Important Formula Simplification and Approximation | Quantitative Aptitude for SSC CGL PDF Download
What is Simplification and Approximation?
Simplification means reducing the expression in a simpler form using various operations while Approximation is simplifying the mathematical expression to its nearest value but not exactly correct. To find the approximate value, we round off the digits in the expression to the nearest value and simplify the expression using BODMAS.
The operations used to simplify follows a fixed order known as BODMAS
where,
B = Bracket
O = of
D = Division
M = Multiplication
A = Addition
S = Subtraction
The simplification and approximation topic is one of the simplest ones in the numerical ability/quantitative aptitude part and simply effective calculation can help candidates answer questions from this section quickly and correctly. The main purpose behind proposing questions from the approximation and simplification point is to examine the understanding of an applicant to manage with numbers and basic predictions. Questions are composed to mislead the candidates with extended decimal numbers and computations which may look confusing and complex but this topic is one where a candidate can secure maximum without initiating errors.
The simplification questions can be examined in two styles:
- Missing numbers – A given equation in the exam paper would ask the candidates to fill in the blank in that particular equation, provided either on the Left-hand side or Right-hand side.
- For example, 240 – __+100 = 5 × 35 + 265. Here the candidates are required to fill the space with the appropriate options.
- Simplifying the equation – Another approach in which the simplification questions may be asked is the direct method of furnishing an equation and solving it to obtain the result.
- For example: 242 – 235 + 90 = ?.
- In such problems, applicants have to respond to what comes in the position of the question mark (?).
Important Terms under Simplification and Approximation
Some important terms related to simplification and approximation are given below.
Vinculum – Vinculum is a horizontal line drawn over a group of terms in a mathematical expression to indicate that they are to be operated on as a single entity by the preceding or following operator.
Brackets – Brackets in simplification are of three types.
- Round brackets – denoted by the symbols ( )
- Curly brackets – denoted by the symbols { }
- Box brackets – denoted by the symbols [ ]
The order in which these brackets are operated is ( ), { } and [ ]. Of means multiplication but it is operated before division. The operation of adding or subtracting can be interchanged or can be performed simultaneously.
Surds and Indices – A surd is an irrational number that can be expressed with roots, such as √12 or ∛12.
An index is a power to which a number is raised and the plural of the index is indices. For example, k12 has an index of 12.
Rules of Simplification and Approximation
Some important rules related to simplification and approximation are given below.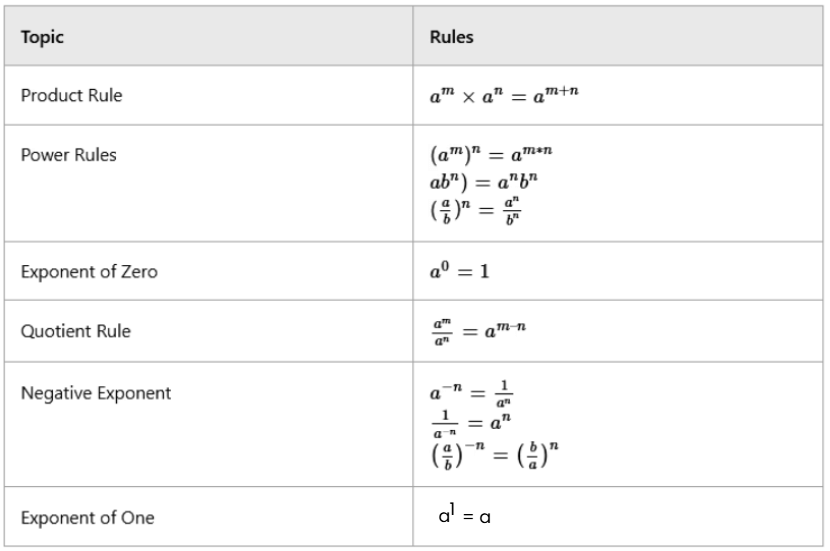
Tips and Tricks to Solve Simplification and Approximation Questions
Candidates can find different tips and tricks below for solving the questions related to simplification and approximation:
- If all the fractions have a common denominator, then the integer part and the fraction part can be calculated separately.
- To find the approximate value of an expression containing decimals, just convert the decimals into integers and solve the expression.
- That is, the numbers that are presented in a decimal format, practice a rounded-off value for those numbers. For example, 46.72 can be taken as 47, 21.10 can be taken as 21, and so on.
- Always determine the approximation or simplification problems following the BODMAS rule.
- Memorizing tables at least till 20 can be of great help for the aspirants and would help them save some extra time for the complex question.
- Do not overcomplicate the problems and make sure that the hard calculations require to be skipped in order to work the equations in the shortest time possible.
- Remember the primary important formulas which can be applied in such question:
(a + b)2 = a2 + b2 + 2ab
(a−b)2 = a2 + b2 − 2ab
a2 − b2 = (a + b)(a − b)
a3 + b3 = (a + b)(a2 − ab + b2)
(a + b)3 = a3 + b3 + 3ab(a + b)
(a − b)3 = a3 − b3 − 3ab(a−b)
Simplification and Approximation Important Topics
Some of the important simplification and Approximation Topics with the below table: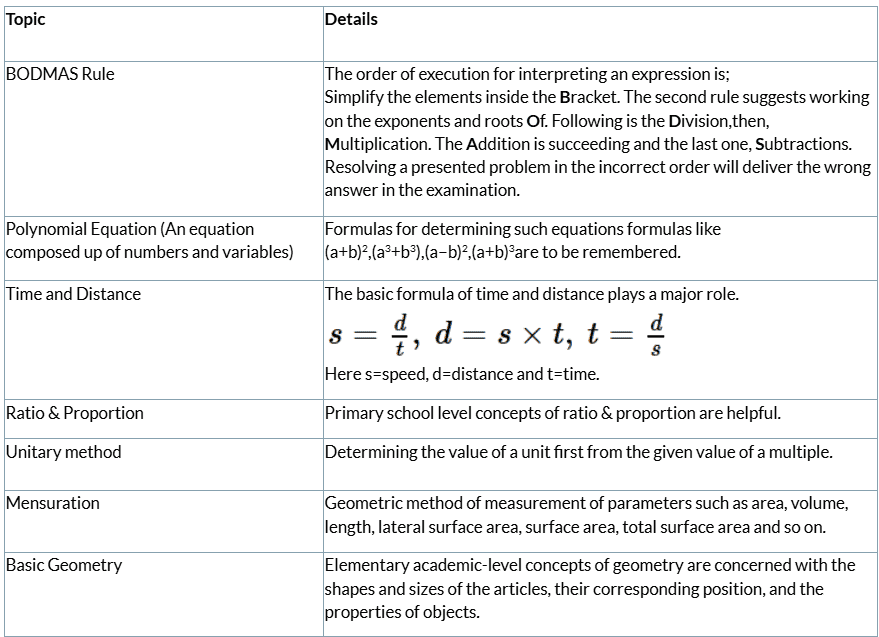
|
317 videos|290 docs|185 tests
|

















