Introduction & Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics | Physical Chemistry PDF Download
Thermodynamics
“The study of the flow of heat or any other form of energy into or out of a system as it undergoes a physical or chemical transformation, is called thermodynamics.”
Thermodynamics Terms and Basic Concepts
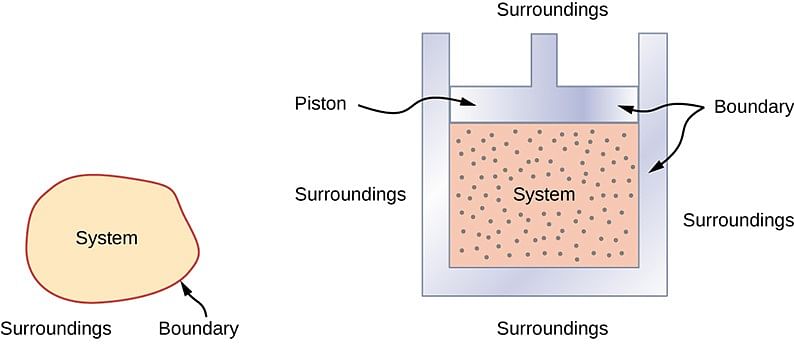
System, Boundary, Surroundings:
- System: “A system is that part of the universe which is under thermodynamic study and the rest of the universe is surroundings.”
- Boundary: “A real or imaginary surface separating the system from the surroundings is called the boundary.”
- “When a system is uniform throughout, it is called a Homogeneous system & a Heterogeneous system is one which consists of two or more phase.”
- Surroundings: The surroundings contain everything other than the system. The system and the surroundings together make up the universe.
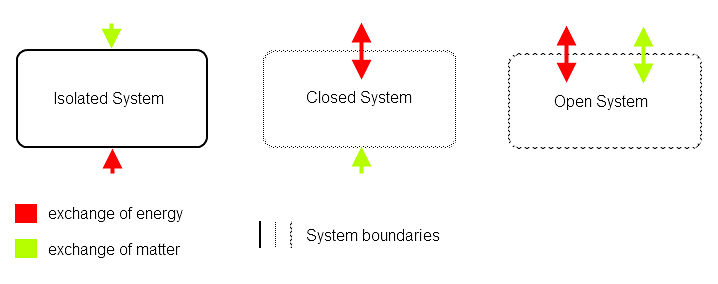
Types of Thermodynamics Systems
1. Open system: An open system is one that can transfer both energy and matter to and from its surroundings
2. Closed system: A closed system is one that cannot transfer matter but transfer energy in the form of heat, work & radiation to and from its surroundings.
3. Isolated system: An isolated system is one that can transfer neither matter nor energy to and from its surroundings.
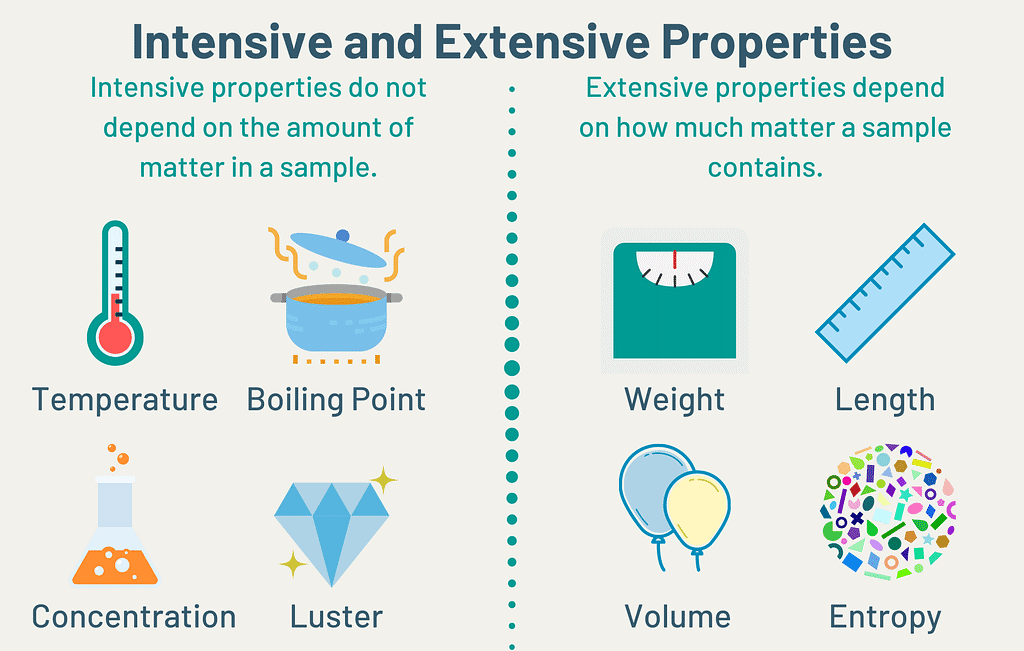
Intensive & Extensive Property
A. Intensive property: A property that does not depend on the quantity of matter present in the system is known as an intensive property.
Example: Temperature (T), pressure (P), and density (r) are examples of Intensive properties.
B. Extensive property: A property that depends on the quantity of matter present in the system, is called an extensive property.
Example: Volume, number of moles, enthalpy, entropy and Gibb’s free energy etc. “Extensive properties are additive while intensive properties are not”.
Thermodynamics Process
1. Isothermal process: The process in which the temperature remains fixed, are termed isothermal process.
For an isothermal process dT = 0
2. Adiabatic process: The process in which no heat can flow into or out of the system are, called adiabatic process.
For an adiabat ic process dq = 0
3. Isobaric process: The processes which take place at constant pressure are called isobaric process.
For an isobaric process dp = 0
4. Isochoric process: Those processes in which the volume remains constant are known as isochoric process.
For isochoric process dV = 0

Cyclic Process
When a system in a given state goes through a number of different processes and finally returns to its initial state, the overall process is called a cycle or cyclic process.
For cyclic process dE = 0, dH = 0.
State Functions
A thermodynamic system is said to be in a certain state when all its properties are fixed.
These states of a system are pressure (P), temperature (T), volume (V), mass, and composition. Change in certain property alters the state of the system, these are referred to as state variables or state functions, or thermodynamic parameters.
The state functions P, V, T are in the form of an algebraic relationship called the equation of state. Thus for 1 mole of pure gas, the equation of state is
PV = RT (R is gas constant)
“All the thermodynamic quantity like P, T, V, H, G, U, A, S, µ are state function”. Work and heat are path functions and not state functions.
Euler's Theorem
In a mathematical way, a function is said to be a state function if it follows Euler’s theorem.
Let z be a thermodynamic quantity then it is said to be a state function if it follows Euler’s theorem.
then 
Let 

⇒ dz = A dx + B dy
if 
then z said to be a state function. and this is Euler’s theorem.
if 
then z is not state function if z is state function then

⇒
i.e., when we change the operator then the constant will also change.
Cyclic Rule for State Functions
Let z is the function of x & y then

For a cycle dz = 0
Then 


This is cyclic rule.
This cyclic rule applicable only for state functions.
|
83 videos|142 docs|67 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction & Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics - Physical Chemistry
| 1. What is thermodynamics? |  |
| 2. What are state functions in thermodynamics? |  |
| 3. What does the cyclic rule for state functions state? |  |
| 4. What are the basic concepts of thermodynamics? |  |
| 5. How does thermodynamics relate to everyday life? |  |