end with several steps in between.
- It could be about almost anything that can be broken down into stages, for example, the outline of a lecture or essay, an application process, the stages of a training course or a short manufacturing process.
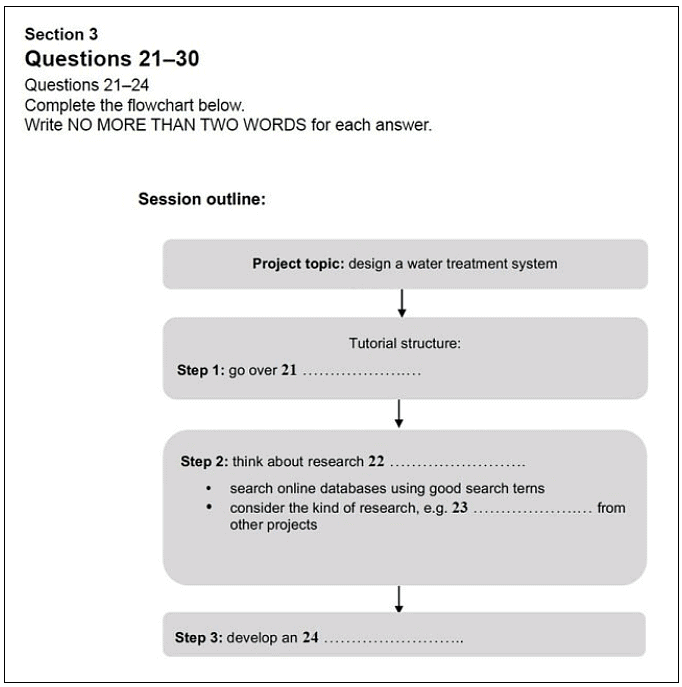
- The graphic in the sample question below shows the 3 stages of a project to design a water treatment system. Like most flowchart completion questions, it occurs in Section 3 where the recording will be a conversation between up to four people set in an educational or training context.
IELTS Listening Practice Tests – 2: Water Treatment System
Strategy & Tips
You will have a short time to prepare before the speakers begin talking. Use this time to familiarise yourself with the question and focus your mind on what you need to listen out for.
1. Read the instructions
Read the instruction carefully, paying particular attention to how many words you’re allowed to write for the answer.
The instructions for our sample diagram question state that you must,
Write NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER for each answer.
If you write more than three words, your answer will be marked incorrect even if the information you give is correct.
Other questions might tell you to write NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS or ONLY ONE WORD, so be careful. Don’t lose marks over silly mistakes like this.
2. Read the labels & title
Learn as much as you can from the title and existing labels. The information you get from them will help you to understand the diagram and give you clues as to what the speaker(s) will talk about.
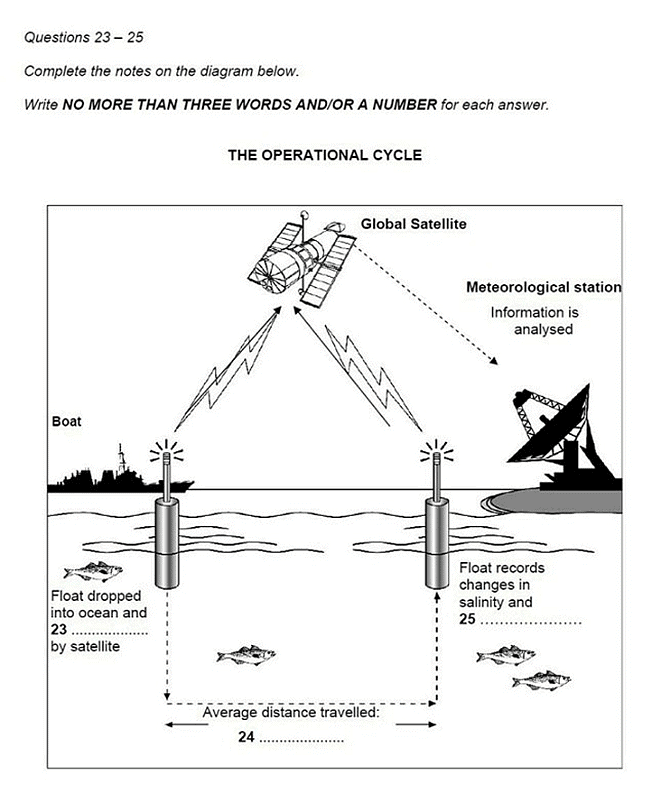
Here’s the diagram from our IELTS Listening practice test. Spend a few moments looking at it to see what you can learn. 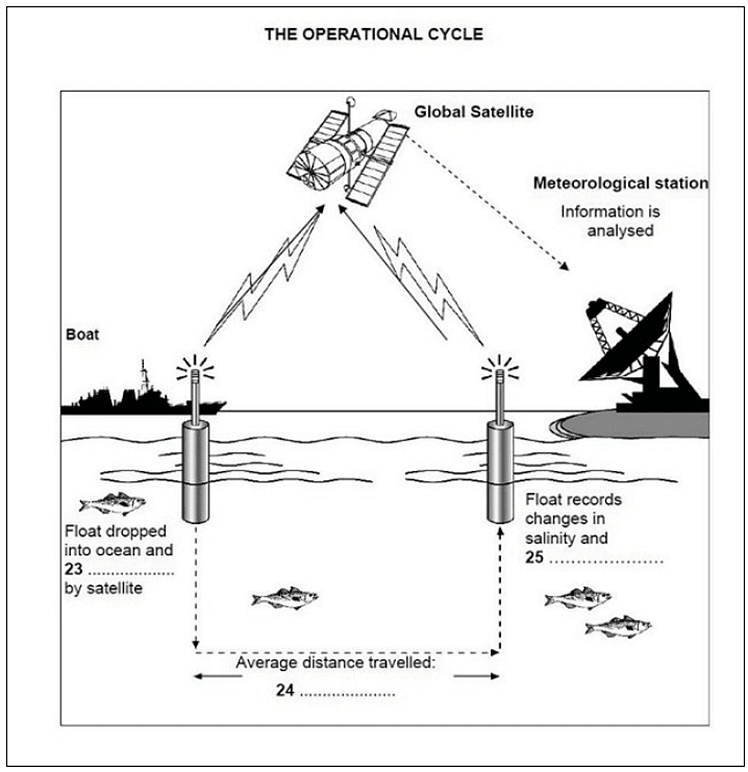
3. Predict the answers
Try to predict what the answers might be. This will focus your mind on what to listen out for in the recording.
Occasionally, you’ll be able to predict the actual word but mostly it’s one of these things that you’ll be able to determine:
- The type of information required, e.g. a name, a number, a percentage.
- The type of word required, e.g. noun, adjective, verb.
Any clues you can get will help you to understand the recording and identify the information needed for the answers.
Have a go at predicting some of the answers in our practice question. Then have a look at my predictions below.
- Predictions:
- 23 – a verb
- 24 – a number (measurement)
- 25 – a noun
4. Synonyms and paraphrasing
- In all types of Listening questions, you need to listen out for synonyms and paraphrasing. These are something else that you may be able to predict. This is another quick task that can be done in your preparation time.
- Scan the information on the diagram to identify key words that are likely to be paraphrased and think of some synonyms or phrases that might be used. For example, the words ‘studied' or 'examined’ might be used instead of ‘analysed’.
- As you’re listening to the recording, remind yourself that you are not only looking for the exact words used in the diagram but words and phrases that have the same meaning.
- We’ll look at how the information this in IELTS Listening practice test has been paraphrased when we review the answers.
5. The introduction
Before the first speaker begins talking, there will be an introduction in which you’ll be told what the recording is about. For this question, we are told,
You will hear a part of a seminar entitled Understanding the World's Oceans given by a climate scientist.
The first speaker will then begin the talk or conversation by introducing themselves and the subject or purpose of the talk. This will help you to understand the context and give you more detail about the subject.
Here’s the first sentence of the recording.
- Scientist: Thanks to all of you for coming along today to hear about how the robotic float project is helping with ocean research.
You can see how important it is to listen carefully right from the start.
6. Answer order
The answers will come in the same order in the recording as they are listed in the question, so for this question, you'll hear answer 23 first, then answer 24 and finally, answer 25. This makes it easier to pick out the answers than if they were in a random order.
7. Watch out for distractors
The examiners may try and catch you out with distractors. A distractor is a word or a phrase that changes or corrects the original piece of information given. So, you may be given an answer and then have it taken away again.
Here are some sample sentences containing distractors. I’ve highlighted the relevant words.
- The project was launched as a collaboration between scientists from 5 countries but it has now expanded to bring together experts from 11 nations.
- It was expected that the device would work efficiently up to a depth of 1000 metres. However, accurate results are being returned from two whole kilometres down in the water.
- Funding for the project runs out in March 2022 although, we expect it to be financed for a further two years.
The use of ‘but’ and ‘however’ are particularly common distractors but there are many different words and phrases that can be used to change or correct a piece of information so be alert for them.
8. Guess if necessary
My final tip is to never leave a blank space on the answer sheet. If you miss an answer, take an educated guess. This gives you at least some chance of getting it right. Don’t stress about a missed answer or it will affect your ability to answer the next set of questions. Just make your choice and move on.
Practice Activity
It’s now time for you to practice using this strategy on our sample question. Here it is again.
IELTS Listening Practice Test – Float Project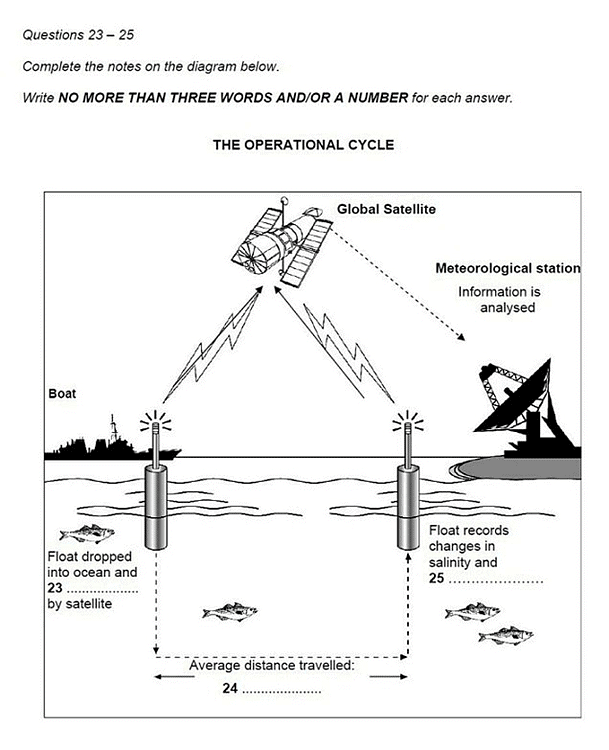
Listen to this recording and identify the answers. Refer back to the strategy as you need to and when you’ve completed the practice activity, go through the answers below.
The section of the recording in which you’ll hear the answers to this diagram question begins 1 minute 55 seconds into the recording. Listen out for the lady in the audience saying, ‘That's impressive’.
I've included the first part of the recording, for which there are two note completion questions not covered in this lesson, so that you can hear the introduction and understand the context of the seminar.
IELTS Listening Practice Test Recording – Float Project
Answers
Here are the answers. The words in brackets are correct but optional.
Answers:
23 (is) activated
24 (average) (around/about/approximately) 50 kilometres/kilometers
25 All these answer options are correct:
- change(s) in temperature
- (water/ocean/sea) temperature
- (water/ocean/sea) temperature change(s)
- temperature of water/ocean/sea
We’ll now look at them in context and examine the language that's been used, especially synonyms and paraphrasing.
Answer 23: (is) activated
Here are the diagram label and the section of the recording this answer appears in.
Question: Float dropped into ocean and 23 …………………. by satellite
The operational cycle goes like this; each of the floats is dropped in the ocean from a boat at a set point and activated from a satellite.
The examiners have been kind here as the language is almost identical in the diagram and the recording with no use of paraphrasing.
Answers 24: (average) (around/about/approximately) 50 kilometres/kilometers
Here are the diagram label and the section of the recording this answer appears in.
Question: Average distance travelled: 24 ………………….
Scientist: It stays at this depth for about 10 days and is carried around by the currents which operate in the ocean at this level. During this time, it's possible for it to cover quite large distances, but the average is 50 kilometres.
The information in the diagram is paraphrased. The words ‘average’ and ‘distance’ have been repeated but ‘travelled’ has been paraphrased in these two phrases:
- carried around by the currents
- cover quite large distances
Answers 25: All these answer options are correct:
- change(s) in temperature
- (water/ocean/sea) temperature
- (water/ocean/sea) temperature change(s)
- temperature of water/ocean/sea
Here are the diagram label and the section of the recording this answer appears in.
Question: Float records changes in salinity and 25 ………………….
Audience: So, what is it actually recording?
Scientist: Well, at this stage nothing, but as it rises to the surface it collects all sorts of data. Most importantly, variations in salinity, that's salt levels, and the changes in temperature - a bit like underwater weather balloons.
This section of text contains a distractor (but) which might have confused you.
- In answer to the question as to what the float is ‘actually recording’, the speaker at first say ‘nothing’. He then goes on to explain when information is recorded and what that information is.
- If you were listening out for the keyword ‘salinity’ (or a synonym), which you could guess would come before the answer, you should have been able to identify the answer when it was spoken.
- This is a typical example of how examiners try and catch you out with distractors, so beware.
|
75 videos|43 docs
|

|
Explore Courses for IELTS exam
|

|

















