Introduction - G.S.T. Goods & Service Tax - Commerce PDF Download
Introduction
- Goods and Services Tax (GST) is levied at the prescribed rate on every supply, i.e., sale of goods and/or services except alcohol for human consumption and petroleum.
- Supply of goods means the sale of goods, whereas the supply of services means the rendering of service. It is possible that supply is both goods and services.
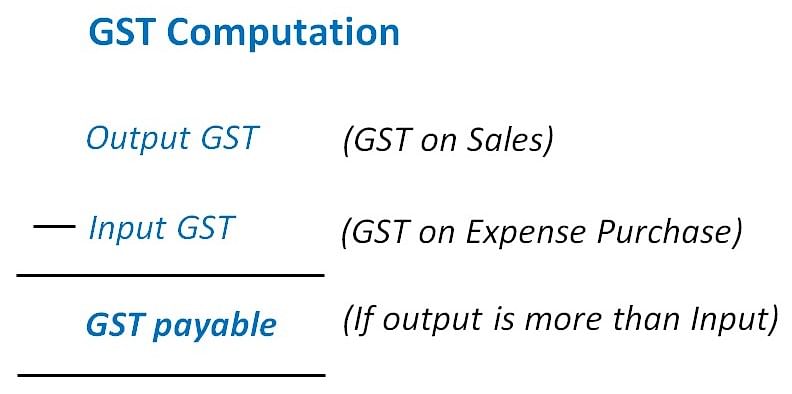
- GST is a Value Added Tax because GST Paid (termed as Input GST) is set off against GST Collected (termed as Output GST). As a result, GST is on the incremental value of goods and/or services supplied (sold).

- In effect, GST Paid (Input GST) on purchases of goods and/or services is not a cost for the purchaser (except in cases discussed later) but is an asset since it can be set off against GST Collected on sales.
- Similarly, GST Collected (Output GST) on the sale of goods and/or services is not an income of the seller but is a liability.
GST is levied under the following three categories:
1. Central GST (CGST)
- CGST is levied on intra-state supply (i.e., supply within the state) of goods and services.
- In the case of intra-state supply (sale), both CGST and SGST (or UTGST) are levied at half of the prescribed rate of tax.
- For example, if the rate of GST is 18%, 9% will be levied as CGST and 9% as SGST (or UTGST).
2. State GST (SGST) or Union Territory
- GST (UTGST)SGST (or UTGST) is also levied on intra-state supply (i.e., supply within the state) of goods and services.
- In the case of intra-state supply (sale), both SGST (or UTGST) and CGST are levied at half of the prescribed rate of tax.
- For example, if the rate of GST is 18%, 9% will be levied as CGST and 9% as SGST (or UTGST).
For the discussion, SGST and UTGST are referred to as SGST.
3. Integrated GST (IGST)
- IGST is levied on inter-state supply (i.e., supply outside the state) of goods and/or services, import of goods and/or services into India, and export of goods and/or services from India.
Which GST is to be levied on the Supply?
GST is of three types, i.e., Central GST (CGST), State GST (SGST), and Integrated GST (IGST). Now, we need to know which type of GST will be levied on the supply of goods and/or services.
1. CGST and SGST are levied on intra-state (within the state) supply of Goods and/or Services: Whether a supply (sale) of goods and/or services is intra-state will depend on the place from where the supply is made and the place to which supply is made.
For example, if both seller and purchaser of goods and/or services are located within the same State (say West Bengal), both CGST and SGST will be levied.
2. IGST is levied on inter-state supply (sale) of Goods and/or Services: Whether a supply (sale) is inter-state will also depend on the place from where the supply is made and the place to which supply is made.
For example, if the seller is located in Delhi and the purchaser is located in Kolkata, IGST will be levied.
Reverse Charge Mechanism
- Certain purchases of goods and services are placed under Reverse Charge Mechanism.
- It means that the seller of goods and/or services will not charge GST, but instead, the purchaser of goods and/or services will deposit GST in the Government Account and claim it as Input GST.
- Goods and/or services falling under Reverse Charge Mechanism are Payment of a fee to Lawyers; Payment for Use of Copyright; Purchase of Goods and/or Services by Registered Person from Unregistered Person; Transport of Goods; Insurance Commission; and Sponsorship.
Categorizing GST for Accounting Purpose
- GST Paid (Input GST) individually Input (CGST, SGST, and IGST) is set off against GST Collected (Output GST) individually Output (CGST, SGST, and IGST) in a prescribed order.
- Therefore, it is necessary that separate accounts for Input GST and Output GST for each category of GST, i.e., CGST, SGST, and IGST, are maintained.
- It will enable the enterprise to follow the prescribed order of setting off each category of GST.
The GST Accounts maintained are:
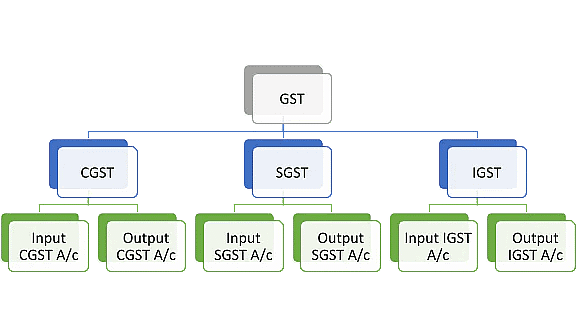
1. Input CGST: Input CGST is the CGST Paid on intra-state purchase (supply) of Goods and/or Services and it can be set off against GST Collected, i.e., Output CGST and Output IGST in that order. Besides the above, taxpayers may pay CGST in Government Account.
2. Input SGST: Input SGST is the SGST Paid on intra-state purchase (supply) of Goods and/or Services and it can be set off against GST Collected, i.e., Output SGST and Output IGST in that order. Besides the above, taxpayers may pay SGST in Government Account.
On intrastate supply of goods and/or services, both CGST and SGST are levied at 50% of the specified rate. For example, if the specified rate is 18%, both CGST and SGST will be levied at 9% each.
3. Input IGST: Input IGST is the IGST Paid on inter-state purchase (supply) of Goods and/or Services, and it is allowed to be set off against GST Collected, i.e., Output IGST, Output CGST, and Output SGST in that order. IGST is also levied on goods and/or services imported from outside the country. Besides the above, taxpayers may pay IGST in Government Account.
4. Output CGST: Output CGST is the CGST Collected on an intra-state sale (supply) of Goods and/or Services along with SGST.
5. Output SGST: Output SGST is the SGST Collected on an intra-state sale (supply) of Goods and/or Services along with CGST.
6. Output IGST: Output IGST is the IGST Collected on inter-state sale (supply) of Goods and/or Services. In the case of an inter-state sale, only IGST is levied.
Accounting of GST
(a) GST Paid (Input GST): GST Paid on the purchase of goods and/or services is an asset, except where it is not allowed to be set off and is accordingly debited to Input GST, i.e, Input CGST Account, Input SGST Account or Input IGST Account.
(b) GST Collected (Output GST): GST Collected on the sale of goods and/or services is a liability and is accordingly credited to Output GST, i.e., Output CGST Account, Output SGST Account, or Output IGST Account.
Order for Setting Off Input GST Against Output GST
Input GST (Paid) is set off against Output GST (Collected) but in the prescribed order.
It is explained below with the help of a diagram:
ACCOUNTING OF GST PAID (INPUT GST)
When is GST Paid on Supply (Purchase) an Asset?
- GST Paid is an asset for the enterprise when GST Paid (Input GST) can be set off against GST Collected (Output GST).
- GST Paid on purchases of goods and/or services that can be set off against GST Collected is debited to Input GST under (CGST, SGST or IGST as per category of GST Paid) Account.
- Therefore, accounting of GST Paid on purchase of goods and/or services will differ depending on whether GST Paid can be set off against GST Collected or not.
When is GST Paid on Supply (Purchase) a Cost?
- GST Paid is a cost when input credit for GST Paid is not allowed to be taken,i.e., it cannot be set off against GST Collected.
- In such cases, GST Paid on purchases of goods and/or services that cannot be set off against GST collected is debited to the account where the transaction is debited.
- For example, Mohit visits a restaurant and paid a bill of Rs. 1,200 inclusive of CGST Rs. 100 and SGST Rs. 100. GST Paid for food and beverages bill is not allowed to be set off against GST Collected (Output GST). It means that Mohit should debit Business Promotion Account by Rs. 1,200.
- Examples of supply (Purchase) of Goods and/or Services on which GST Paid cannot be set off and thus, is Cost are:
(i) Food and Beverages Expenses (Restaurant Bills);
(ii) Membership Fee of Club, Health and Fitness Centre;
(iii) Health Insurance;
(iv) Repairs and Maintenance (Building);
(v) Free Gifts to Staff;
(vi) Purchase of Vehicles by non-transport enterprises;
(vii) Goods and/or Services for personal consumption; and
(viii) Goods and/or services purchased for sale which is exempt from levy of GST.
GST Paid (Input GST) is Reversed in the following cases:
(i) Goods lost or stolen;
(ii) Goods destroyed;
(iii) Goods written off;
(iv) Goods given as a gift (charity);
(v) Goods given as free sample; and
(vi) Goods as may be prescribed.
Supply of the following goods and/or services are exempt from levy of GST:
(i) Salaries and Wages;
(ii) Supply of Services to Government;
(iii) Supply to Embassies of other countries;
(iv) UNO;
(v) Educational Services;
(vi) Health Services; and
(vii) Electricity and Water Bills.
Accounting Entries
Examples of entries passed for accounting of GST Paid or Collected are given below:
(i) Purchase of Fixed Assets
Fixed Asset A/c (Say Machinery) | ...Dr. |
Input CGST A/c | ...Dr. |
Input SGST A/c | ...Dr. |
Input IGST A/c | ...Dr. |
To Vendors' A/c |
(Being the machinery purchased and Input CGST, Input SGST and Input IGST claimed)
(ii) Journal Entry for Purchase of Goods
Purchases A/c | ...Dr. |
Input CGST A/c | ...Dr. |
Input SGST A/c | ...Dr. |
Input IGST A/c | ...Dr. |
To Creditors' A/c | |
| (Being the purchases made) |
(iii) Journal Entry for Sale of Goods
Debtors' A/c | ...Dr. |
To Sales A/c | |
To Output CGST A/c | |
To Output SGST A/c | |
To Output IGST A/c | |
(Being the sales made) |
(iv) Journal Entry for Purchases Return
Creditors' A/c | ...Dr. |
To Purchases Returns A/c | |
To Input CGST A/c | |
To Input SGST A/c | |
To Input IGST A/c | |
(Being the purchases returns) |
In the case of Purchases Return, Input GST (CGST, SGST, or IGST) Account is credited because at the time of purchase of goods and/or services, Input GST (CGST, SGST, or IGST) Account was debited.
(v) Journal Entry for Sales Return
Sales Returns A/c | ...Dr. |
Output CGST A/c | ...Dr. |
Output SGST A/c | ...Dr. |
Output IGST A/c | ...Dr. |
To Debtors' A/c | |
(Being the sales returns) |
In the case of Sales Return, Output GST (CGST, SGST, or IGST) Account is debited because, at the time of sale of goods and/or services, Output GST (CGST, SGST, or IGST) Account was credited.
(vi) Journal Entry for Expenses
Printing & Stationery Expenses A/c | ...Dr. |
Telephone Expenses A/c | ...Dr. |
Input CGST A/c | ...Dr. |
Input SGST A/c | ...Dr. |
To Cash/Bank A/c | |
(Being the stationery purchased and telephone bill Paid, Input CGST and Input SGST claimed) |
(vii) Journal Entry for Drawings of Goods by Partner, Goods Given as Free Samples, Goods Destroyed, Goods Stolen, etc.
Partner's Capital/Current A/c | ...Dr. |
Advertisement A/c | ...Dr. |
Loss by Fire A/c | ...Dr. |
Loss by Theft A/c | ...Dr. |
To Purchases A/c | |
To Input CGST A/c | |
To Input SGST A/c | |
To Input IGST A/c | |
(Being the goods taken by the partner for personal use, hence Input CGST, Input SGST and Input IGST reversed) |
(viii) Setting off Input CGST against Output CGST
Output CGST A/c | ...Dr. |
To Input CGST A/c | |
(Being the Input CGST set off against Output CGST) |
As a result of this entry, either Input CGST or Output CGST Account will become nil.
(ix) Setting off Input CGST against Output IGST
Output IGST A/c | ..Dr. |
To Input CGST A/c | |
(Being the Input CGST set off against Output IGST) |
(x) Setting off Input SGST against Output SGST
Output SGST A/c | ...Dr |
To Input SGST A/c | |
(Being the Input SGST set off against Output SGST) |
As a result of this entry, either Input SGST or Output SGST Account will become nil.
(xi) Setting off Input SGST against Output IGST
Output IGST A/c | ...Dr. |
To Input SGST A/c | |
(Being the Input SGST set off against Output IGST) |
(xii) Setting off Input IGST against Output IGST
Output IGST A/c | ...Dr. |
To Input IGST A/c | |
(Being the Input IGST set off against Output IGST) |
(xiii) Setting off Debit Balance in Input CGST or SGST against Credit Balance in
Output IGST | ...Dr. |
Output IGST A/c | ...Dr. |
To Input CGST A/c | |
To Input SGST A/c | |
(Being the Output IGST set off to Input CGST and Input SGST) |
(xiv) Payment of GST
Input CGST A/c | ...Dr. |
Input SGST A/c | ...Dr. |
Input IGST A/c | ...Dr. |
To Bank A/c | |
(Being the GST deposited) |
FAQs on Introduction - G.S.T. Goods & Service Tax - Commerce
| 1. What is GST? |  |
| 2. How does GST benefit the Indian economy? |  |
| 3. Who is liable to pay GST? |  |
| 4. What is the GST rate in India? |  |
| 5. Can GST be claimed as input tax credit? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|