Importance Sustainable Management of Natural Resources | Science for Super TET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Resource |

|
| Why do we need to Manage our Resources? |

|
| Forests and Wildlife |

|
| Stakeholders |

|
| Wildlife Resources |

|
| Conservation Measures |

|
Resource
A source of supply held in reserve, which is useful to man or can be transformed into a more valuable and useful item for mankind.
Natural Resource
A Natural resource is a source obtained from nature.
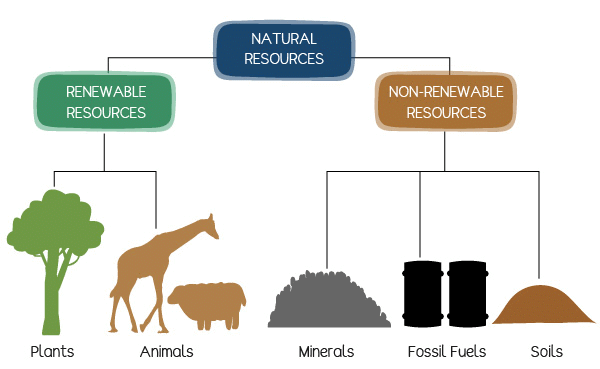
Conservation of Natural Resources
Conservation is the management for the benefit of all life including humankind of the biosphere so that it may yield sustainable benefit to the present generation while maintaining its potential to meet the needs and aspiration of future generations.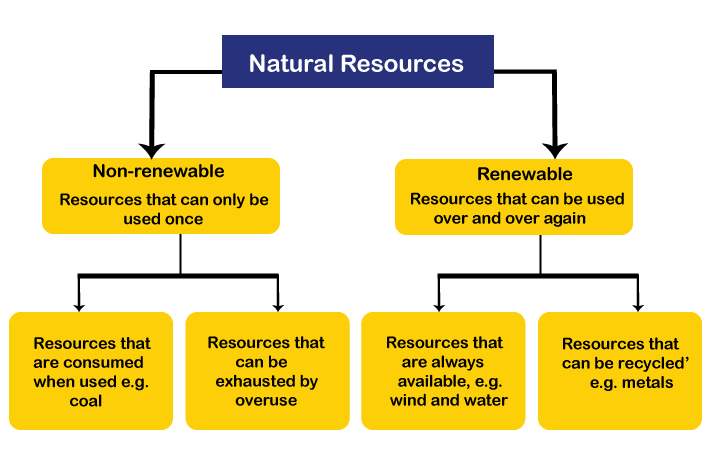
The three R's to save natural resources:
(1) Reduce
(2) Reuse
(3) Recycling

Pollution in Ganga
- The Ganga runs its course of over 2500 km from Gangotri in the Himalayas to Ganga Sagar in the Bay of Bengal.
- It is being turned into a drain by more than a hundred towns and cities in Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and West Bengal.
- Ganga along with its tributaries is the largest and very important river basin of the country.
- Ganga's pollution load and the toxicity kills fish in large sections of the river.

- It has been treated as a symbol of purity but today it is very much polluted due to the following factors:
(i) Disposal of untreated sewage, garbage and excreta by more than a hundred towns and cities situated along the river in Uttrakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and West Bengal.
(ii) Daily Human activities like bathing, washing of clothes immersion of ashes or unburnt corpses.
(iii) Dead bodies of animals and humans
(iv) Wallowing of cattle
(v) Discharge of chemical effluents by the industries
Ganga Action Plan
- Ganga action plan was launched in 1985 Ganga action plan is a multi-crore project to clean river Ganga.
- To reduce the domestic load on the Ganga, some of the schemes to be implemented in three states (UP, Bihar and West Bengal).
- Through which the river runs under the Ganga Action Plan are:
(i) Interception and diversion
(ii) Treatment of wastewater
(iii) Riverfront development
(iv) Electric crematorium
(v) Construction of community toilets
(vi) Conversion of dry toilets to flush toilets
Why do we need to Manage our Resources?
- Over-exploitation and non-Judicious utilisation has become a threat to our natural resources with the phenomenal rise in human population and tremendous development of science and technology, natural resources are being heavily exploited all over the world.
- If we judiciously distribute the resources available to us we can maintain harmony between population growth and utilization of natural resources.
- So that nature can sustain for longs.
Aims of Conservation
- To increase the preservation of a quality environment that have aesthetic and recreational values.
- To ensure a continuous yield of useful plants, animals and materials by establishing a balanced cycle of harvest and renewal.
Forests and Wildlife
- Forests are the invaluable wealth of a country and renewable natural resource. Forests constitute 90% of the global biomass.
- Forests are uncultivated and inhabited land area managed for diverse purposes of forestry.
- Whether covered with trees, shrubs, climbers, etc or not.
Do you know?
According to central forestry commission nearly 22.7% of the total land area of India is occupied by forests.
Importance of Forest
Forests have three broad functions

Deforestation
- Destruction of the forest is known as deforestation. It has been estimated that forests in India have declined from about 7000, million hectares in 1900 to 2890 million hectares in 1975. It has further gone down to 2300 million hectares by 2000.
- Tropical rain forests are the most productive type of forests in the world.
 Deforestation
Deforestation
Major Causes of Deforestation
- Growing food needs
- Raw materials for industrial use
- Forest fire
- Damage caused by pests.
Stakeholders
- Stakeholders are persons or the company that has invested in the business and owns a part of it or someone who has an interest in the success of a system or organisation.
The four stakeholders of forest are:
(a) The people who live in or around the forest
(b) The forest department
(c) The industrialist
(d) The wildlife and nature enthusiasts
Wildlife Resources
Life in any form, plant or animal, which exists in its natural habitat is called wildlife.
Reasons for the Depletion of Wildlife
- Deforestation for various reasons like urbanization, cultivation dam building, road construction, the establishment of industries has caused a considerable loss of wildlife.
- Indiscriminate hunting by man for meat skin and for sport.
- Natural calamities like flood, drought, fire, epidemic have played a major role in the depletion of wildlife.
- Cutting of plants for obtaining timber and fuel deprived wild animals of their most palatable food.
Importance of Wildlife
- The wildlife can be used commercially to earn money through tourism.
- Wildlife is responsible for maintaining the natural balance of the environment.
- Wildlife is a symbol of national pride and represents cultural heritage.
- Since wildlife is a renewable source of a large variety of commercial products like food fur, lac, musk leather, feather, ivory, medicines.
Management and Conservation of Wildlife
- Preservation, protection and utilization of wildlife in such a way that it is not destroyed and can be used later.
Conservation Measures
The Indian Board of wildlife (IBWL) in march 1980 launched a national wildlife action plan for the conservation of wildlife in India.
Establishment of Protected Areas
The protected areas for wildlife conservation are the sanctuaries and national parks.
What is Conservation?
Conservation may be defined as the controlled utilization of natural resources for the benefit of all life so that it may yield sustainable benefit to the present generations as well as the future generations
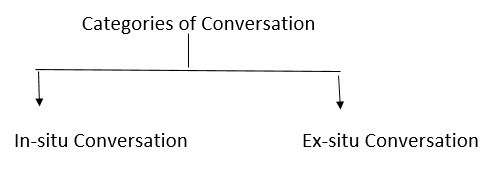 1. In situ conservation
1. In situ conservation
When conservation of natural resources is done in their natural habitats, it is called in situ conservation.
Example: National parks, Wildlife sanctuaries biosphere.
2. Ex-situ conservation
When conservation of natural resources is done outside their habitats it is called ex-situ conservation.
Example: Botanical gardens, zoos, seed banks, pollen storage, tissue culture.
National Parks and sanctuaries
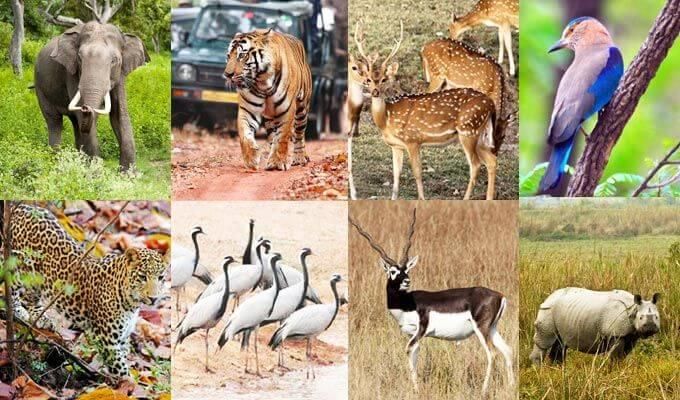

- Jim Corbett National Park, Uttaranchal (tiger).
- Kanha National Park, M.P. (tiger).
- Bharatpur Bird Sanctuary, Rajasthan (winter home of migratory birds, most commonly Siberian crane).
- Nandankanan Biological Park near Bhubaneswar (captive breeding of white tigers).
- Simplipal Biosphere Reserve, Orissa (tigers).
- Gir Sanctuary, Gujarat (Asiatic lion, chital, sambhar).
- Kaziranga Sanctuary, Assam (one-horned rhinoceros).
- Sariska Sanctuary, Haryana (tiger).
- Sultanpur Bird Sanctuary, Haryana (birds).
- Bandipur Sanctuary, Karnataka (Indian elephant).
- Madumalai Sanctuary, Tamil Nadu (Indian elephant).
- National Botanical Garden, West Bengal (rare species of plants).
- Desert National Park, Rajasthan (blackbuck, great Indian bustard, chinkara neelgai).
|
59 videos|118 docs|73 tests
|
FAQs on Importance Sustainable Management of Natural Resources - Science for Super TET
| 1. Why is it important to manage our resources? |  |
| 2. What are some examples of resources that need to be managed? |  |
| 3. Who are the stakeholders in resource management? |  |
| 4. What are some conservation measures for wildlife resources? |  |
| 5. How does sustainable management of natural resources benefit us? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Super TET exam
|

|




















