Introduction to Computer | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
Introduction

A computer is a versatile, general-purpose device that can automatically perform a wide range of operations. Modern computers, powered by integrated circuits, are exponentially more capable and compact than their predecessors. These advanced circuits make computers millions to billions of times more efficient and allow them to occupy only a fraction of the space used by early machines. Today's computers are so small and portable that they can fit into mobile devices, making them iconic tools in the Information Age.
History of Computers
- Abacus: The earliest known tool for computation, the abacus, was developed in China and served as a manual device to assist with arithmetic calculations.
- Pascaline: Blaise Pascal invented one of the first mechanical calculators, called the Pascaline, which could add and subtract, laying the foundation for future computing devices.
- Charles Babbage: Often referred to as the "father of the computer," Babbage invented the Difference Engine in 1822 and later the Analytical Engine in 1837. These devices were the first to store information on punch cards, a precursor to modern data storage methods.
- Alan Turing: Known as the father of modern computing, Alan Turing developed the concept of a theoretical computing machine, which became the foundation for modern computer science and the development of programmable computers.
Characteristics of Computers
- Speed: Computers process data at incredible speeds, using electronic pulses that operate in microseconds, nanoseconds, or even picoseconds.
- Storage: Also known as memory, storage refers to the components and media used to retain digital data. Modern computers can store vast amounts of information and retrieve it almost instantaneously.
- Accuracy: Computers perform tasks with a high degree of accuracy. Errors are usually due to human input mistakes rather than the computer's operation.
- Versatility: Computers are capable of multitasking, meaning they can perform a wide variety of tasks simultaneously and efficiently.
- Automation: Once programmed, computers can automatically execute tasks without human intervention, allowing for repetitive processes to be handled effortlessly.
Limitations of Computers
- No Self-Intelligence: While computers are fast, accurate, and efficient, they lack self-intelligence. They rely entirely on instructions provided by human programmers.
- Decision Making: Although advancements in artificial intelligence have enabled computers to make decisions based on data, they still require human-provided instructions and guidelines.
- Self-Care: Computers are unable to take care of themselves. They depend on humans for maintenance, updates, and troubleshooting.
- Memory Retrieval: While computers can retrieve stored data rapidly, their retrieval process is linear, unlike the human brain, which can access information more intuitively.
- Sensation: Computers cannot experience or respond to sensations or emotions like humans can.
Applications: Education, business, medicine, government, communication, entertainment.
History of Computers
- Abacus: First computing tool (manual arithmetic).
- Pascaline: Mechanical calculator by Blaise Pascal (add/subtract).
- Charles Babbage: Difference Engine (1822) and Analytical Engine (1837); used punch cards.
- Alan Turing: Father of modern computing; conceptualized programmable computers.
- Early Electronic Computers: ENIAC, EDVAC, UNIVAC.
Generations of Computers
First Generation (Vacuum Tubes) [1940-1956]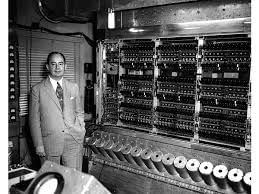
- Technology: Used vacuum tubes for electronic circuits.
- Internal Operating Speed (IOS): Operated at speeds measured in milliseconds.
- Operating Systems (OS): Batch processing systems.
- Languages: Machine language was the primary programming language.
- Examples: UNIVAC-I, IBM-701.
Second Generation (Transistors) [1956-1963]

- Technology: Introduced transistors and diodes, replacing vacuum tubes.
- IOS: Significantly faster, with operations measured in microseconds.
- OS: Time-sharing operating systems.
- Languages: Assembly languages and early high-level languages.
- Examples: UNIVAC-1004, IBM-1401.
Third Generation (Integrated Circuits) [1964-1971]

- Technology: Integrated circuits replaced transistors, further reducing size and cost while increasing speed.
- IOS: Operated in nanoseconds.
- OS: Real-time operating systems.
- Languages: High-level programming languages like FORTRAN, COBOL, and BASIC.
- Examples: UNIVAC-1100, IBM-360, PDP-8.
Fourth Generation (Microprocessors) [1971-1989]

- Technology: Use of large-scale integrated circuits, leading to the development of microprocessors.
- IOS: Reached speeds of picoseconds.
- OS: Time-sharing systems continued to evolve.
- Languages: High-level languages such as Java, C++, and Python became prevalent.
- Examples: ALTAIR-8800, IBM-370, PDP-8.
Fifth Generation (Artificial Intelligence) [1989-Present]
- Technology: Focuses on artificial intelligence, enabling devices to think and respond to their environment. This generation emphasizes parallel processing, quantum computation, nanotechnology, and supercomputing.
- Fields: Applications include gaming, robotics, voice recognition, and real-life simulations.
- Examples: Quantum computers and advanced AI systems.
- Brain Sourcing: Researchers have developed a method using artificial intelligence to analyze brain activity from groups of people to draw conclusions and classify images or recommend content. This technique demonstrates the potential for brain-computer interfaces to enhance data analysis and decision-making.
Classification of Computers Based on Size
- Nano Computer: A computer with microscopic physical dimensions.
- Micro Computer: Often synonymous with a personal computer (PC), it is a complete, small-scale computer designed for individual use.
- Laptop: A portable computer that includes a display, keyboard, touchpad or pointing stick, and speakers within a single unit.
- Netbook: A lightweight, inexpensive laptop designed for basic computing tasks and web access.
- Palmtop/PDA (Personal Digital Assistant): Small, portable devices designed to keep essential information at hand, often used for personal management tasks.
- iPad: A line of tablet computers developed by Apple, known for their sleek design and touch-screen interface.
- iPod: A line of portable media players, also developed by Apple, primarily used for listening to music and other media.
- Simputer: A low-cost portable device aimed at making information technology accessible to the general population, especially in developing regions.
- Tablet Computer: A mobile computer larger than a smartphone, operated via a touch screen and designed for portability and ease of use.
- Mini Computer: Smaller than mainframes, these computers are faster and more affordable, often used in business and scientific environments.
- Mainframe Computer: Powerful systems used by corporations and government agencies for critical applications, such as bulk data processing and large-scale transaction processing.
- Supercomputer: The most powerful and expensive computers, used for tasks requiring immense computational power, such as climate modeling, scientific simulations, and cryptography.
Pratyush Supercomputer
- India's Fastest Supercomputer: Pratyush is India's fastest and first multi-petaflop supercomputer, installed at the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) in Pune. It boasts a computational power of 6.8 petaflops and is the fourth-fastest supercomputer in the world dedicated to weather and climate research.

Top 10 Supercomputers in the World
- Fugaku (Japan): The fastest supercomputer in the world, with a speed of 220 petaflops.
- Summit (USA): Developed by IBM, with a speed of 148.6 petaflops.
- 3. Sierra (USA): Another IBM supercomputer, operating at 94.64 petaflops.
- Sunway Taihulight (China): A powerful supercomputer with a speed of 93 petaflops.
- Tianhe-2A (China): Operating at 61.44 petaflops.
- HPC5 (Italy): With a speed of 35.45 petaflops.
- Selene (USA): A supercomputer operating at 27.58 petaflops.
- Trinity (USA): With a speed of 25.45 petaflops.
- Marconi (Italy): Operating at 21.64 petaflops.
- Piz Daint (Switzerland): A supercomputer with a speed of 21.23 petaflops.
Classification of Computers Based on Work
- Digital Computer: Operates on binary data (0s and 1s), processing information in discrete, digital form.
- Analog Computer: Uses continuously variable physical quantities, such as electrical voltages or mechanical movements, to simulate the problem being solved.
- Hybrid Computer: Combines the features of both digital and analog computers, accepting analog inputs and converting them into digital signals for processing.
Other Types of Computers
- Optical or Photonic Computer: Uses light particles (photons) instead of electric currents to perform digital computations, offering the potential for faster processing speeds.
- Virtual Computer: Allows multiple operating systems to run on a single physical machine simultaneously, without interfering with each other.
- Chemical Computer: An unconventional type of computer that uses chemical reactions to represent and process data.
- DNA Computer: Employs DNA, biochemistry, and molecular biology for computation, offering potential advancements in data storage and processing at the molecular level.
- Neuro Computer (Wetware/Organic Computer): Built from living neurons, this type of computer mimics the human brain's structure and function.
- Quantum Computer: Utilizes quantum mechanics principles like superposition and entanglement to perform calculations at unprecedented speeds, far surpassing traditional computers.
- Embedded Computer System: A computer system designed to perform specific control functions within a larger system, often integrated into other devices and operating as part of a complete unit.
Computer Hardware
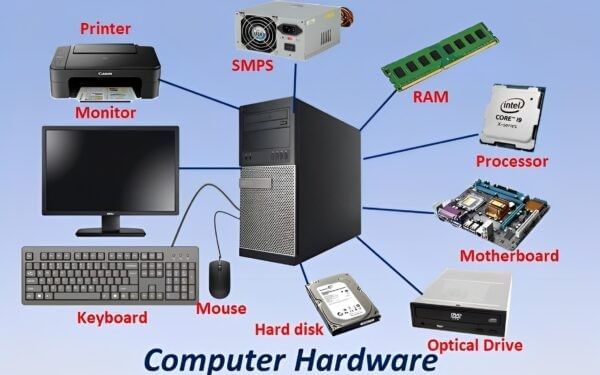
a) Input Devices
Devices that allow the user to enter data into a computer:
- Keyboard: Types – QWERTY, AZERTY, Mechanical, Membrane.
- Mouse: Optical, wireless, trackball.
- Scanner: Converts physical documents/images to digital format.
- Joystick/Gamepad: Gaming and simulations.
- Webcam: Captures video/images.
- Microphone: Audio input.
b) Output Devices
Devices that display or produce the result of computer processing:
- Monitor: CRT, LCD, LED, Touchscreen.
- Printer: Inkjet, Laser, Dot Matrix, 3D printers.
- Speakers / Headphones: Audio output.
- Plotter: Used for high-precision graphics and CAD designs.
c) Storage Devices
Primary Memory
- RAM (Random Access Memory): Volatile, temporary storage. Stores running programs.
- ROM (Read Only Memory): Non-volatile, stores BIOS and startup instructions.
- Cache Memory: High-speed memory close to CPU for faster processing.
- Registers: Small, very fast memory inside CPU for immediate operations.
Secondary Memory
- HDD (Hard Disk Drive): Magnetic storage, high capacity, slower.
- SSD (Solid State Drive): Faster, no moving parts, expensive.
- Optical Discs: CD, DVD, Blu-ray.
- USB Drives / Flash Memory: Portable storage devices.
d) CPU (Central Processing Unit)
- ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit): Performs calculations and logic operations.
- CU (Control Unit): Directs data flow, interprets instructions.
- Registers: Temporary storage for operations.
- Cache: High-speed memory for frequently used instructions/data.
Computer Software

a) System Software
- Operating System (OS): Manages hardware and software resources. Examples: Windows, Linux, MacOS.
- Utility Software: Antivirus, disk defragmenter, compression tools, backup software.
b) Application Software
Programs designed to perform specific tasks:
- MS Office: Word (documents), Excel (spreadsheets), PowerPoint (presentations).
- Browsers: Chrome, Firefox, Edge.
- Media Players: VLC, Windows Media Player.
Number Systems & Data Units
Number Systems
- Binary (0,1): Computers process data in binary.
- Octal (0–7), Decimal (0–9), Hexadecimal (0–F): Used in programming, memory addressing.
- Conversions: Binary ↔ Decimal, Binary ↔ Hexadecimal, etc.
Data Units
- Bit (b): Smallest unit (0 or 1)
- Byte (B): 8 bits
- KB (Kilobyte): 1024 Bytes
- MB (Megabyte): 1024 KB
- GB (Gigabyte): 1024 MB
- TB (Terabyte): 1024 GB
Networking & Internet Basics
- Internet: Global network of computers for information sharing.
- Intranet: Private network within an organization.
- Extranet: Extended network allowing controlled access to external users.
- IP Address: Unique identifier for devices on a network.
- Domain Name: Human-friendly website address (e.g., www.ssc.nic.in).
- URL (Uniform Resource Locator): Web page address.
- Email Components: To, CC, BCC, Subject, Body, Attachments.
- Network Devices:
- Router: Connects networks, directs traffic.
- Switch: Connects devices in a network, forwards data.
- Modem: Converts digital signals to analog and vice versa.
Cyber Security Basics
- Virus: Malicious program that spreads and damages data.
- Worm: Self-replicating malware that spreads over networks.
- Trojan Horse: Malware disguised as legitimate software.
- Spyware: Software that spies on user activities.
- Firewall: Filters network traffic to prevent unauthorized access.
- Antivirus: Detects and removes malicious software.
- Encryption: Secures data by converting it into unreadable format.
- Cyber Safety: Use strong passwords, avoid phishing, secure browsing.
Current Trends in Computers
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Enables computers to make decisions based on data. Examples: chatbots, self-driving cars.
- Cloud Computing: Remote storage and services via the internet. Examples: Google Drive, AWS.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Smart devices connected to the internet. Examples: Smart TVs, Smartwatches.
- Big Data: Handling and analyzing huge datasets for patterns.
- Digital India Initiatives: BHIM app, DigiLocker, UMANG.
|
528 videos|2113 docs|339 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction to Computer - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. What is the history of computers? |  |
| 2. What are the characteristics of computers? |  |
| 3. What are the limitations of computers? |  |
| 4. What are the generations of computers? |  |
| 5. What are the different types of computers based on size? |  |
















