Important Points: Matter in Our Surroundings | Science Class 9 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Matter? |

|
| Characteristics of Particles of Matter |

|
| States of Matter |

|
| Interconversion of States of Matter |

|
| Density and Volume |

|
What is Matter?
- Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass.
- It consists of small particles, which may be molecules, atoms, or ions.
- Matter exists in three primary states: solids, liquids, and gases.
 Matter
Matter
Characteristics of Particles of Matter
Motion and Kinetic Energy:
- The particles of matter are always in a state of motion and, hence, possess kinetic energy.
- Kinetic energy is Lowest in solids, Intermediate in liquids & Highest in gases.
 Kinetic Energy & Intermolecular Forces
Kinetic Energy & Intermolecular Forces
Intermolecular Forces:
- Particles of matter are attracted to each other by intermolecular forces.
- These forces are: Strongest in solids, Weaker in liquids, Weakest in gases.
Intermolecular Spaces:
 Intermolecular Spaces
Intermolecular Spaces
- The spaces in between the particles of matter are called intermolecular spaces.
- Intermolecular spaces are smallest in solids, larger in liquids, and largest in gases.
- The smaller the intermolecular spaces, the stronger the intermolecular forces.
States of Matter
1. Solids:
- Particles are tightly packed with very little movement.
- They have strong intermolecular forces, small intermolecular spaces, and low kinetic energy.
- Solids have a definite shape and volume.
 Properties of Solid, Liquid & Gas
Properties of Solid, Liquid & Gas
2. Liquids:
- Particles are loosely packed and can move past each other.
- They have moderate intermolecular forces, larger intermolecular spaces, and higher kinetic energy compared to solids.
- Liquids have a definite volume but take the shape of their container.
3. Gases:
- Particles are far apart and move randomly.
- They have very weak intermolecular forces, maximum intermolecular spaces, and the highest kinetic energy.
- Gases do not have a definite shape or volume, filling the space of their container.
Change in States of Matter
The states of matter are interconvertible and can be changed by changing the temperature and pressure.
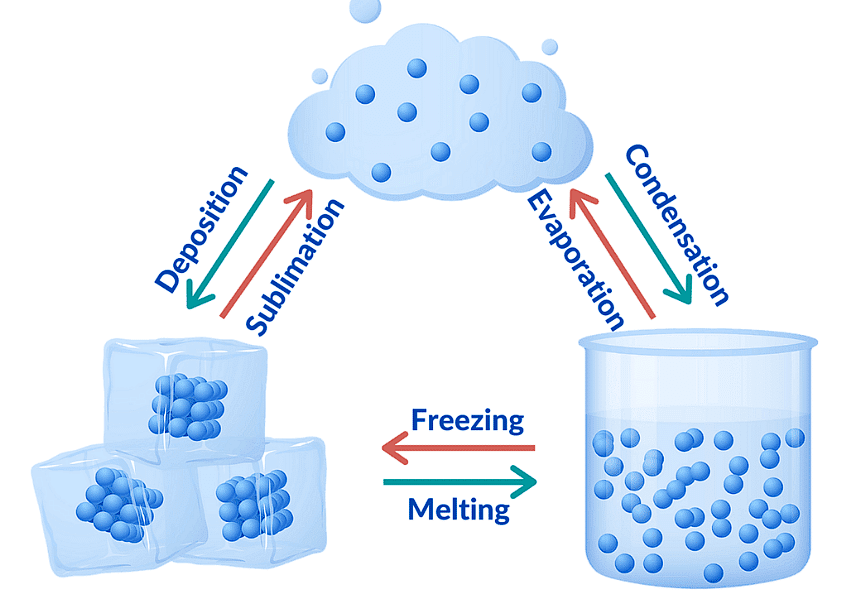 Interconversion of States of Matter
Interconversion of States of Matter
- Sublimation: A solid changes directly into gas without passing through the liquid state. This occurs on heating, and the reverse is also possible (gas to solid).
- Fusion (Melting): A solid turns into a liquid. The temperature at which this occurs is called the melting point.
- Vaporization (Boiling): A liquid turns into a gas at a specific temperature, known as the boiling point. Boiling is a bulk phenomenon, meaning particles throughout the liquid change into vapor.
Interconversion of States of Matter
Evaporation
Evaporation is a surface phenomenon where particles from the surface of a liquid gain enough energy to overcome intermolecular forces and turn into vapor.
 Evaporation
Evaporation
- Factors affecting evaporation are:
Surface area exposed
Temperature
Humidity
Wind speed
- Cooling Effect: Evaporation causes cooling as heat energy is taken away by the evaporating particles, reducing the temperature of the remaining liquid.
Latent Heat:
- Latent heat of vaporization: The heat energy required to convert 1 kg of liquid to gas at atmospheric pressure at its boiling point.
- Latent heat of fusion: The heat energy required to convert 1 kg of solid to liquid at its melting point.
Density and Volume
Density: The mass of a substance per unit of volume, i.e., density = mass/volume.
SI unit of density is kg m-3
Volume: All solids occupy a fixed volume. The shape occupied by a substance is called volume.
The unit of volume is m3 (cubic meter). The common unit of volume is L (liter).
1m3 = 1000 dm3 = 1000 L
1 L = 1 dm3
1 L = 1000 ml = 1000 cm3
|
87 videos|369 docs|67 tests
|
FAQs on Important Points: Matter in Our Surroundings - Science Class 9
| 1. What is matter and why is it important? |  |
| 2. What are the characteristics of particles of matter? |  |
| 3. What are the different states of matter? |  |
| 4. What is evaporation and how does it occur? |  |
| 5. How does temperature affect the state of matter? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|


















