India and International Economic Institutions - 2 | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| BRICS (Brazil-Russia-India-China-South Africa) |

|
| African Development Bank Group |

|
| Organisation of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) |

|
| MERCOSUR |

|
| Regional Financial Institutions |

|
BRICS (Brazil-Russia-India-China-South Africa)

BRICS is a coalition of five major emerging economies: Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa. South Africa joined the group in 2010. The first BRICS summit took place on June 16, 2009, in Yekaterinburg, Russia, and the term "BRICS" was coined by economist Jim O’Neill. To enhance cooperation and stimulate economic growth, BRICS established several institutions, including the New Development Bank, the Contingent Reserve Arrangement, and a Fiber Optic Cable Network. The 14th BRICS Summit was hosted by China via video conferencing in June 2022.
13th BRICS Summit
India hosted the 13th BRICS Summit on September 9, 2021, through video conferencing. The summit's theme was "BRICS@15: Intra-BRICS Cooperation for Continuity, Consolidation, and Consensus." During this summit, member countries agreed to focus on four priority areas: promoting multilateralism, counter-terrorism, utilizing digital and technological tools for achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), and enhancing people-to-people cooperation. The BRICS leaders adopted the New Delhi Declaration at this event.
IBSA (India-Brazil-South Africa)
IBSA is an international group promoting cooperation among India, Brazil, and South Africa. It was formalized in Brasilia on June 6, 2003. The fifth and most recent IBSA Summit was held in Pretoria on October 18, 2011. The group aims to promote South-South cooperation and build consensus on global issues of importance.
BASIC
The BASIC countries—Brazil, South Africa, India, and China—are a coalition of four newly industrialized nations formed by an agreement on November 28, 2009. The group pledged collective action at the Copenhagen Climate Summit and even considered a united walkout if their minimum stance wasn’t recognized by developed nations.
- G-15: The Group of 15 (G-15) is an informal forum established to foster cooperation and provide insights to other international groups like the WTO and the Group of 7. It was founded in 1989 and is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland. Member nations include Algeria, Argentina, Brazil, Egypt, India, Indonesia, Jamaica, Malaysia, Mexico, Nigeria, Peru, Senegal, Venezuela, Yugoslavia, and Zimbabwe.
- G-20: The G-20 is an intergovernmental forum of 19 countries and the European Union, focusing on global economic issues, climate change mitigation, and sustainable development. It represents 90% of global gross national product, 80% of world trade, and two-thirds of the world’s population. India has been a member since its inception in 1999 and held the G-20 Presidency from December 1, 2022, to November 30, 2023. The G-20 Delhi Summit was scheduled to take place in Pragati Maidan, New Delhi, in 2023.
- G-7 (Formerly G-8): The Group of Seven (G-7) is an informal gathering of seven advanced economies that meet annually to discuss global finance, security, energy, and trade issues. It was established in the 1970s, with Russia joining in 1994 to form the G-8 but being expelled in 2014 following the annexation of Crimea. G-7 members include the USA, Canada, Germany, Britain, France, Italy, and Japan. The 47th summit was held in Britain.
- G-77: The G-77 is a coalition of 134 developing countries designed to advance their collective economic interests and enhance their negotiating capacity within the United Nations. It was established on June 15, 1964, by 77 non-aligned nations, and is headquartered in Geneva. Cuba chaired the group in 2023, succeeding Pakistan.
African Development Bank Group

The African Development Bank Group (AfDB) is a multilateral finance institution headquartered in Abidjan, Ivory Coast, since 2014. It provides financial assistance to African governments and private companies investing in Regional Member Countries (RMC). Founded in 1964, it comprises three entities: the African Development Bank, the African Development Fund, and the Nigeria Trust Fund. India became a member in 1983, holding 14,813 shares.
European Union (EU)
The European Union is a political and economic union of 27 member states primarily located in Europe. The EU was awarded the 2012 Nobel Peace Prize for advancing peace, reconciliation, democracy, and human rights. The UK's decision to leave the EU, known as Brexit, officially took effect in 2020.
Euro
The Euro is the currency used by the institutions of the European Union and is the official currency of 19 of the 27 EU Member States, collectively known as the Eurozone. It was established by the 1992 Maastricht Treaty.
Eurasian Economic Union (EEU)
The Eurasian Economic Union (EEU) has been in effect since January 2015, offering cooperation between Western Europe and the Asia-Pacific region. The EEU comprises Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Armenia, and Kyrgyzstan, with its headquarters in Moscow, Russia.
Eurasian Development Bank
The Eurasian Development Bank (EDB), founded in 2006 and headquartered in Almaty, Kazakhstan, is crucial in investing in market economies and supporting Eurasian integration through financing projects that contribute to economic growth and trade expansion among its member states.
Organisation of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)
 OPEC is a permanent inter-governmental organization established in 1960 by Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela. Initially headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, OPEC moved to Vienna, Austria, in 1965. Its mission is to coordinate petroleum policies to ensure stable prices, an efficient petroleum supply, and fair returns for industry investors. Current members include Algeria, Angola, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Venezuela.
OPEC is a permanent inter-governmental organization established in 1960 by Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela. Initially headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, OPEC moved to Vienna, Austria, in 1965. Its mission is to coordinate petroleum policies to ensure stable prices, an efficient petroleum supply, and fair returns for industry investors. Current members include Algeria, Angola, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Venezuela.
Asia-Pacific Economic Co-operation (APEC)
APEC is the premier forum for fostering economic growth, cooperation, trade, and investment in the Asia-Pacific region. Established in 1989, APEC operates on non-binding commitments and aims to reduce trade barriers, promote efficient domestic economies, and increase exports. The Bogor Goals, adopted in 1994, target free and open trade and investment in the Asia-Pacific by 2010 for industrialized economies and 2020 for developing economies.
Gulf Co-operation Council (GCC)
The Gulf Co-operation Council (GCC) is a regional political and economic union comprising Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates. Established on May 25, 1981, the GCC is headquartered in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Its objectives include coordinating regulations across various fields and establishing joint ventures and a unified military force, the Peninsula Shield Force.
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO)
The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) is a Eurasian political and economic alliance comprising China, Russia, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan, India, and Pakistan. Formed in 2001 and headquartered in Beijing, the SCO aims to cooperate on issues related to terrorism, separatism, and extremism. India and Pakistan became full members of the SCO on June 9, 2017. The 2022 SCO summit was held in Samarkand, Uzbekistan, on September 15-16.
G-24: The G-24 is a group of countries coordinating developing countries' positions on international monetary and financial issues. Established in 1971 in Lima, Peru, the G-24 operates as a chapter of the G-77 and is headquartered in Washington, D.C.
Asian Clearing Union (ACU)
The Asian Clearing Union (ACU) was founded in 1974 to promote regional cooperation and facilitate payments among member countries on a multilateral basis, reducing the use of foreign exchange reserves and transfer costs. The ACU is headquartered in Tehran, Iran, and includes Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Iran, Maldives, Myanmar, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.
Financial Stability Board (FSB)
The Financial Stability Board (FSB) was established in 2009 following the G-20 London Summit. Based in Basel, Switzerland, the FSB was created to address vulnerabilities in the global financial system and to develop and implement policies to promote financial stability.
International Labour Organization (ILO)
The International Labour Organization (ILO) was established in 1919 as part of the League of Nations to address social reform at an international level. It became the first specialized agency of the United Nations in 1946. The ILO has pioneered key aspects of industrial society, such as the eight-hour workday, maternity protection, and child labor laws. It has 187 member states and is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC)
The Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations, responsible for coordinating the economic and social work of the UN and its family of organizations. ECOSOC has 54 members elected by the General Assembly for three-year terms and meets throughout the year. Lachezara Stoeva of Bulgaria was elected as the 77th President of ECOSOC on July 25, 2022.
MERCOSUR

MERCOSUR, established in 1991, is a trading bloc in South America that includes Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay. Its primary goal is to promote the free movement of goods, services, capital, and people among its member countries. Modeled after the European Union, MERCOSUR is the fourth-largest integrated market globally, following the European Union (EU), the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN). Efforts are also underway to create a Free Trade Area between MERCOSUR and India, focusing initially on increasing trade and granting mutual tariff preferences.
Bank for International Settlements (BIS)
The Bank for International Settlements (BIS), founded in 1930, is one of the oldest international financial institutions. Known as the "Bank for Central Banks," BIS aims to foster international monetary and financial stability. It offers various financial services, including interest-bearing accounts, currency transactions, asset management, and short-term collateralized loans. BIS is governed by central bank members, a Board of Directors, and the Bank's management. Located in Basel, Switzerland, BIS had 63 central bank members as of January 2022.
Regional Financial Institutions

New Development Bank (NDB)
The New Development Bank (NDB), originally the BRICS Development Bank, was established by the BRICS countries—Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa. The bank, headquartered in Shanghai, China, admitted Bangladesh, UAE, and Uruguay as new members in September 2021, and Egypt joined in December 2021. The idea for the NDB was first proposed by India at the 4th BRICS Summit in 2012. The bank officially launched following the 6th BRICS Summit in Fortaleza, Brazil, in July 2014. The NDB focuses on mobilizing resources for infrastructure and sustainable development projects in BRICS and other emerging economies.
Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB)
The Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) is a 21st-century multilateral development bank, initiated by Chinese President Xi Jinping and Premier Li Keqiang in 2013. By the end of March 2015, the AIIB had grown to include 57 Prospective Founding Members, with its headquarters in Beijing. As of October 2021, the AIIB had 104 members. The bank aims to foster economic growth and infrastructure development across Asia and beyond.
Asian Development Bank (ADB)
The Asian Development Bank (ADB), established in 1966, is a partnership of 68 member countries with its headquarters in Manila, Philippines. ADB was created following the recommendations of the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific, aiming to promote economic growth and cooperation in the Asia-Pacific region. India is a founding member. The ADB's primary functions include providing loans and equity investments for economic and social development, offering technical assistance for development projects, and coordinating development policies among its member countries.
Report published by International Organisation:
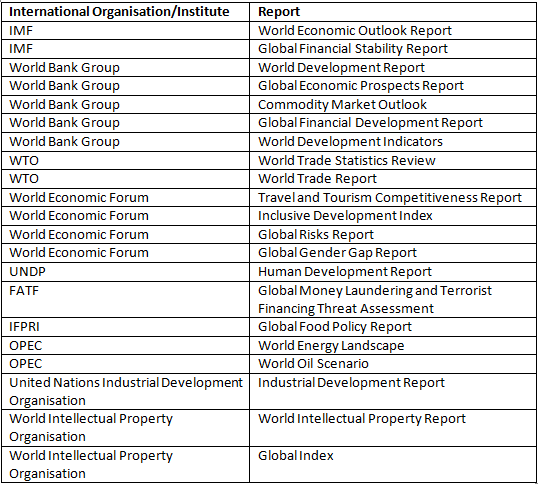
International organisations and their Headquarters:
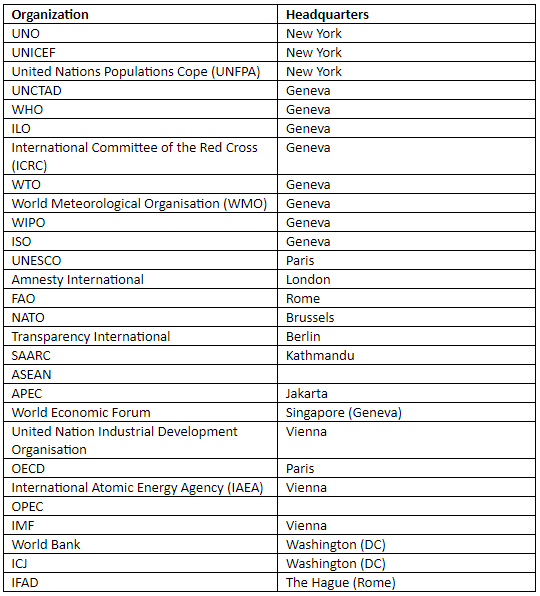
|
157 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on India and International Economic Institutions - 2 - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What is the role of BRICS in the global economy? |  |
| 2. How does the African Development Bank Group contribute to economic development in Africa? |  |
| 3. What is the purpose of the Organisation of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)? |  |
| 4. What is MERCOSUR and how does it impact trade in South America? |  |
| 5. How do regional financial institutions support economic development in their respective regions? |  |















