International Boundaries | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What are Boundary Lines? |

|
| Hindenburg Line: Germany-Poland |

|
| Durand Line: Pakistan-Afghanistan, 1893 |

|
| McMohan Line: India-China, 1914 Shimla Convention |

|
Introduction
- An international border is a defined space that separates sovereign states, each governed by its own jurisdiction unaffected by others. It marks the extent of a government's control over its territory.
- The International Boundary holds the distinction of being the world's longest international land boundary, dividing Canada and the United States. Additionally, this vast border also encompasses Canada's shared boundary with Alaska.
What are Boundary Lines?
A boundary line is defined as the dividing line between two countries or property areas. An example of this is the Line of Control (LOC), which serves as the frontier between India and Pakistan.
Radcliffe Line: India-Pakistan-Bangladesh
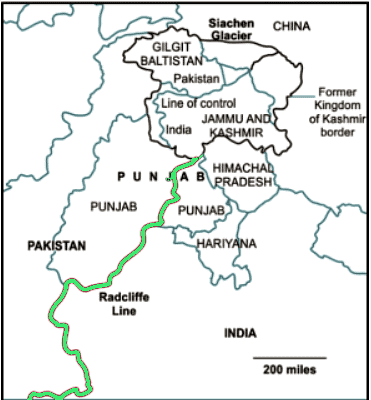
The Radcliffe Line was responsible for partitioning the Indian and Pakistani provinces of Punjab and Bengal, named after its architect, Sir Cyril Radcliffe. Presently, this border is divided into two sections: the West Radcliffe Line marking the Indo-Pakistan border and the East Radcliffe Line marking the Indo-Bangladesh border. However, disagreements emerged concerning certain regions, including the Chittagong Hill Tracts and the Gurdaspur District.
Hindenburg Line: Germany-Poland
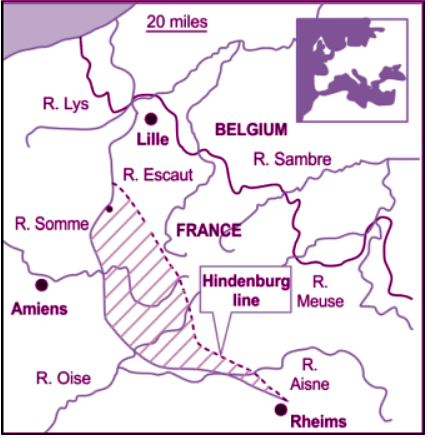
The Siegfried Line, constructed in 1917 and 1918 on the Western Front of the First World War, served as the German Army's most robust and ultimate line of defense. It comprised three well-fortified trench systems. The Weimar Republic extended this defensive line as an extension of the Hindenburg defensive line.
Durand Line: Pakistan-Afghanistan, 1893
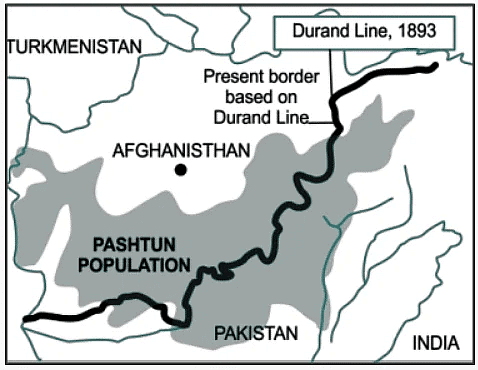
The Durand Line serves as the international border between Afghanistan and Pakistan in South Asia. Originally established in 1893, it was intended to define the borders between British India and Afghanistan, with the aim of enhancing diplomatic and trade relations by delineating their respective areas of influence. While Pakistan acknowledges this western boundary, Afghanistan does not fully recognize it.
McMohan Line: India-China, 1914 Shimla Convention
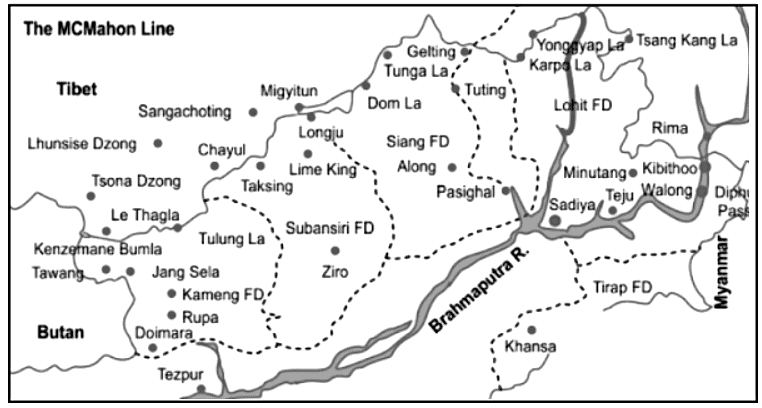
- During the 1914 Simla Convention, British colonial governor Sir Henry McMahon put forward the McMahon Line as a proposed boundary between British and Tibetan officials. This line now represents the legal separation between China and India.
- India views the McMahon Line as its legal national border; however, China rejects both the Simla Accord and the McMahon Line. China's stance is based on the assertion that Tibet was not a sovereign state and, therefore, lacked the authority to engage in treaty agreements.
- In the eastern portion of its border with India, China acknowledges a Line of Actual Control that largely corresponds to the "McMahon Line."
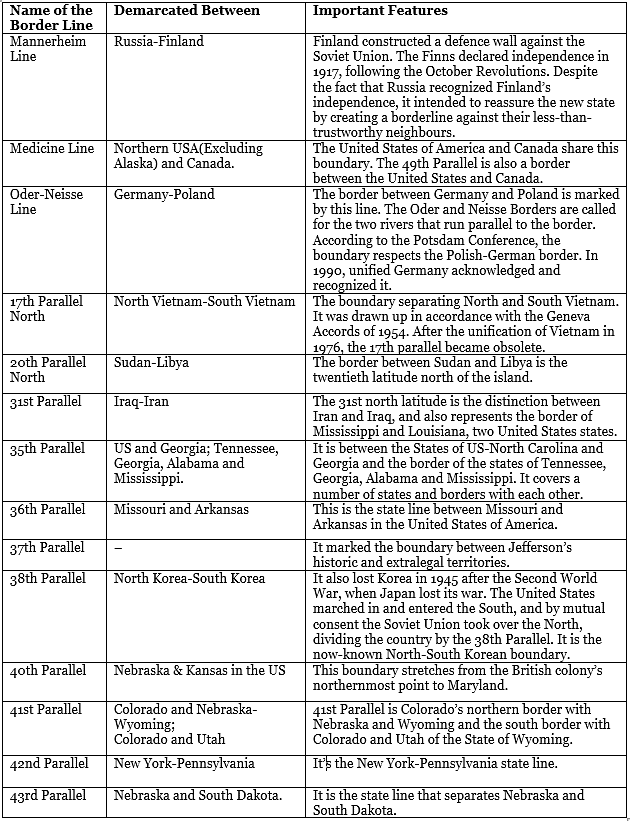
Other Boundary Lines of the World
|
744 videos|1444 docs|633 tests
|




















