Important Questions: Fundamentals of Anatomy, Physiology and Kinesiology in Sports | Physical Education Class 11 (XI) - CBSE and NCERT Curriculum PDF Download
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1: Define anatomy.
Ans: Anatomy is the study of the structure of human body. Term anatomy comes from Greek words: ANA means apart and TOMY means to cut. It is because anatomy was first obtained through dissection.
Q2: Define physiology.
Ans: Physiology is the study of functions of human body. In other words physiology is the science of mechanical, physical, bioelectrical, biochemical functions of human organs and the cells of which they are composed of.
Q3: Name any four physiological systems of human body.
Ans:
- Skeletal System
- Muscular System
- Digestive System
- Respiratory System
Q4: Define skeletal system.
Ans: The skeletal system is the bony framework of our body. It consists of all the bones of the body. It supports the body and gives it a shape.
Q5: What do you understand by joint?
Ans: Joint is the place at which two or more bones meet in the skeleton of the body. Joint may be fixed or movable.
Q6: Which is the longest and the smallest bone in human body?
Ans: The longest bone in human body is Femur (thigh bone). And the smallest bone in the human body is stapes (ear bone).
Q7: What is a muscle?
Ans: Muscle is the tissue composed of fibers capable of contracting to effect bodily movements or muscle is the body tissue that can contract and produce movement.
Q8: Enlist types of muscles.
Ans:
- Voluntary/skeletal/striated muscle
- Involuntary or smooth or spindle muscle
- Cardiac muscle
Q9: Which is the hardest working muscle in our body?
Ans: Cardiac muscle is the hardest working muscle in our body.
Q10: Which is the strongest muscle in our body?
Ans: Jaw muscle is the strongest muscle in our body.
Q11: How many bones are there in a Child and an Adult?
Ans: A child has 213 bones and an adult has 206 bones.
Q12: What is tidal volume?
Ans: It is the volume of air that is taken in or given out during normal breathing.
Q13: What is vital capacity?
Ans: It is the volume of air that can be breathed out by force expiration after taking a deep breath. It is about 4800 cc in males and about 3100 cc in females.
Q14: What is heart rate?
Ans: It is the number of pumping/contractions of heart in one minute. It is about 72 times per minute under normal conditions in an adult.
Q15: What is stroke volume?
Ans: It is the volume of blood pumped out by heart in one beat/contraction. It is approximately 80 ml/beat in normal adult, whereas trained players have 110 ml/beat as stroke volume.
Q16: What is cardiac output?
Ans: Cardiac Output = stroke volume x heart rate. It is 5 to 6 litres at basal level. In untrained person, it can go upto 20 litres and in trained athletes it can go upto 40 litres.
Short Answer Questions
Q17: Explain structure of the muscle with the help of a diagram.
Ans: There are about 600 voluntary muscles in the body. Each muscle is made up of thousands of long and narrow muscle cells called muscle fibers.
These muscle fibers are arranged in bundles and enclosed within a tough layer of connective tissue called epimysium (sarcolema). Every muscle fiber is made up of very large number of microscopic threads called myofibrils. Myofibrils consists of protein molecules called actin and myosin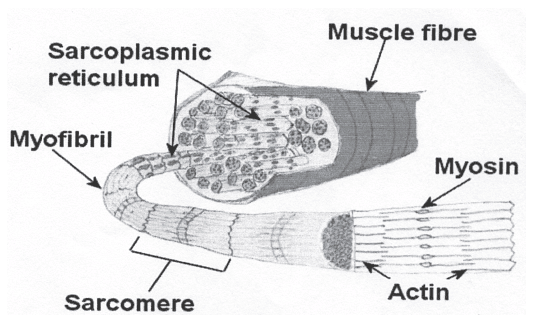
Q18: Explain external and internal respiration.
Ans: Inhalation and exhalation are the two processes of external respiration.
This breathing process oxygenate to the blood. It gets purified as carbon dioxide is removed from the blood. External respiration takes place in the lungs. Internal respiration is the process of respiration that takes place in the tissues and cells. Blood full of oxygen reaches the tissue where oxygen is used up during energy production process and carbon dioxide is then taken by the blood to the lungs.
Q19: Define the phenomenon of second wind. What are its causes and symptoms?
Ans: The breathlessness caused due to prolonged exercise is removed automatically by our body within short span of time of such exercise. This sense of relief is called ‘second wind’.
Causes of second wind: When we perform strenuous exercise, our body takes some time to adjust according to the increased demand of energy. So, the second wind occurs before the adjustment.
Symptoms of second wind:
- Faster breathing
- Signs of tension and worry on the face
- Headache
- Suffocation in the chest appears
- Pain in muscles
- Condition of giddiness appears.
These painful feelings disappear with the onset of second wind.
Q20: What are the functions of respiratory system?
Ans: The main functions of respiratory system are given as under:
- To exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air and blood.
- To produce sound. It helps vocal chords to produce sound.
- To regulate blood Ph.
- To protect against some micro organism.
Respiratory system blocks the entry of microorganism in the body at various levels, thus it provides protection against harmful microorganisms like virus, bacteria, etc.
Q21: Explain the functions of heart.
Ans: The main functions of heart are given below.
- It circulates the pure blood to all parts of the body. This is called systemic circulation.
- It carries the impure blood from all parts of the body to the lungs for purification. This is called pulmonary circulation.
- It regulates the blood pressure.
- It regulates the heart rate.
- Regular exercise improves the efficiency of the heart.
Long Answer Questions
Q22: What are the functions of blood?
Ans: Important functions of blood are given as under:
- Transport of oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs.
- It carries food material absorbed from the intestines to the tissue, cells for growth, energy and repair process.
- It carries the waste products of cellular activity and carries them to kidneys, lungs and intestines for excretion.
- It carries hormones, vitamin and other chemicals to the place of need.
- It helps to maintain water balance in the body.
- It regulates the body temperature.
- White blood cells of the blood acts as a defensive mechanism
Q23: What are the functions of skeletal system?
Ans: Main functions of skeletal system are given below.
- Shape and structure: The boney framework gives human being its shape and structure like tall or small, thin or stout.
- Support: it gives support to the body that comes out as a human body. The bones provide support to our muscular system.
- Protection: bones protect our vital org
- Protection: bones protect our vital organs. Example: skull protects brain, thoracic cage protects heart, lungs and pancreas.
- Lever: bones act as a lever like a simple machine. For example while lifting a weight, movable joints like elbow joint acts like fulcrum and length of arm bone acts like crow bar to reduce effort and helps to lift weight.
- Store house: The hollow space of bones acts like a storehouse of different minerals and salts like calcium, potassium, iron, etc.
- Production of RBCs: red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow. It is the factory to produce RBCs.
- Junction: bones provide junction or attachment to skeletal muscle that helps in visible movement.
- Self repair: Whenever bones are damaged, they are capable of doing self repair.
Q24: Explain the structure of heart with the help of diagram.
Ans: The human heart is a four- chambered muscular organ, shaped and sized roughly like a man’s closed fist with two- thirds of the mass to the left of midline.
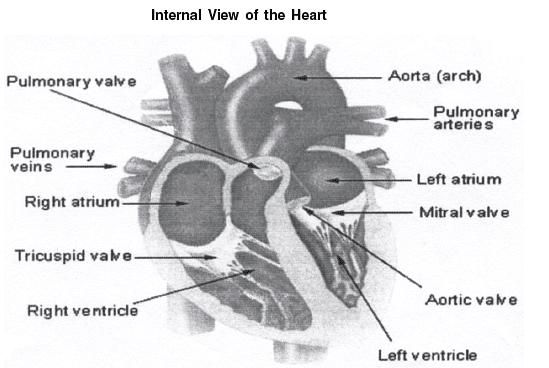
Chambers of the Heart
The internal cavity of the heart is divided into four chambers:
- Right atrium
- Right ventricle
- Left atrium
- Left ventricle
The two atria are thin- walled chambers that receive blood from the veins.
The two ventricles are thick- walled chambers that forcefully pump blood out of the heart.
The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from systemic veins; the left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins.
Valves of the Heart
Pumps need a set of valves to keep the fluid flowing in one direction and the heart is no exception. The heart has two types of valves that keep the blood flowing in the correct direction. The valves between the atria and ventricles are called atrioventricular valves (also called cuspid valves), while those at the bases of the large vessels leaving the ventricles are called semilunar valves. When the ventricles contract, atrioventricular valves close to prevent blood from flowing back into the atria. When the ventricles relax, semilunar valves close to prevent blood from flowing back into the ventricles.
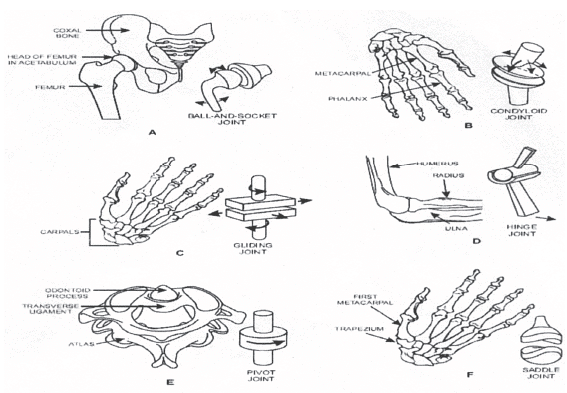
Q25: Explain different types of joints in human body.
Ans: Following are the different types of joints,
i. Immovable or fibrous joints.
They are fixed joints. They never move. Example: joints of skull.
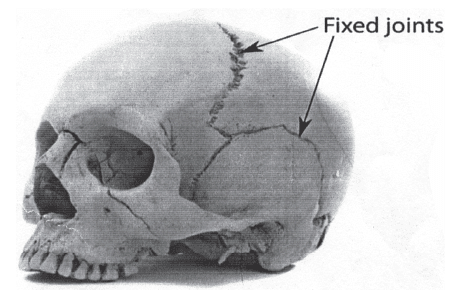
ii. Slightly movable or cartilaginous joints.
These joints provide very little movement. Example: backbone joints, pelvic joints.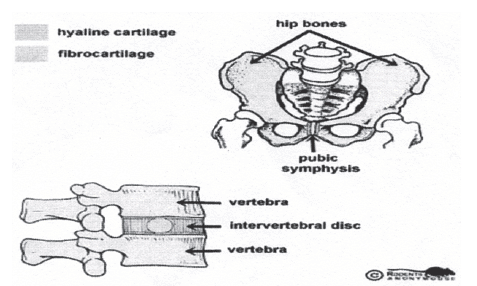
iii. Freely movable or synovial joints.
These joints provide different movements. There are five main types of movable joints.
- Hinge joint. These joints allow a forward and backward movement. Example: knee joints, elbow joints.
- Pivot joint. These joints give a rotation movement. Such as the movement of neck.
- Ball and socket joint. In these joints one bone has ball like shape and other has a socket like shape. They are fit together to make a free movable joint. Example shoulder joint and hip joint.
- Saddle joint. It is a joint where one of the bones forming the joint is shaped like a saddle with the other bone resting on it like a rider on a horse. Example: wrist joint.
- Gliding joint. It is a joint in which articulation of contiguous bones allows only gliding movements, as in the wrist and the ankle.
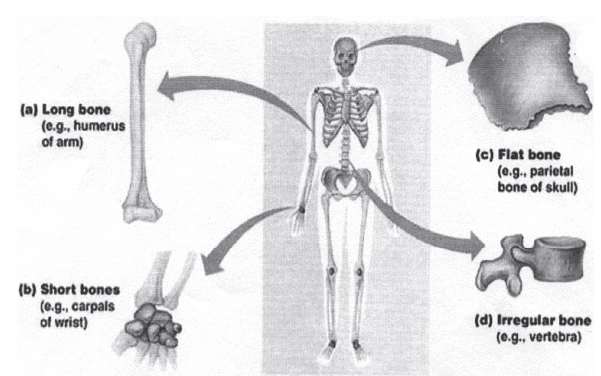
Q26: Write in detail about classification of bones.
Ans: Classification Of Bones
- Long bones: They are long and wide. They act as lever. They are found in legs and arms. Example: humerus, femur, tibia and fibula.
- Short bones: They are short in size and cube shaped. They are found in wrist and phalanges. Example: metatarsal and carpal.
- Flat bones: These bones are flat and thin. They are composed of a central layer of sponge bone fixed between two outer layers of compact bone. Example: ribs and shoulder.
- Sesamoid bones: These bones are seed like shaped and developed in the tendons where there is more friction. Example: palms of hands, sole of feet and knee caps.
- Irregular bones: These bones have complexed shaped as compared to other types. The bones of spinal column and skull are examples of these bones.
- Sutural bones: They are situated in sutural joints in the skull.
Q27: Elucidate the importance of anatomy and physiology in the field of sports.
Ans: Study of anatomy and physiology plays very important role in the field of sports because of following reasons.
- Helps in physical fitness: Strong and fit body is an inevitable asset in the field of sports. Study of anatomy and physiology helps a sport person to understand the structure and function of different parts of human body and to acquire a fit and healthy body.
- Provides knowledge about body structure: on the basis of knowledge of body structure, a sport person knows about the strength and weakness of his body and accordingly they can develop forte in the field of game which is suitable for the sport person as per their body structure.
- Helps in selection of games: on the basis of knowledge of body structure, the coach and player can choose an appropriate sport/ game which is suitable for a particular sport. Like tall students can be selected for basketball and volleyball. And short and stout students can be selected for weight lifting.
- Protects from sports injuries: on the basis of anatomy, sports equipments are designed that help in safe play.
- Helps in the process of rehabilitation: knowledge of ligaments, tendons and muscles helps in rehabilitation from the injuries sustained during the game or sport.
- Helps in maintaining healthy body: study of anatomy and physiology provides detailed knowledge about all body parts, their nature and functions. This helps the player to adopt good, safe and healthy use of body.
- Helps to know about individual differences: there is a lot of difference between the body of male and female. The knowledge of anatomy and physiology helps in understanding these individual differences. On the basis of these differences, the size of the court, time of game and equipment are designed differently for male and female players.
|
33 videos|47 docs|23 tests
|
















