Important Questions for Class 8 Science - Light
Q1. How is seeing possible, and why can't we see objects in the dark?
Ans: Seeing occurs when light from an object enters our eyes. This light is essential for our vision because it reflects off objects and allows us to perceive them.
In the dark, we cannot see objects because:
- There is no light available to reflect off the objects.
- Without light, our eyes cannot detect anything, making vision impossible.
Q2. What are the laws of reflection, and how do they relate to the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection?
Ans: The laws of reflection state that:
- The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
- Both angles are measured from the normal line to the reflecting surface.
This means that when light hits a surface, it bounces off at the same angle at which it arrived.
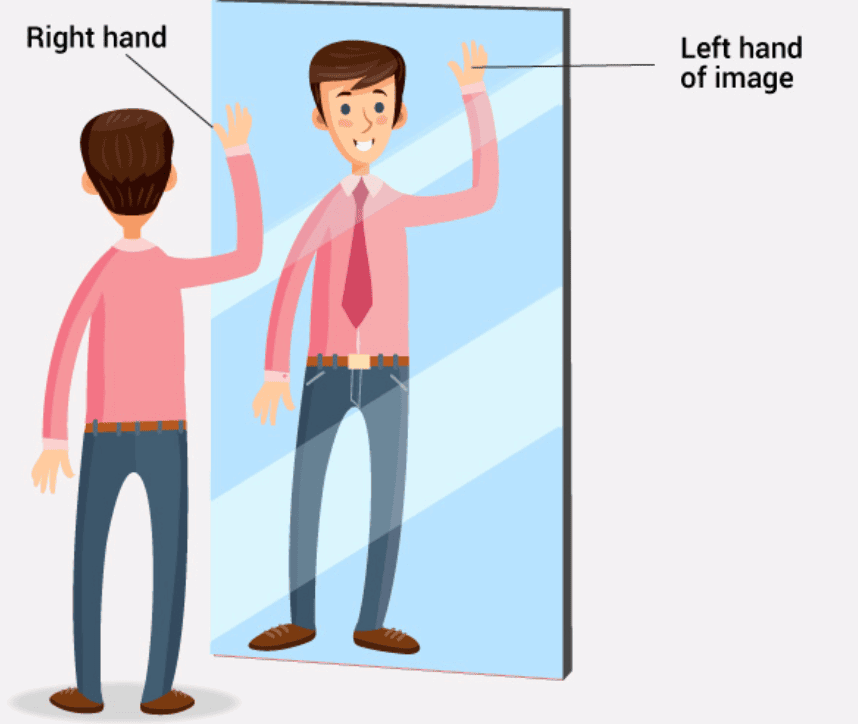
Q3. Explain why lateral inversion occurs in a mirror image.
Ans: Lateral inversion occurs in a mirror image due to the way light reflects off the mirror. When you look into a mirror:
- The left side of the object appears on the right side of the image.
- The right side of the object appears on the left side of the image.
This effect happens because the mirror reverses the direction of light rays, creating the illusion of a flipped image.
Q4. Differentiate between regular and diffused reflection. What causes diffused reflection?
Ans: Regular reflection occurs on smooth surfaces, such as mirrors, which produce clear images. In contrast, diffused reflection happens on rough or uneven surfaces, leading to scattered light and less distinct images.
The primary cause of diffused reflection is the irregularities present on the reflecting surface. These imperfections scatter light in multiple directions, preventing the formation of a clear image.
Q5. What happens when two plane mirrors are placed at an angle to each other, and why is this used in kaleidoscopes?
Ans: When two mirrors are positioned at an angle, they generate multiple images due to the light reflecting between them. This principle is the basis for kaleidoscopes, which create stunning patterns by:
- Reflecting light from different angles.
- Producing symmetrical and intricate designs.
- Allowing the viewer to see a variety of patterns with slight movements.
The combination of these effects results in the captivating visual experience characteristic of a kaleidoscope.
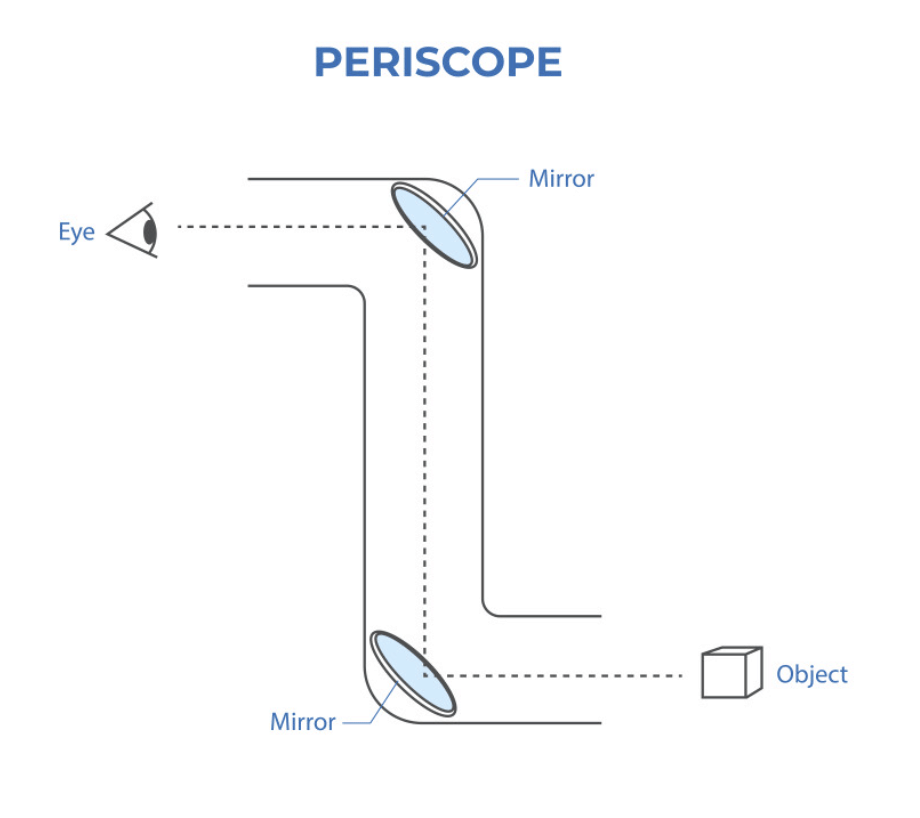
Q6. How do periscopes work, and where are they commonly used?
Ans: Periscopes operate by using two plane mirrors to reflect light, enabling users to see objects that are out of direct sight.
They are commonly found in:
- Submarines - allowing crew members to observe above water while remaining submerged.
- Tanks - providing a view of the battlefield without exposing the crew.
- Bunkers - enabling observation of the surroundings while maintaining cover.
Q7. How does the eye function as a sense organ, and what are the different components of the eye?
Ans: The eye functions as a sense organ by focusing light onto the retina, where nerve cells convert light into signals for the brain to interpret. The main components of the eye are:
- Cornea: The transparent front part that helps focus light.
- Iris: The coloured part that controls the size of the pupil.
- Pupil: The opening that allows light to enter the eye.
- Lens: Focuses light onto the retina.
- Retina: Contains nerve cells that detect light and send signals to the brain.
Q8. Explain the role of the iris in controlling the amount of light entering the eye.
Ans: The iris plays a crucial role in controlling the amount of light that enters the eye by adjusting the size of the pupil. Here's how it works:
- In bright light, the iris constricts, making the pupil smaller. This reduces the amount of light that enters, protecting the retina.
- In dim light, the iris relaxes, allowing the pupil to enlarge. This increases light intake, helping us see better in low-light conditions.
Q9. What is the function of cones and rods in the retina, and what is the blind spot in the eye?
Ans: Cones and rods are two types of photoreceptor cells in the retina that play key roles in vision:
- Cones detect colour and operate best in bright light.
- Rods are more sensitive to dim light and help with vision in low-light conditions.
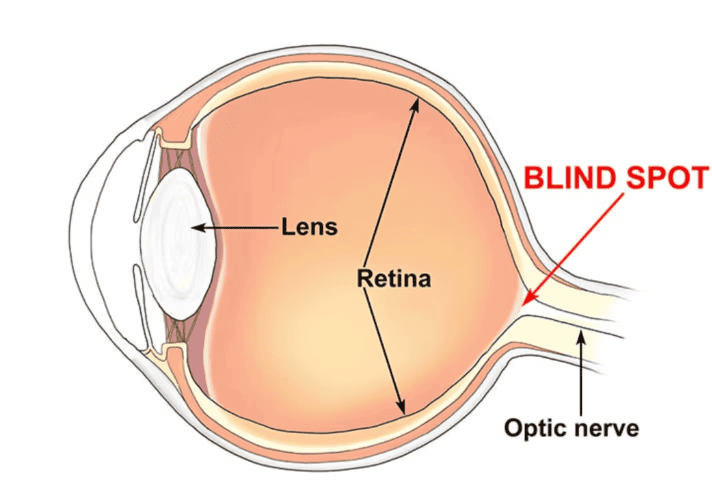
The blind spot is an area on the retina without sensory cells, resulting in a lack of vision in that spot.
Q10. How does persistence of vision explain the phenomenon of movies and animation?
Ans: Persistence of vision refers to the way our retina holds onto an image for a short time, typically less than a second. This phenomenon is crucial in understanding how:
- Movies and animation create the illusion of motion.
- These forms of media show a rapid sequence of separate images.
- When displayed faster than 16 frames per second, our brain blends these images together.
This blending tricks our eyes into perceiving continuous movement, making it possible for us to enjoy films and animated sequences.
Q11. Why is it important to protect your eyes from excessive or insufficient light, and what precautions should be taken?
Ans: Protecting your eyes from both excessive and insufficient light is crucial for overall eye health. Here are the reasons and precautions:
- Excessive light can damage the retina, leading to potential vision problems.
- Insufficient light can result in eyestrain and headaches, making it harder to focus.
To safeguard your eyes, consider these precautions:
- Avoid looking directly at the Sun.
- Refrain from rubbing your eyes to prevent irritation.
- Ensure adequate lighting when reading or working to reduce strain.
- Maintain a proper distance from screens and books.
Q12. How does the deficiency of vitamin A in the diet affect the eyes, and what are some good dietary sources of vitamin A?
Ans: Vitamin A deficiency can significantly impact eye health, leading to issues such as:
- Night blindness - difficulty seeing in low light.
- Dry eyes - can result in further complications.
- Increased risk of eye infections.
To maintain healthy eyes, include these dietary sources of vitamin A in your meals:
- Raw carrots
- Green vegetables
- Cod liver oil
- Eggs
- Milk
- Fruits like papaya and mango
Q13. How do visually impaired individuals read and write using the Braille system, and what is its significance?
Ans: Visually impaired individuals read and write using the Braille system, a tactile method that allows them to recognise characters by touch. Key points include:
- Braille consists of raised dots arranged in specific patterns to represent letters and numbers.
- Each character is formed within a grid of six dots, allowing for combinations to create the entire alphabet.
- This system empowers visually impaired people to access written information independently.
- Significance: Braille is essential for education, communication, and access to literature.
Q14. Explain the structure and function of the cornea and lens in the eye's ability to focus light.
Ans: The cornea and lens play crucial roles in how our eyes focus light:
Cornea: Refracts (bends) light to help direct it into the eye.
Lens:
- Flexible and thicker in the centre, it adjusts shape for focusing.
- Works with the cornea to concentrate light onto the retina.
Together, they ensure that we can see objects clearly at various distances.
Q15. What is cataract, and how is it treated in modern technology?
Ans: Cataract is the clouding of the eye lens, resulting in blurred vision.
Modern treatments include:
- Removing the cloudy lens through a small incision.
- Inserting an artificial lens to restore clear vision.
- Using advanced techniques such as phacoemulsification for quicker recovery.
This procedure is typically safe and effective, helping many patients regain their sight.
|
90 videos|415 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Important Questions for Class 8 Science - Light
| 1. What is light and how does it travel? |  |
| 2. What are the different properties of light? |  |
| 3. How does light behave in different mediums? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the visible spectrum? |  |
| 5. How does light interact with matter? |  |






















