Introduction to Spectroscopy & its Types | Organic Chemistry PDF Download
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy means the dispersion of light into component colours. In simple words, it is a method to measure how much light is absorbed by a chemical substance and at what intensity of light passes through it.
- As per analytical science, every element or compound has unique characteristic spectrum. Each compound absorbs and disperses light over a certain range of wavelengths.
- Spectroscopy is using light to determine what kind of substance it is. While spectroscopic techniques vary wildly in nature, all have one thing in common- “They shine light be a subject and look at what's coming out of it to determine what's inside”.
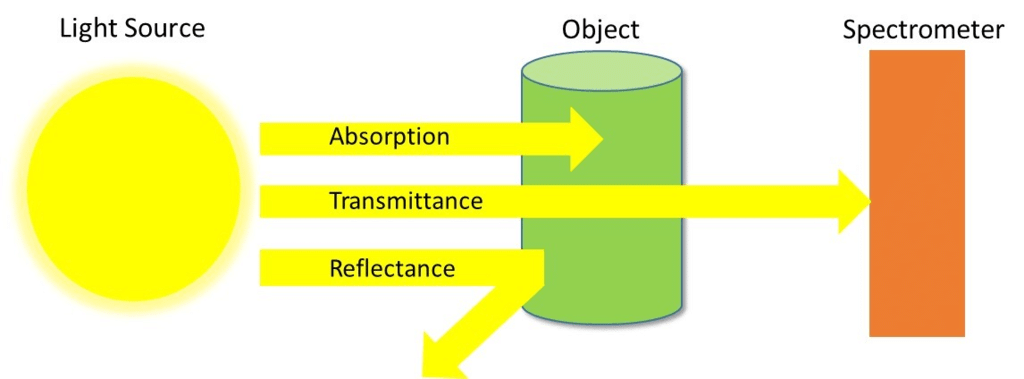
- In Chemistry, Spectroscopy helps to study or analyse various chemical compounds or elements, whereas, in Physics, it helps to determine the makeup of the atmospheres of planets.
Spectroscopy can be used to know:
- How atoms are connected together?
- Which bonds are single, double, or triple?
- What functional groups exist in the molecule?
- If we have a specific stereoisomer?
“The field of organic structure determination attempts to answer these questions”.
Instrumental Methods of Structure Determination
Various Methods of Structure Determination are:
1. Infrared Spectroscopy (IR) -Triggering molecular vibrations through irradiation with infrared light. Provides mostly information about the presence or absence of certain functional groups.
2. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) – Excitation of the nucleus of atoms through radiofrequency irradiation. Provides extensive information about molecular structure and atom connectivity
3. Mass spectrometry – Bombardment of the sample with electrons and detection of resulting molecular fragments. Provides information about molecular mass and atom connectivity.
4. Ultraviolet spectroscopy (UV) – Promotion of electrons to higher energy levels through irradiation of the molecule with ultraviolet light. Provides mostly information about the presence of conjugated p systems and the presence of double and triple bonds.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is a range of frequencies, wavelengths and photon energies covering frequencies from below 1 hertz to above 1025Hz corresponding to wavelengths which are a few kilometres to a fraction of the size of an atomic nucleus in the spectrum of electromagnetic waves.
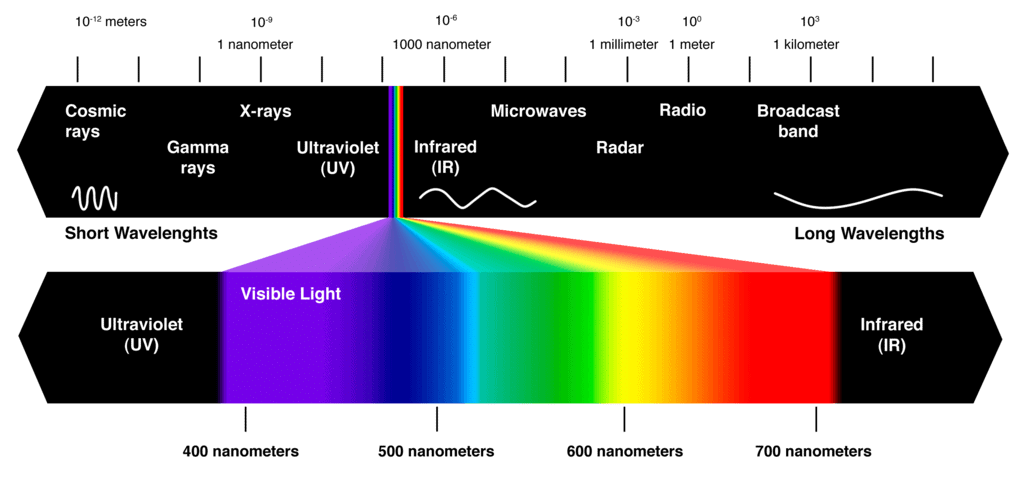
- Most organic spectroscopy uses electromagnetic energy, or radiation, as the physical stimulus.
- Electromagnetic energy (such as visible light) has no detectable mass component. In other words, it can be referred to as “pure energy.”
- Other types of radiation such as alpha rays, which consist of helium nuclei, have a detectable mass component and therefore cannot be categorized as electromagnetic energy.
The important parameters associated with electromagnetic radiation are:
- Energy (E): Energy is directly proportional to frequency, and inversely proportional to wavelength, as indicated by the equation below.
- Frequency (v)
- Wavelength (λ)
- E = hv
Effect of Electromagnetic Radiation on Molecules
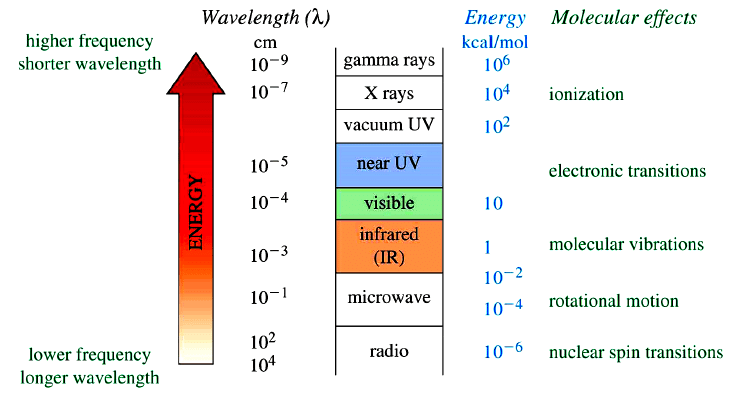
Types of Spectroscopy
IR Spectroscopy
The type of spectroscopy which deals with the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum is Infrared Spectroscopy. The rays of the infrared region have longer wavelength whereas having a lower frequency than light.
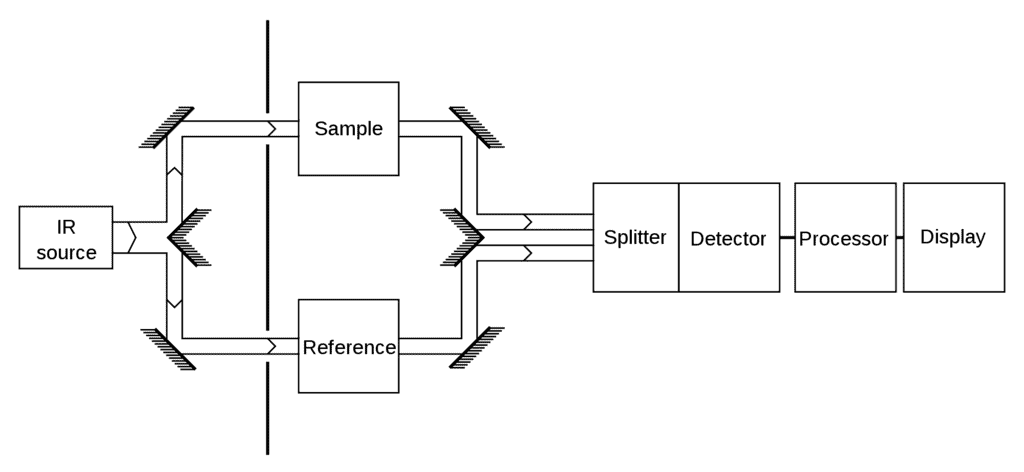 IR Spectroscopy Apparatus
IR Spectroscopy Apparatus
- IR is a type of absorption spectroscopy- it measures the amount of IR light absorbed by the sample as a function of wavelength.
- It returns the absorbance (A) in the form of transmittance (T). o A = 2 – log10 T
- IR region extends from above the visible region up to the microwave region
- IR wavelengths are typically expressed in terms of wavenumber- the reciprocal of wavelength (Unit: cm–1).
- Wave numbers are directly proportional to frequency and energy.
- Region typically extends roughly from 4000 cm–1 to 400 cm–1.
- A typical IR spectrum is obtained as a subtraction plot of the absorbance from the sample and absorbance from the background.
- Infrared photons do not have enough energy to excite electrons (like in UV spectroscopy), but they can excite groups of atoms to vibrate with respect to the bonds that connect them
- Different bonds (C—H, C—C, C=C, C≡C, C≡N, C—O, C=O, N—H etc.) have different characteristic vibrational frequencies.
- We can detect the presence of these bonds (and hence various functional groups) by identifying these characteristic frequencies as transmittance bands in the IR spectrum.
Raman Spectroscopy
Raman Spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique that is used to analyze vibrational, rotational, and other low-frequency modes in a system.
- Raman’s spectroscopy is commonly used in the branch of chemistry to provide a fingerprint by which molecules can be identified. As the name suggests, this phenomenon is named after Sir C. V. Raman.
- This phenomenon relies on the inelastic scattering of monochromatic light which is also known as Raman scattering.
- The energy of the laser photons shifts up & down due to the interaction of the light with the molecules or phonons of an object.
- This up-down shift of laser photon forms the vibrational modes of an object or system.
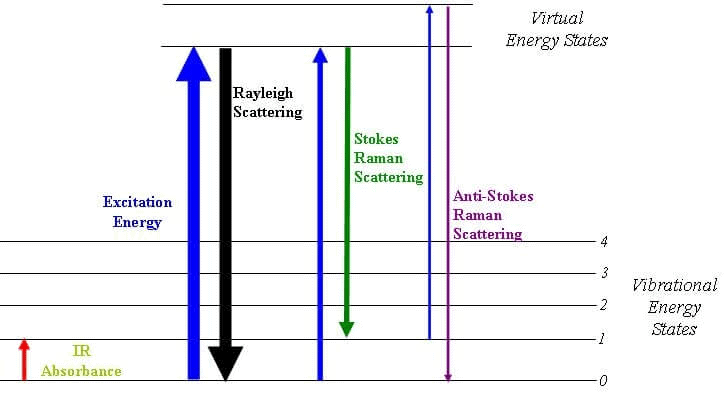 Raman Energy Levels
Raman Energy LevelsNMR Spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is the study of molecules by recording the interaction of radiofrequency (Rf) electromagnetic radiations with the nuclei of molecules placed in a strong magnetic field.
- Zeeman first observed the strange behaviour of certain nuclei when subjected to a strong magnetic field at the end of the nineteenth century, but the practical use of the so-called “Zeeman effect” was only made in the 1950s when NMR spectrometers became commercially available.
- It is a research technique that exploits the magnetic properties of certain atomic nuclei. The NMR spectroscopy determines the physical and chemical properties of atoms or molecules.
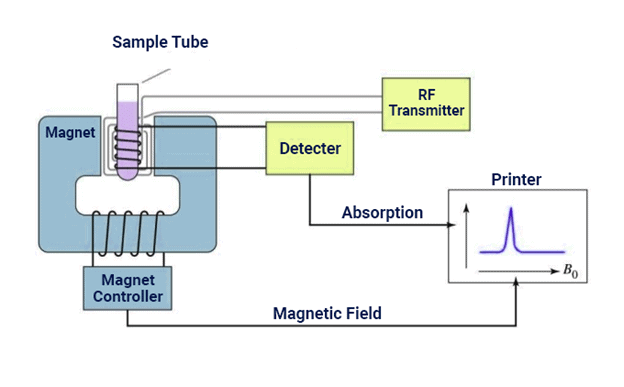 NMR Spectroscopy Instrumentation
NMR Spectroscopy Instrumentation
UV- Visible Spectroscopy
Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region.
- Ultraviolet-Visible (UV-VIS) Spectroscopy is an analytical method that can measure the analyte quantity depending on the amount of light received by the analyte.
- Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV / Vis) in the ultraviolet-visible spectral field refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy.
- In the visible and neighboring (near-UV and near-infrared (NIR)) ranges, this means that it uses light.
|
35 videos|92 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction to Spectroscopy & its Types - Organic Chemistry
| 1. What is spectroscopy? |  |
| 2. What is the electromagnetic spectrum? |  |
| 3. What are the types of spectroscopy? |  |
| 4. How does absorption spectroscopy work? |  |
| 5. What are the applications of spectroscopy? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Chemistry exam
|

|


















