Important Questions: Open Economy Macroeconomics | Economics Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Which two transactions determine the balance of trade?
Ans: Export and import of visible items determine the balance of trade.
Q2: What does Balance of Payments account of a country record?
Ans: The Balance of Payments (BoP) account of a country records the payments and receipts of a country with the rest of the world, during one year.
Q3: What is the difference between the values of exports of goods and imports of goods called?
Ans: The difference between the values of exports of goods and imports of goods is called balance of trade.
Q4: What do you mean by Balance of Payment on current account?
Ans: The Balance of Payments on current account is the sum of balance of merchandise trade, services and net transfers received from rest of the world.
Q5: What is current account deficit in the Balance of Payments?
Ans: Current account is said to be in deficit when the export of goods and services and unilateral transfers falls’ short of the import of goods and services and unilateral transfers.
Q6: What is foreign exchange rate?
Ans: Foreign exchange is the price of one unit of the foreign currency in terms of the domestic currency.
Q7: Define foreign exchange market.
Ans: Foreign exchange market is the market where the national currencies are traded for one another.
Q8: How can increase in Foreign Direct Investment affect the price of foreign exchange ?
Ans: Increase in Foreign Direct Investment increases the supply of foreign exchange and hence decreases the price of foreign exchange.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q9: Name the board categores of transactions recorded in the ‘current account’ of the balance of payments account.
Ans: The main components of the current account of the Balance of Payments accounts include:
- Import and export of goods
- Import and export of services
- Unilateral transfers
The deficit in current account indicates that the current imports of goods and services and unilateral transfers to rest of the world are greater than the exports of goods and services and unilateral transfers from rest of the world.
Q10: Define “Trade surplus”. How is it different from “Current account surplus”?
Ans: Trade surplus refers to excess of value of export of visible items over value of import of visible items in the balance of payment account of a country. In other words it only includes trade of goods. Current account surplus refers to excess of receipts from value of exports of visible items and invisible items; and unilateral transfers over payment for value of imports of visible items and invisible items; and unilateral transfer. It is a relatively broader concept as compared to trade surplus.
Q11: Distinguish between Trade Deficit’ and ‘Current Account Deficit’.
Ans: Trade deficit refers to excess of value of imports of visible items over value of exports of visible items in the balance of payment account of a country. In other words.it only includes trade of goods. Current account deficit refers to excess of payment for value of imports of visible items and invisible items; and unilateral transfer over receipts from value of exports of visible items and invisible items; and unilateral transfers. It is a relatively broader concept as compared to trade deficit.
Q12: Explain the impact of rise in exchange rate on national income.
Ans: A rise in the foreign exchange rate implies that the price of foreign currency, in terms of domestic currency, has increased. Since domestic goods and services have become cheaper, the foreign country can now buy higher quantity from one unit of its currency. This will result in increased demand for Indian exports. Moreover, depreciation of domestic currency will make the imports from foreign countries more expensive. Thus, there will be increase in exports and fall in imports, causing the net exports to rise. Consequently, the net aggregate demand for domestically produced goods will increase and so will the national income.
Q13: Give two reasons for a rise in demand for a foreign currency when its price fells.
Ans: Following are the two reasons for the rise in the demand for a foreign currency when its price falls:
- When the price of a foreign currency falls, the imports from that country become cheaper. As a result, imports increase, and hence, the demand for the foreign currency also rises.
- When a foreign currency becomes cheaper in terms of domestic currency, people plan investment in foreign country. As a result, demand for that foreign currency rises.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q14: State any four items each of current account and capital account of the Balance of Payments account.
Ans: Items of Current Account
- Export and Import of Goods: Current account shows exports and imports of visible items i.e., goods like machinery, wheat, steel, etc.
- Export and Import of Services: Current account shows exports and imports of invisible items i.e., services like banking, tourism, insurance, etc.
- Unilateral Transfers: These are those receipts which residents of a country receive or payments that the residents of a country make without getting anything in return. Receipts from abroad are entered as positive items and payments abroad are entered as negative items.
- Private Transfers: These are gifts that domestic residents receive from or make to foreign residents.
Items of Capital Account
- Private Transactions: These are transactions that affect the assets or liabilities of individuals, business, etc. and other non-government entities.
- Official Transactions: These are the transactions that affect the assets and liabilities by the government and its agencies.
- Direct Investment: Direct investment means the act of purchasing an asset and at the same time acquiring control of it.
- Portfolio Investment: It is the acquisition of an asset that does not give the purchase control over the asset.
Q15: Give the meaning of‘foreign exchange and foreign exchange rate’. Giving reason explain the relation between foreign exchange rate and demand for foreign exchange.
Ans: Foreign Exchange: Foreign exchange is the conversion of one currency into another currency.
Foreign Exchange Rate: Foreign exchange rate is the price of one currency in terms of another currency. Relation between Foreign Exchange Rate and Demand for Foreign Exchange There is an inverse relation between foreign exchange rate and demand for foreign exchange. The relationship can be explained with the help of a diagram.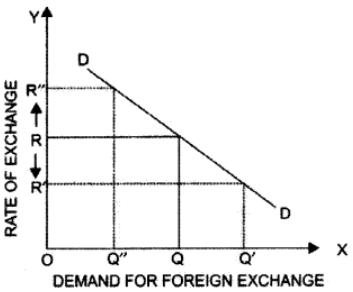
In the diagram, X axis shows the quantity of foreign exchange demanded and Y axis shows the price of foreign exchange. The curve showing demand for the foreign exchange (DD) slopes downward from left to right. This implies that higher the exchange rate, lower would be the demand for foreign exchange, and vice-versa. The diagram shows that when the exchange rate is OR then the demand for foreign exchange is OQ. When the exchange rate declines to OR’, foreign goods become cheaper than the domestic goods. Thus, the demand for foreign exchange increases to OQ’. On the contrary, when the exchange rate increases to OR’, foreign goods become expensive than the domestic goods. Thus, the demand for foreign exchange decreases to OQ’.
Q16: Explain the causes of disequilibrium in the Balance of Payments.
Ans: Disequilibrium in the Balance of Payments (BoP) occurs when there is an imbalance between a country's exports and imports of goods and services, leading to a surplus or deficit. Several factors can contribute to this disequilibrium:
- Trade Imbalance: The most obvious cause of disequilibrium is an imbalance between exports and imports. If a country imports more goods and services than it exports, it will face a trade deficit. This can happen due to a variety of reasons, such as lack of competitiveness, high domestic demand for foreign goods, or unfavorable exchange rates.
- Fluctuating Exchange Rates: Exchange rates play a crucial role in a country's trade balance. If a country's currency depreciates significantly, its exports become cheaper for other countries, potentially increasing exports. Conversely, if the domestic currency appreciates, exports become more expensive, potentially leading to a trade deficit.
- Economic Recession: During economic downturns, both domestic consumption and international demand for exports tend to decrease. If imports remain stable or decrease at a slower rate than exports, it can lead to a trade surplus. Conversely, if a country faces a recession while continuing to import at previous levels, it can lead to a trade deficit.
- Government Policies: Government policies, such as tariffs, quotas, and subsidies, can impact the balance of trade. Tariffs (taxes on imports) and quotas (limits on the quantity of imports) can reduce imports and potentially create a trade surplus. Subsidies given to domestic industries can make exports cheaper and more competitive, potentially leading to a trade surplus.
- Consumer and Business Confidence: High consumer and business confidence can boost domestic demand, leading to increased imports. If confidence is low, domestic demand decreases, potentially reducing imports and creating a trade surplus.
- Rise in Oil Prices: For oil-importing countries, a significant increase in oil prices can lead to higher import costs, contributing to a trade deficit. This situation can also lead to higher production costs for domestic industries, affecting their competitiveness in the global market.
- Economic Policies: Monetary and fiscal policies can influence the exchange rate and, consequently, a country's trade balance. For instance, if a country pursues expansionary monetary policies, it can lead to a depreciation of the domestic currency, potentially making exports more competitive and reducing imports.
- Speculative Capital Flows: Sudden inflows or outflows of speculative capital can impact a country's exchange rate, affecting its trade balance. If speculative capital leads to a significant appreciation of the domestic currency, exports can become more expensive, potentially leading to a trade deficit.
|
64 videos|308 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Important Questions: Open Economy Macroeconomics - Economics Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is open economy macroeconomics? |  |
| 2. How does international trade affect an open economy? |  |
| 3. What are capital flows in open economy macroeconomics? |  |
| 4. How are exchange rates determined in open economy macroeconomics? |  |
| 5. What are the consequences of exchange rate changes in an open economy? |  |





















