Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Geography for GCSE/IGCSE > Inequalities in Development
Inequalities in Development | Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Stages of development |

|
| The development gap |

|
| Differences within Countries |

|
| Causes of regional inequalities |

|
Stages of development
- All countries progress through various development stages.
- The United Nations identifies four primary stages of development.

The development gap
- The development gap reflects the varying levels of development between the least and most developed nations globally.
- Several factors contribute to these development disparities.
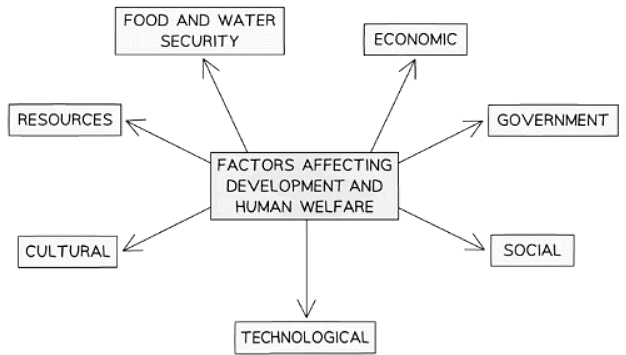
- Physical Geography
- Landlocked countries face challenges in trade, leading to slower development.
- Small nations exhibit slower growth due to limited human and natural resources.
- Countries with extreme climates also experience slower development.
- The physical geography influences the availability of natural resources.
- Natural resources are provided by the physical environment:

- Some countries rely solely on their own natural resources for sustenance.
- Several nations must import resources unavailable within their borders, impacting their supply security.
- Dependence on imported resources exposes countries to supply risks during conflicts or political instability.
- Essential for progress, water, food, and energy security are pivotal in fostering a nation's growth.
Demographic Influences
- The population composition, influenced by birth rates, death rates, and immigration, directly affects the workforce availability.
- Nations witnessing significant drops in birth rates often exhibit rapid growth rates.
Technological Advancements
- Technological innovations play a crucial role in enhancing water, food, and energy security.
- Advancements such as farm mechanization boost yields, while improved land surveying uncovers additional energy sources.
- Efficient resource utilization is facilitated through technological interventions.
Societal Factors
- Education levels directly impact individuals' skills, with higher education correlating with national development.
- Healthcare quality influences workforce productivity by affecting individuals' well-being and capacity to work.
- Inequality within a society can hamper overall productivity.
Governmental Policies
- Government stability and efficacy play pivotal roles in driving development and enhancing human welfare.
- Regions with democratically elected governments typically experience higher levels of development and human welfare.
- Corrupt administrations often neglect investments in national development and the betterment of citizens' lives.
- Economic policies enacted by governments significantly influence both development and human welfare by:
- Advocating for an open economy that promotes foreign investment, leading to accelerated development.
- Implementing policies that prioritize higher savings rates and reduced spending relative to GDP, fostering additional development efforts.
Question for Inequalities in DevelopmentTry yourself: What are some factors that contribute to development disparities between countries?View Solution
Differences within Countries
- Disparities in development are not only evident between countries but also within them, regardless of their development status.
- Development tends to be concentrated in specific regions within countries.
- Inequalities within nations arise from various factors.
- The theory of cumulative causation offers one explanation for regional disparities:
- Growth in core regions attracts skilled labor and investment capital.
- Peripheral areas experience declines as skilled labor relocates and investment concentrates in the core regions.
- This disparity between core and peripheral regions widens over time.
- Eventually, the growth of core regions may stimulate development in the periphery due to increased demand for raw materials.

Stages of Regional Inequality
- Pre-industrial stage: This initial phase marks the period where regional differences are minimal and least pronounced.
- Period of rapid economic growth: During this phase, regional differences start to widen as some regions experience swift economic development while others lag behind.
- Regional economic convergence: In this final stage, wealth generated in core regions begins to spread to peripheral areas, reducing disparities.
Causes of regional inequalities
- Residence: Urban areas tend to attract more investments, leading to increased business opportunities and incomes. However, disparities in income may still exist within urban areas.
- Ethnicity: Discrimination based on ethnicity can result in certain ethnic groups having significantly lower income levels compared to the dominant groups in a country. This can limit the opportunities available to these marginalized groups.
- Employment: The division between formal and informal employment has a direct impact on incomes. Formal employment typically offers higher wages and additional benefits like paid leave.
- Education: Individuals with higher levels of education generally secure better-paying jobs, emphasizing the importance of education in improving income levels.
- Land Ownership: Inequalities in land ownership are closely linked to income disparities, highlighting the significance of land distribution in economic well-being.
The document Inequalities in Development | Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Geography for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
57 videos|70 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Inequalities in Development - Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What are the stages of development? |  |
Ans. The stages of development refer to the different phases that a country goes through as it progresses from a less developed to a more developed state. These stages typically include the traditional society, preconditions for take-off, take-off, drive to maturity, and high mass consumption.
| 2. What is the development gap? |  |
Ans. The development gap refers to the disparities in economic prosperity, living standards, and overall development between different countries or regions. It highlights the unequal distribution of resources and opportunities globally, leading to significant differences in development levels.
| 3. How do differences within countries contribute to regional inequalities in development? |  |
Ans. Differences within countries, such as disparities in income, education, healthcare, and infrastructure, can contribute to regional inequalities in development. These internal variations can further widen the gap between prosperous and disadvantaged regions within a country, leading to uneven economic growth and social development.
| 4. What are some causes of regional inequalities in development? |  |
Ans. Regional inequalities in development can be caused by factors such as uneven distribution of resources, inadequate infrastructure, lack of investment in education and healthcare, political instability, corruption, and historical legacies of colonization or conflict. These factors can create disparities in economic development and living standards between different regions.
| 5. How can inequalities in development be addressed? |  |
Ans. Inequalities in development can be addressed through policies and initiatives that promote equal access to education, healthcare, infrastructure, and economic opportunities. Governments, international organizations, and civil society can work together to implement targeted interventions, reduce disparities, and promote inclusive growth for all regions and populations.
Related Searches


















