Internet Banking & Mobile Banking | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Internet Banking? |

|
| Types of Internet Banking |

|
| Types of Fund Transfers |

|
| What is Mobile Banking? |

|
| Types of Mobile Banking Services |

|
| Features of Mobile Banking |

|
What is Internet Banking?

- Internet banking enables users to access banking services online through websites or applications provided by banks.
- Clients can manage their accounts using various devices, such as smartphones, desktops, or tablets.
- This digital service allows users to perform essential banking functions, including transferring funds, viewing transaction histories, paying bills, and more—all of which previously required visiting a physical branch and waiting in lines.
- As more individuals connect to the internet, most banking services have shifted online, making them easily accessible from anywhere.
- To use internet banking, a person needs an active bank account, which must be registered online.
- Most banks offer dedicated applications, and customers are required to log in with their credentials.
- This process helps verify their identity and grants access to various banking services, which are secured with multiple authentication measures.
- Some banks operate entirely online without physical branches, reducing costs and improving digital services.
- However, using internet banking requires caution, as there are risks associated with online transactions.
- Customers should ensure their personal and financial information remains private to prevent fraud.
- Most banks do not charge for standard internet banking services, but some fees may apply depending on the transaction.
- Many people now rely solely on internet banking for tasks such as paying utility bills, transferring funds, or managing payment cards.
- With increasing adoption, internet banking has become the new norm, and governments are implementing measures to improve its safety and accessibility.
Types of Internet Banking
The scope of internet banking varies depending on the bank and its offerings, which are often influenced by budget and whether the bank is private or public. Private banks frequently offer more advanced digital banking solutions. Here are the main types of internet banking:
- Informational Internet Banking: This basic form of internet banking provides information about a bank’s services and financial products through its website or application. Customers can browse details like account types, branch locations, loan offerings, and other services. Communication is typically one-way, with the bank sharing promotional material or service updates. For example, a customer might visit the website to learn about different account options or email the bank for more information.
- Communicative Internet Banking: This type of internet banking enables limited interaction between customers and the bank. Users can raise queries, often answered by chatbots, which provide general information like account balances, loan details, and fund transfer procedures. For example, a customer might ask a chatbot about loan interest rates, compare them with other banks, and choose the best option without needing to contact a branch directly.
- Transactional Internet Banking: Transactional internet banking allows customers to perform monetary transactions, such as transferring funds, paying bills, or investing in securities. This more advanced form of banking requires the customer to log in with secure credentials like passwords or PINs. For example, a customer can pay their credit card bill online through their bank’s website, without the need to visit a branch.
Types of Fund Transfers
There are several methods of transferring funds through transactional internet banking, each suited to different needs:
- NEFT (National Electronic Fund Transfer): Transfers money between banks using the recipient's account number and IFSC code. This method is widely used for non-urgent transfers.
- RTGS (Real Time Gross Settlement): Designed for large transactions, typically with a minimum of two lakhs, and provides instant transfers, often within 30 minutes.
- IMPS (Immediate Payment Service): A quick transfer method that combines the benefits of NEFT and RTGS. It has no minimum limit and enables instant payments using the recipient’s mobile number and IMPS ID.
- UPI (Unified Payments Interface): This fast and convenient method allows transfers using only a mobile number or virtual payment address, with a cap of one lakh per transaction.
Applications of Internet Banking
Internet banking offers a wide range of functions, including:
- Checking account balances and viewing transaction histories.
- Setting up automatic bill payments.
- Transferring funds quickly and easily.
- Accessing account statements for budgeting or tax purposes.
- Ordering payment cards and chequebooks.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Internet Banking
Advantages:
- Simplifies fund transfers and other transactions at low costs.
- Enables 24/7 monitoring of accounts.
- Allows users to open deposits like fixed or recurring accounts from home.
- Facilitates bill payments for utilities like electricity, internet, and cable.
- Offers convenient ordering of payment cards and chequebooks online.
Disadvantages:
- Cash deposits still require a visit to a physical branch.
- A reliable internet connection and device are necessary for access.
- Internet banking may be complex for those unfamiliar with technology.
- Vulnerability to cyber-attacks necessitates caution.
- Fraud and security risks are common concerns.
Examples of Internet Banking
- Checking account balances online using a bank’s app and viewing past transactions.
- Companies paying employee salaries through methods like NEFT or IMPS.
What is Mobile Banking?
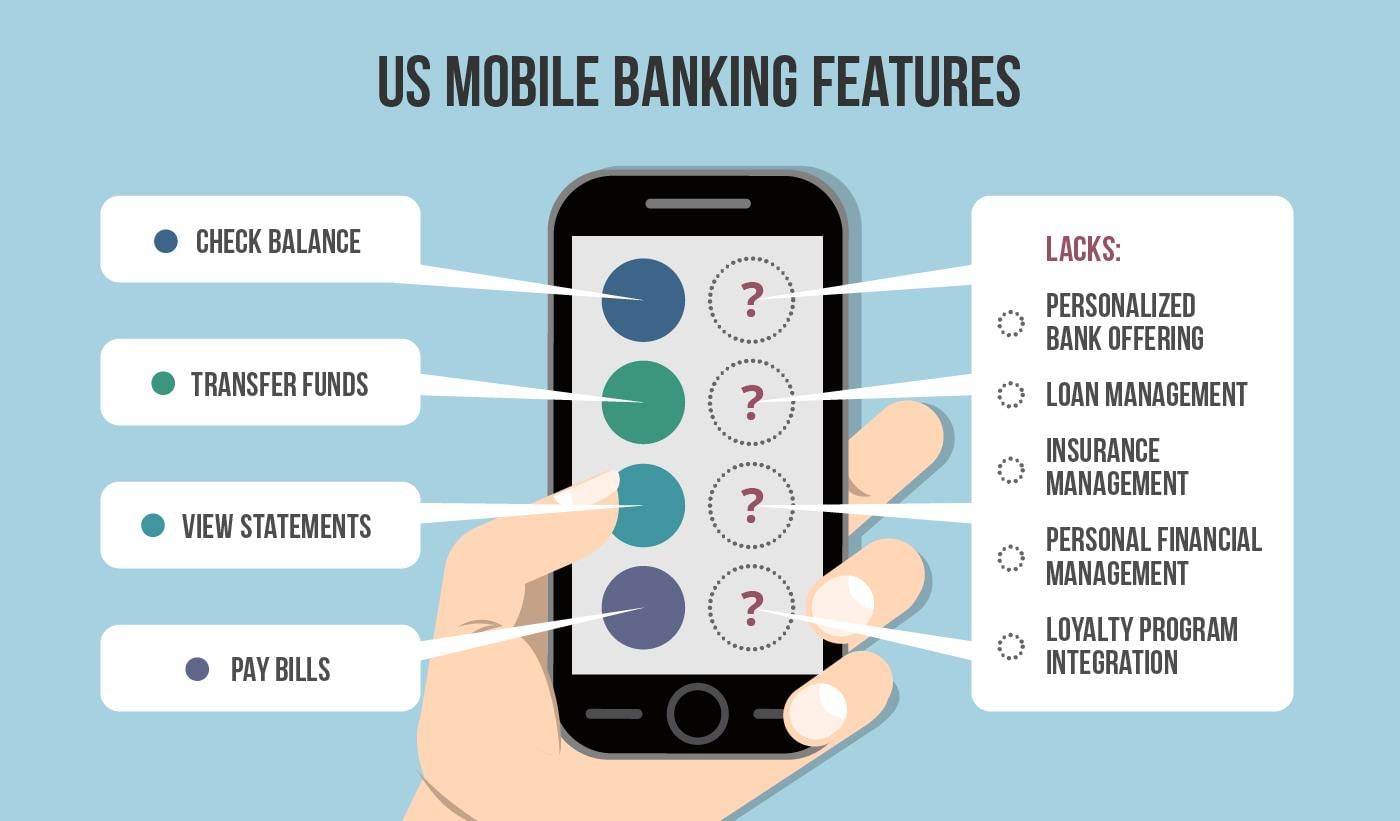
- Mobile banking refers to accessing banking and financial services via a mobile device.
- Banks offer this service to their customers, enabling them to transfer money, pay bills, and check account information conveniently from their phones.
- Understanding mobile banking is crucial for the economy, as it helps people stay informed about the latest banking services.
- It fosters a digital connection between customers and banks, encouraging more reliance on mobile banking for everyday financial tasks.
- This, in turn, reduces the effort required for basic banking needs.
- Mobile banking encompasses all services provided by banks through mobile devices, including SMS, USSD, or banking applications.
- The USSD service caters to individuals without internet access, allowing them to transfer funds using a specific USSD number.
- Most banks provide mobile banking through their websites or apps, requiring users to register and log in using their banking details.
- These services are secured by multiple layers of protection, such as passwords, with verification required at various stages, like logging in to check account balances.
- Mobile banking plays a vital role in the Indian economy, promoting digital transactions and fostering a cashless society.
- Understanding mobile banking enhances safety and reduces the risk of fraud when accessing these services.
Types of Mobile Banking Services
Mobile banking consolidates many services that previously required in-person branch visits. These include account management, financial transactions, investments, loans, customer support, and even consumer complaints.
Account Information:
Mobile banking provides easy access to account information through an app. After registering and logging in, users can:
- View bank statements and past transactions
- Enable or disable account alerts
- Monitor recurring and fixed deposits
- Review loan terms and statements
- Access debit and credit card details
- Explore insurance options and investments
Transactions:
- With mobile banking, users can effortlessly transfer funds between accounts, make payments to other bank accounts, and pay bills, premiums, or loans. Many banks also offer discounts for online shopping, facilitating transactions through their apps.
Investments:
- Mobile banking enables users to manage deposits, add or withdraw funds, and in some cases, trade securities and purchase insurance.
Loans:
- Users can manage loan accounts, pay EMIs, and track loan statuses. Some banks even offer small digital loans via their mobile apps.
Customer Support:
- Banks provide customer support through mobile apps or websites, where users can resolve issues, request new cards or chequebooks, and access helpful guides to better understand mobile banking.
Content Services:
- Banks offer content services where users can stay informed about discounts and general financial news.
Consumer Complaints:
- Mobile banking apps allow users to report fraud or invalid transactions, streamlining the complaint process.
Features of Mobile Banking
Understanding mobile banking also requires familiarity with its key features:
- Accessibility: Mobile banking is available 24/7, unlike traditional banking hours. Users can access transactions, account history, and perform transfers anytime.
- Security: Mobile banking employs multiple layers of security, such as passwords, biometrics, or security questions, making online transactions safer.
- Transferability: Fund transfers via mobile banking are secure, requiring OTPs and passwords for authentication.
- Investment Management: Users can monitor investments, track returns, and engage in trading through mobile banking apps.
- Digital Payments: Many mobile banking apps support QR code-based payments for merchant transactions, along with traditional transfer methods.
- Customer Service: Mobile banking apps often provide live chat options to assist with issues, available around the clock.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Mobile Banking
Advantages:- 24/7 Access: Users can manage their finances anytime, anywhere.
- Fund Transfers: Mobile banking simplifies fund transfers and enables tracking over time.
- Quick Problem Reporting: Issues can be promptly reported through customer service options.
- Faster Complaint Resolution: Requests and complaints are resolved quicker through mobile apps.
- Digital Shopping Benefits: Payments for online shopping are simplified, sometimes with discounts.
- Investment Management: Users can handle various investments and deposits through banking apps.
- Promotes Cashless Economy: Mobile banking encourages cashless transactions, reducing theft risks.
Disadvantages:
- Tech Barrier: Those unfamiliar with technology may find mobile banking challenging to use.
- Susceptible to Fraud: Digital payments carry risks of cybercrime.
- Complex Interfaces: Many apps are not user-friendly, making navigation difficult for some.
- Network Issues: Internet connectivity problems can disrupt transactions.
- Follow-Up Challenges: Complex issues may still require contacting the bank directly.
Conclusion
Understanding mobile banking is crucial for India as it promotes the adoption of digital financial services. This shift reduces the need for frequent branch visits and lowers operational costs for banks. Authorities must ensure robust security measures to boost confidence in mobile banking and encourage wider adoption across the population.
|
157 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Internet Banking & Mobile Banking - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What is Internet Banking? |  |
| 2. What are the types of Internet Banking? |  |
| 3. What are the types of fund transfers available in Internet Banking? |  |
| 4. What is Mobile Banking? |  |
| 5. What are the features of Mobile Banking? |  |




















