Grade 11 Exam > Grade 11 Notes > Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE) > Isotopes
Isotopes | Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE) PDF Download
Defining Isotopes
- Isotopes are variations of an element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
- The symbol for an isotope consists of the chemical symbol followed by a dash and the mass number.
- For example, C-14 (carbon-14) is an isotope of carbon with 6 protons, 6 electrons, and 8 neutrons (14 - 6) = 8 neutrons
- It can also be written as 14C or 146C
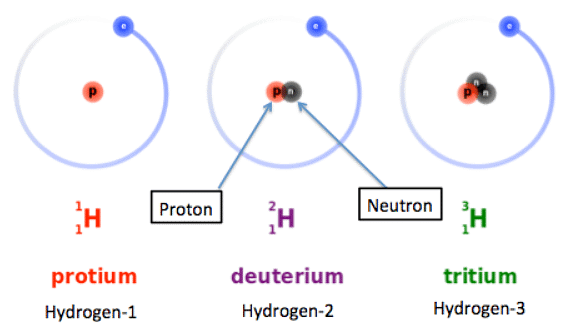
Why Isotopes Share Properties
- Isotopes of the same element exhibit similar chemical behaviors.
- This similarity arises from having identical numbers of electrons in their outer shells, leading to the same electronic configuration, which fundamentally influences an atom's chemistry.
- The distinguishing factor between isotopes lies in the varying neutron count within the nucleus, impacting mass exclusively.
- Differences in mass contribute to distinct physical attributes like density, boiling point, and melting point.
- Despite different masses, isotopes appear indistinguishable externally; for instance, distinguishing C-14 from C-12 is visually impossible.
- Deuterium oxide, known as 'heavy' water due to its higher relative atomic mass of 20 compared to 18 for regular water, mirrors the appearance, taste, and feel of normal water. However, it's hazardous for consumption as it disrupts cellular biochemical reactions.
Question for IsotopesTry yourself: How do isotopes of the same element differ from each other?View Solution
Calculating Relative Atomic Mass
Relative Atomic Mass
- The symbol for the relative atomic mass is denoted as Ar.
- In the Periodic Table, you can find the relative atomic mass for each element alongside the atomic number.
- While atoms are too tiny to be weighed accurately, scientists needed a method to compare their masses.
- Carbon-12 serves as the standard atom with a fixed mass of 12 units, against which other atom masses are compared.
- Relative atomic mass (Ar) is defined as the average mass of an element's isotopes compared to 1/12th of the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
- The relative atomic mass of Carbon is 12.
- The relative atomic mass of Magnesium is 24, indicating it is twice as heavy as Carbon.
- The relative atomic mass of Hydrogen is 1, meaning it has one-twelfth the mass of a Carbon-12 atom.
- The relative atomic mass of an element can be determined using the mass number and the relative abundances of its isotopes. This calculation can be done with the following formula:

- The top line of the equation can be extended to include the number of different isotopes of a particular element present.
Is mass number and relative atomic mass the same thing?
- Look at the Periodic Table during your exam to observe lithium's relative atomic mass of 7.
- The relative atomic mass differs from the mass number as it is a rounded figure that accounts for isotopes.
- It represents the average mass of all isotopes for a specific element.
- For simplicity, relative atomic masses are commonly rounded to the nearest whole number.
 The relative atomic mass (RAM) of lithium is 6.94 when rounded to two decimal places. However, when rounded to the nearest whole number, the RAM is 7, which aligns with the mass number of this specific isotope of lithium.
The relative atomic mass (RAM) of lithium is 6.94 when rounded to two decimal places. However, when rounded to the nearest whole number, the RAM is 7, which aligns with the mass number of this specific isotope of lithium.
Question for IsotopesTry yourself: Which atom serves as the standard for calculating the relative atomic mass?View Solution
The document Isotopes | Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE) is a part of the Grade 11 Course Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE).
All you need of Grade 11 at this link: Grade 11
|
103 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on Isotopes - Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE)
| 1. What are isotopes and how do they affect the properties of an element? |  |
Ans. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. They share similar chemical properties due to having the same number of electrons, but their physical properties, such as atomic mass, may vary.
| 2. Why do isotopes share similar chemical properties even though they have different masses? |  |
Ans. Isotopes share similar chemical properties because they have the same number of electrons, which determines an element's chemical behavior. The differences in mass due to varying numbers of neutrons do not significantly impact an element's chemical characteristics.
| 3. How can the relative atomic mass of an element be calculated when considering isotopes? |  |
Ans. The relative atomic mass of an element can be calculated by taking into account the abundance of each isotope and its respective atomic mass. This involves multiplying the atomic mass of each isotope by its abundance in decimal form, then summing these values to determine the overall relative atomic mass.
| 4. Can isotopes of the same element have different physical properties? |  |
Ans. Yes, isotopes of the same element can have slightly different physical properties due to variations in atomic mass. For example, heavy isotopes may have different boiling points or densities compared to lighter isotopes of the same element.
| 5. How do scientists use isotopes in various fields such as archaeology, geology, and forensics? |  |
Ans. Scientists use isotopes in these fields to trace the origins of materials, determine the age of artifacts, study geological processes, and identify individuals through isotopic fingerprinting. Isotopic analysis provides valuable information about the history and composition of substances in these disciplines.

|
Explore Courses for Grade 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches

















