IIT JAM Physics: All You Need to Know About the Exam | IIT JAM Physics Mock Test Series 2025 PDF Download
The IIT JAM Physics Exam 2024 offers a gateway to prestigious Indian institutions, including the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) and the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), for admission to M.Sc. (Two Years) and Integrated Ph.D. programs in Physics on a national level. The vibrant academic ambiance and research infrastructure of IISc Bangalore & IITs motivate the students to pursue Research and Development careers in frontier areas of basic sciences as well as interdisciplinary areas of science and technology.

IIT JAM Physics Overview
JAM serves as a national benchmark for undergraduate science education. The Integrated Ph.D. Programme at IISc, initiated in the early 1990s, allows students to pursue a Ph.D. directly after completing their B.Sc. The M.Sc. (Two Years), Joint M.Sc.-Ph.D., M.Sc.-Ph.D. Dual Degree, and other Post-Bachelor’s Degree Programmes at the IITs, along with the Integrated Ph.D. Programmes at IISc, offer world-class education.These programs are designed to nurture academic talent, preparing students for challenging and rewarding professional lives. The curricula are regularly updated at IISc and IITs, incorporating interdisciplinary content to equip students with practical skills. All programs are conducted in English, providing students with a global learning experience.
Educational Qualification for IIT JAM Physics
IIT JAM aspirants for physics test papers may choose a regular MSc. degree, or they can combine it with materials engineering to make it a dual degree. Joint MSc. and Ph.D. programs are also available for physics aspirants. The minimum educational requirements for these degrees are mentioned below:
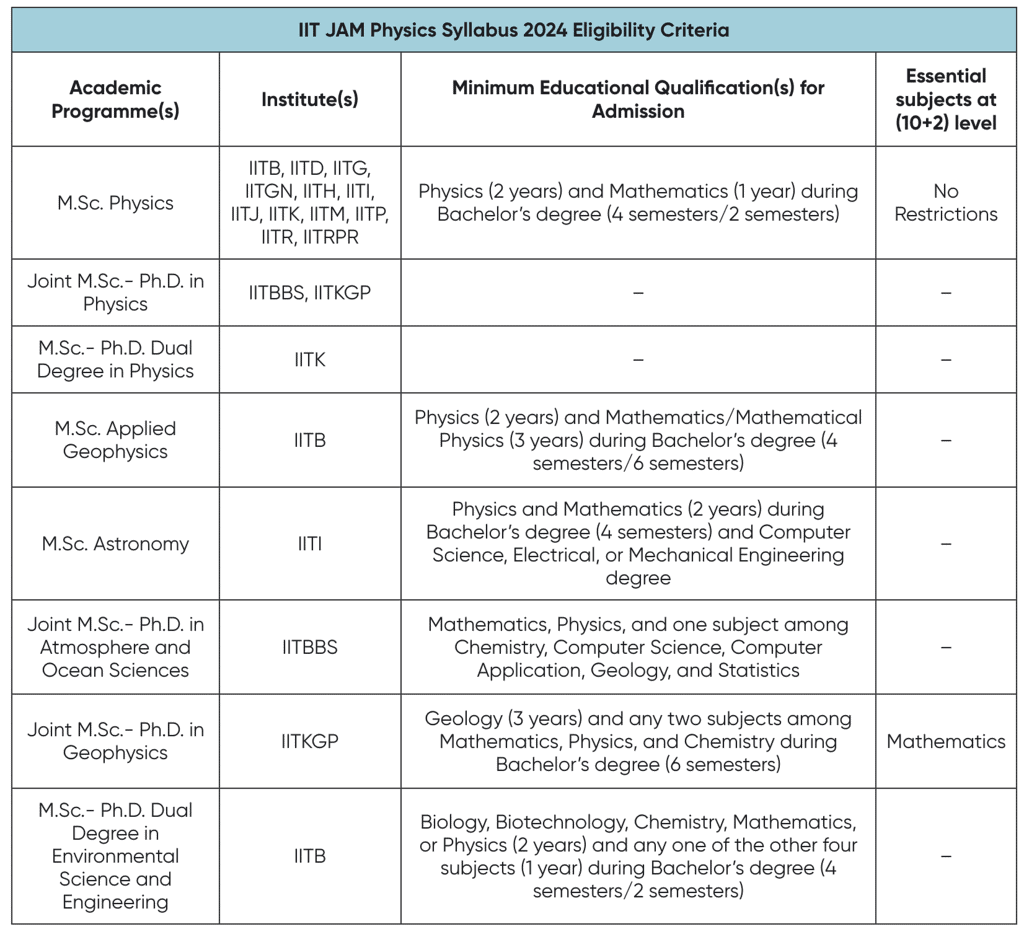 Educational Qualification for IIT JAM Physics
Educational Qualification for IIT JAM Physics
Eligibility for IIT JAM Physics
- Candidates from all over India, as well as foreign nationals, are eligible to appear for the IIT JAM Physics Exam.
- There is no age restriction for the exam, and candidates can attempt it as many times as they wish.
IIT JAM Physics Syllabus and Important Topics
The detailed syllabus of IIT JAM Physics is given below:
Mathematical Methods: Calculus of single and multiple variables, partial derivatives, Jacobian, imperfect and perfect differentials, Taylor expansion, Fourier series. Vector algebra, Vector Calculus, Multiple integrals, Divergence theorem, Green’s theorem, Stokes’ theorem. First-order equations a linear second-order differential equations with constant coefficients. Matrices and determinants, Algebra of complex numbers.
Mechanics and General Properties of Matter: Newton’s laws of motion and applications, Velocity and acceleration in Cartesian, polar, and cylindrical coordinate systems, uniformly rotating frame, centrifugal and Coriolis forces, Motion under a central force, Kepler’s laws, Gravitational Law and field, Conservative and non-conservative forces. System of particles, Center of mass, equation of motion of the CM, conservation of linear and angular momentum, conservation of energy, and variable mass systems. Elastic and inelastic collisions. Rigid body motion, fixed axis rotations, rotation and translation, moments of Inertia and products of Inertia, parallel and perpendicular axes theorem. Principal moments and axes. Kinematics of moving fluids, equation of continuity, Euler’s equation, Bernoulli’s theorem.
Oscillations, Waves and Optics: Differential equation for simple harmonic oscillator and its general solution. Superposition of two or more simple harmonic oscillators. Lissajous figures. Damped and forced oscillators, resonance. Wave equation, traveling and standing waves in one dimension. Energy density and energy transmission in waves. Group velocity and phase velocity. Sound waves in media. Doppler Effect. Fermat’s Principle. General theory of image formation. Thick lens, thin lens, and lens combinations. Interference of light, optical path retardation. Fraunhofer diffraction. Rayleigh criterion and resolving power. Diffraction gratings. Polarization: linear, circular, and elliptic polarization. Double refraction and optical rotation.
Electricity and Magnetism: Coulomb’s law, Gauss’s law. Electric field and potential. Electrostatic boundary conditions, Solution of Laplace’s equation for simple cases. Conductors, capacitors, dielectrics, dielectric polarization, volume and surface charges, electrostatic energy. Biot-Savart law, Ampere’s law, Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, Self and mutual inductance. Alternating currents. Simple DC and AC circuits with R, L and C components. Displacement current, Maxwell’s equations, plane electromagnetic waves, Poynting’s theorem, reflection and refraction at a dielectric interface, transmission and reflection coefficients (normal incidence only). Lorentz Force and motion of charged particles in electric and magnetic fields.
Kinetic theory, Thermodynamics: Elements of Kinetic theory of gases. Velocity distribution and Equipartition of energy. Specific heat of Mono-, di- and tri-atomic gases. Ideal gas, van-der-Waals gas, and equation of state. Mean free path. Laws of thermodynamics. Zeroth law and concept of thermal equilibrium. First law and its consequences. Isothermal and adiabatic processes. Reversible, irreversible, and quasi-static processes. Second law and entropy. Carnot cycle. Maxwell’s thermodynamic relations and simple applications. Thermodynamic potentials and their applications. Phase transitions and Clausius-Clapeyron equation. Ideas of ensembles, Maxwell-Boltzmann, Fermi-Dirac and Bose-Einstein distributions.
Modern Physics: Inertial frames and Galilean invariance. Postulates of special relativity. Lorentz transformations. Length contraction, time dilation. Relativistic velocity addition theorem, mass-energy equivalence. Blackbody radiation, photoelectric effect, Compton effect, Bohr’s atomic model, X-rays. Wave-particle duality, Uncertainty principle, the superposition principle, calculation of expectation values, Schrödinger equation and its solution for one, two, and three-dimensional boxes. Solution of Schrödinger equation for the one-dimensional harmonic oscillator. Reflection and transmission at a step potential, Pauli exclusion principle. Structure of atomic nucleus, mass, and binding energy. Radioactivity and its applications. Laws of radioactive decay.
Solid State Physics, Devices and Electronics: Crystal structure, Bravais lattices and basis. Miller indices. X-ray diffraction and Bragg's law; Intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors, variation of resistivity with temperature. Fermi level. p-n junction diode, I-V characteristics, Zener diode, and its applications, BJT: characteristics in CB, CE, CC modes. Single-stage amplifier, two-stage R-C coupled amplifiers. Simple Oscillators: Barkhausen condition, sinusoidal oscillators. OPAMP and applications: Inverting and non-inverting amplifier. Boolean algebra: Binary number systems; conversion from one system to another system; binary addition and subtraction. Logic Gates AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR exclusive OR; Truth tables; a combination of gates; de Morgan’s theorem.
Here is the list of subjects based on their importance and weightage in the exam:
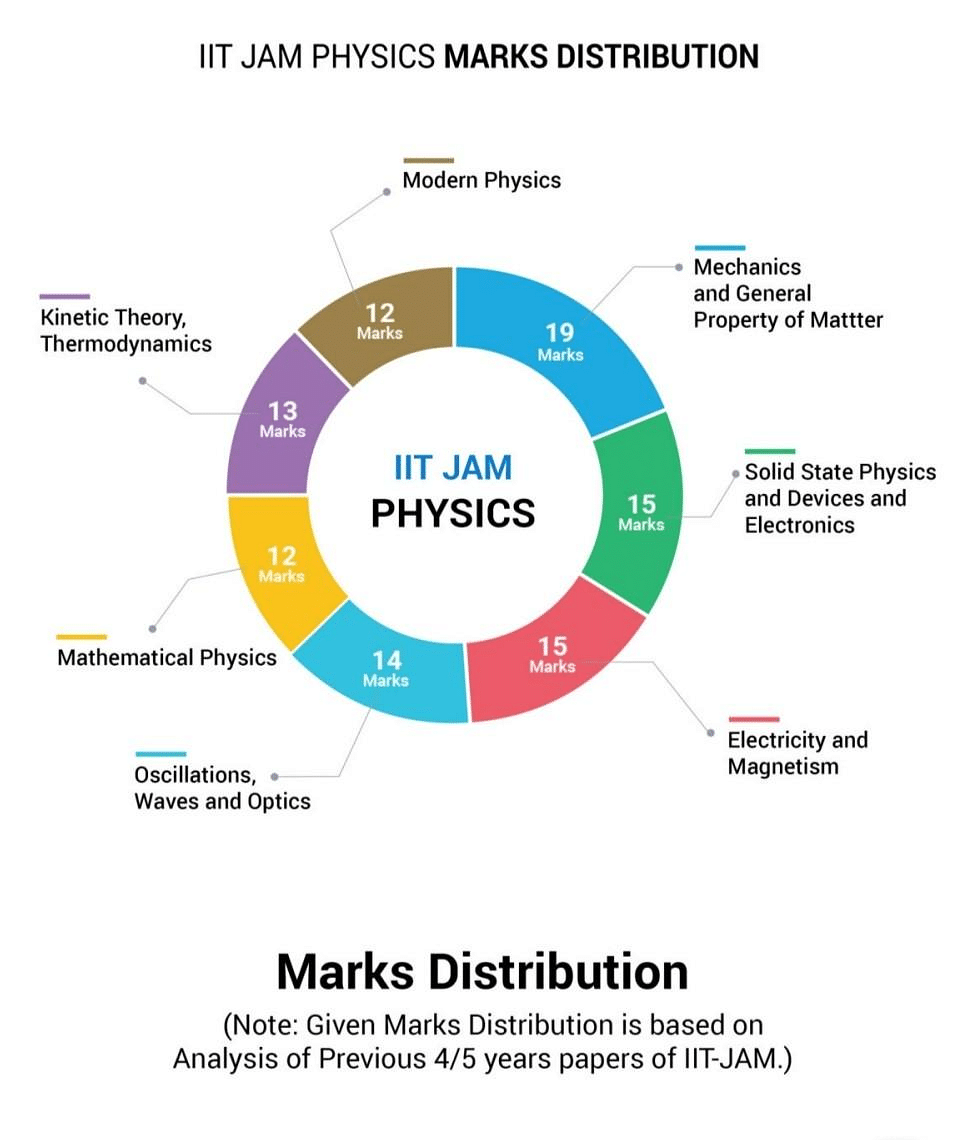 Weightage of Different Subjects in IIT JAM Physics
Weightage of Different Subjects in IIT JAM Physics
IIT JAM Physics Exam Pattern
The JAM Examination will be conducted online as a Computer Based Test (CBT). Candidates will view the questions in a random sequence on their computer screens. The exam will last for 3 hours and will be conducted only in English. There will be a total of 60 questions, carrying 100 marks, divided into three sections, A, B, and C, all of which are mandatory. The question types in each section are as follows:
 Exam Pattern of IIT JAM Physics
Exam Pattern of IIT JAM Physics
Negative Marking and General Rules for IIT JAM Physics
There are certain rules for negative marking in IIT JAM Physics, which are summarised below:
- Not attempting questions in any section will result in zero marks.
- In Section A (MCQ), incorrect answers will lead to negative markings. For each wrong answer to a one-mark question, 1/3 mark will be deducted, and for each wrong answer to a two-mark question, 2/3 mark will be deducted.
- Section B (MSQ) does not have negative marking or partial marking provisions.
- There is no negative marking in Section C (NAT).
Apart from the above rules, there is some other set of instructions that candidates must keep in mind while appearing for the exam:
- An online virtual calculator will be available for use during the exam, so candidates are not allowed to bring any calculators.
- Mobile phones and other electronic devices are strictly prohibited inside the examination hall. Charts, graph sheets, and tables are also not allowed.
- A scribble pad will be provided for rough work, which must be returned at the end of the examination.
- Candidates must select answers for MCQ and MSQ questions using the mouse.
- For NAT questions, answers can be entered using a virtual numeric keypad (the computer keyboard will be disabled).
- The exam will automatically end after 3 hours.
IIT JAM Physics Cutoff Marks
Every year, the specific IIT responsible for conducting the exam for the particular year releases the cutoff marks for IIT JAM Physics in three categories, namely, General, OBC/EWS, SC/ST/PwD. The cutoff each year varies every year depending on the number of candidates and the difficulty level of the exam. However, the table below summaries the cutoffs for the last five years:
 Cutoff Marks for IIT JAM Physics for Years 2020-2024
Cutoff Marks for IIT JAM Physics for Years 2020-2024
IIT's Seat Allocation for Admissions Based on IIT JAM Physics
Seat allocations can vary each year based on several factors including the number of applicants, available seats, and institute-specific policies. The seat availability for M.Sc. Physics through IIT JAM 2024 has not been announced yet. In 2023, 765 seats were offered for the Physics M.Sc. program and integrated Ph.D. in total across various IITs. The distribution of seats for JAM 2023 in different IITs for M.Sc. Physics is detailed in the table below. For specific category-wise seat allocation, please refer to the IIT JAM Seat Matrix.
 Seats Allocation for M.Sc Physics in IITs
Seats Allocation for M.Sc Physics in IITs
Career Opportunities after Completing M.Sc. (Physics) from IITs
An M.Sc. in Physics from IIT opens doors to a wide range of career opportunities for those passionate about the field. Here are some promising paths to consider:
- Private Sector Jobs: Several IT companies, including Wipro, Infosys, TATA, and CTS, value physics graduates’ analytical and problem-solving skills. You can explore job opportunities in software development, data analysis, and various technical roles.
- Government Sector Jobs: Government organizations such as BARC (Bhabha Atomic Research Centre), ONGC (Oil and Natural Gas Corporation), BHEL (Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited), NTPC (National Thermal Power Corporation), and ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation) offer diverse job roles for physics graduates. These roles often involve research, development, and scientific contributions to important projects.
- Research Scientist or Analyst: If you dream of working on groundbreaking research projects internationally, opportunities with renowned organizations like NASA or ISRO can be pursued. These positions involve cutting-edge research and innovation in physics and space science.
- Ph.D. Programs in IITs or IISc: If you aspire to delve deeper into the world of physics and contribute to cutting-edge research, pursuing a PhD program at prestigious institutions like the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) or the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) is an excellent choice.
- Physics Lecturer & Researcher: Sharing your knowledge and passion for physics as a lecturer at academic institutions while engaging in research is a fulfilling career option. It allows you to inspire and educate the next generation of physicists.
|
4 docs|21 tests
|
FAQs on IIT JAM Physics: All You Need to Know About the Exam - IIT JAM Physics Mock Test Series 2025
| 1. What is the minimum educational qualification required to appear for IIT JAM Physics? |  |
| 2. What are the important topics covered in the IIT JAM Physics syllabus? |  |
| 3. What is the exam pattern for IIT JAM Physics? |  |
| 4. Is there negative marking in the IIT JAM Physics exam? |  |
| 5. What are the career opportunities after completing M.Sc. (Physics) from IITs through IIT JAM Physics? |  |




















