Class 8 Civics Chapter 1 Important Question Answers - The Indian Constitution
Q 1. What is democracy?
Ans: Democracy is a form of government where the people have the power to make decisions about how they are governed. Example of democracy- India, where citizens vote to elect leaders who represent them and make decisions on their behalf.
Q 2. Define the term constitution. Why do we need a constitution?
Ans: A constitution is a set of fundamental principles or laws that outline how a country or organization is governed. It defines the structure of the government, the powers of different branches, and the rights and duties of citizens.

We need constitution as it serves several purposes:
- First, it lays out certain ideals that form the basis of the kind of country that we, as citizens aspire to live in.
- A constitution tells us what the fundamental nature of our society is. A country is usually made up of different communities of people who share certain beliefs but may not necessarily agree on all issues.
- A constitution helps serve as a set of rules and principles that all persons in a country can agree upon as the basis of the way in which they want the country to be governed.
- This includes not only the type of government but also an agreement on certain ideals that they all believe the country should uphold.
- The constitution often lays down rules that guard against this misuse of power by our political leaders.
Q 3. Differentiate between a monarchy and a democracy?
Ans:
A monarchy is a form of government where a king, queen, or emperor holds power, often inherited through family lines. For example, Saudi Arabia is a monarchy where the king has significant control over governance.
A democracy, on the other hand, is where the people have the power, usually by voting for leaders to represent them. For example, India is a democracy where citizens elect their government officials.
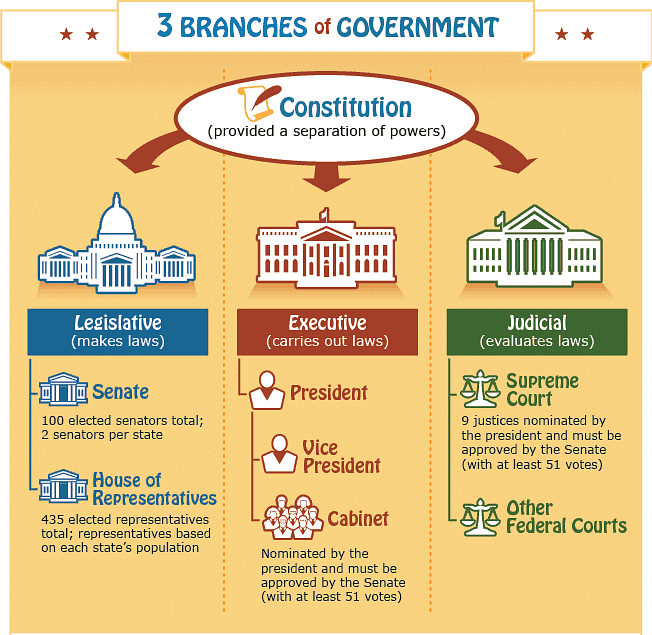
Q 4. Explain the functions of organs of government.
Ans: According to the constitution, there are three organs of the state:
- The legislature refers to our elected representatives. It forms laws and procedures.
- The executive is a smaller group of people who are responsible for implementing laws and running the government.
- The judiciary refers to the system of courts in this country.

Q 5. What do you mean by the tyranny of the majority?
Ans: The tyranny of the majority refers to a situation in which the majority in a democracy imposes its will on the minority in an unfair or oppressive way. This can happen when the majority uses its power to make decisions or pass laws that disregard the rights and needs of minority groups.
For example, if a majority religion in a country imposes laws that restrict the practices of a minority religion, that would be an example of the tyranny of the majority.
Q 6. Describe in detail the various features of the Indian constitution.
Ans:
(a) Federalism
- This refers to the existence of more than one level of government in the country.
- Under federalism, the states are not merely agents of the federal government but draw their authority from the constitution as well. All persons in India are governed by laws and policies made by each of these levels of government.
(b) Parliamentary Form of Government
- The different tiers of government consist of representatives who are elected by the people. The constitution of Indian guarantees universal adult suffrage for all citizens. This means that the people of India have a direct role in electing their representatives. Also, every citizen of the country, irrespective of his/ her social background, can also contest in elections.
(c) Separation of Powers
According to the Constitution, there are three organs of the state.
- The legislature refers to our elected representatives.
- The executive is a smaller group of people who are responsible for implementing laws and running the government.
- The judiciary refers to the system of courts in this country.
(d) Fundamental Rights
- The section on Fundamental Right has often been referred to as the ‘conscience’ of the Indian Constitution. Colonial rule had created a certain suspicion of the state in the minds of the nationalists, and they wanted to ensure that a set of written rights would guard against the misuse of state powers in independent India. It protects citizens against the arbitrary and absolute exercise of power by the state.
- A secular state is one in which the state does not officially promote any one religion as the state religion.
Ans:
- The long experience of authoritarian rule under the colonial state convinced Indians that free India should be a democracy in which everyone should be treated equally and be allowed to participate in government.
- This was not done by one person but by a group of around 300 people who become members of the constituent assembly who had a huge task before them.
- The country was made up of several different communities who spoke different languages, belonged to different religions, and had district culture. Also, when the constitution was being written, India was going through considerable turmoil.
Q 9. What is the importance of the constitution?
Ans: The constitution plays an important role in laying out certain guidelines that govern decision-making within society.
- It lays down rules that guard against the misuse of power by our political leaders.
- It also contains rules to prevent tyranny.
- It also helps to protect us against certain adverse effects on the larger principle that the country believes in.
Q 10. What did Dr Ambedkar state about scheduled caste?
Ans: He stated that although the laws might exist, Scheduled Castes still had reason to fear because the administration of these laws was in the hands of ‘caste Hindu officers’. He, therefore, urged Scheduled Castes to join the government as well as the civil services.
|
63 videos|424 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Civics Chapter 1 Important Question Answers - The Indian Constitution
| 1. भारतीय संविधान क्या है और इसकी आवश्यकता क्यों है? |  |
| 2. भारतीय संविधान में मौलिक अधिकार क्या हैं? |  |
| 3. संविधान सभा का गठन कब और क्यों हुआ? |  |
| 4. भारतीय संविधान की प्रमुख विशेषताएँ क्या हैं? |  |
| 5. भारतीय संविधान में संशोधन कैसे किया जाता है? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|