Kaizen Costing | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Kaizen Costing? |

|
| Principles of Kaizen Costing |

|
| Features of Kaizen Costing |

|
| Scope of Kaizen Costing |

|
| Types of Kaizen Costing |

|
| 5S of Kaizen Costing |

|
What is Kaizen Costing?

Kaizen costing is a manufacturing approach that focuses on continuous improvement, aiming to enhance processes while reducing costs. The method involves identifying and eliminating waste, optimizing productivity, and improving efficiency to boost profitability.
Principles of Kaizen Costing
Kaizen costing is a cost management technique rooted in the Japanese concept of "continuous improvement." It seeks to enhance business operations by identifying and cutting costs. The core idea is to constantly look for ways to improve while saving money.
Key principles of Kaizen costing include:
Continuous Improvement (Kaizen): The foundation of Kaizen costing is the pursuit of ongoing, incremental improvements in processes, products, and systems. The objective is to create a culture where everyone in the organization, from frontline workers to top management, actively seeks opportunities to enhance efficiency, quality, and productivity.
Cost Reduction through Small Improvements: Kaizen costing focuses on reducing costs through small, manageable changes rather than large-scale initiatives. This approach minimizes resistance to change, optimizes resource use, and achieves sustainable cost savings over time.
Employee Involvement and Empowerment: A critical aspect of Kaizen costing is engaging employees at all levels in the improvement process. Empowered employees are more motivated, innovative, and committed to contributing their ideas and efforts towards achieving organizational goals.
Data-Driven Decision Making: Kaizen costing relies on data and performance metrics to guide decision-making and evaluate the effectiveness of improvement initiatives. By analyzing data, organizations can identify inefficiencies, monitor progress, and justify investments in improvement projects.
Standardization and Sustainability: Kaizen costing emphasizes the importance of standardizing improved processes and sustaining gains over the long term. Standardization ensures consistent performance, reduces variability, and integrates improved practices into daily operations.
Customer Focus and Quality Enhancement: Kaizen costing prioritizes meeting customer needs and enhancing product or service quality through continuous improvement initiatives. By improving quality, organizations can boost customer satisfaction, reduce defects, and strengthen their market reputation.
Features of Kaizen Costing

Kaizen costing is characterized by several key features that foster a culture of continuous improvement:
Continuous Improvement Culture: Kaizen costing encourages a culture of continuous improvement at all organizational levels. Employees are motivated to consistently seek small, incremental improvements in processes, products, and systems. Organizations support this culture by promoting open communication, empowering employees, and providing training in Kaizen principles and problem-solving techniques.
- Example: Regular Kaizen events where teams brainstorm and implement improvement ideas reinforce a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
Focus on Small, Incremental Changes: Rather than making large, disruptive changes, Kaizen costing emphasizes small, manageable improvements. This approach reduces resistance, minimizes disruptions, and allows organizations to build on previous successes.
- Example: Incremental changes like standardizing work procedures, enhancing workplace ergonomics, or optimizing supply chain logistics illustrate the Kaizen approach.
Empowerment of Employees: Kaizen costing involves active employee participation and empowerment in the improvement process. Empowered employees are more engaged and motivated to contribute to organizational goals. Organizations support this by providing training and resources, fostering a sense of ownership and accountability.
- Example: Cross-functional Kaizen teams, regular feedback mechanisms, and recognition programs for successful initiatives empower employees to drive positive change.
Data-Driven Decision Making: Kaizen costing depends on data and performance metrics to guide decision-making and assess the impact of improvements. Organizations use data to identify inefficiencies, track progress, and justify investments.
- Example: Using tools like Pareto analysis to prioritize improvements, conducting time studies to identify bottlenecks, or using Kaizen boards to visualize project status are examples of data-driven approaches.
Holistic Approach to Cost Management: Kaizen costing integrates cost reduction initiatives with overall business objectives, aiming for sustainable cost reductions while maintaining or improving quality, customer satisfaction, and employee morale.
- Example: Implementing lean manufacturing to reduce waste, optimizing inventory levels, or redesigning processes to enhance efficiency and reduce costs are examples of Kaizen's holistic approach to cost management.
Scope of Kaizen Costing
Kaizen costing extends its focus beyond mere cost reduction to include process improvement, quality enhancement, employee engagement, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement and sustainability. By addressing these areas comprehensively, organizations can achieve operational excellence, increase customer satisfaction, and gain sustainable competitive advantages in their industries.
Process Improvement
Kaizen costing places significant emphasis on improving processes at every level of the organization. This includes manufacturing processes, service delivery workflows, administrative procedures, and supply chain operations. The main objective is to eliminate waste, reduce inefficiencies, and optimize process flow to enhance productivity, quality, and customer satisfaction.
- Examples: Initiatives such as streamlining production lines, reducing setup times, improving order processing, and standardizing procedures fall under process improvement.
Cost Reduction
The goal of Kaizen costing is to achieve cost reductions through continuous improvement activities. This involves identifying and eliminating unnecessary expenses, reducing resource waste, and optimizing resource utilization. By lowering production costs, overhead expenses, and operational inefficiencies, organizations can boost profitability, competitiveness, and financial performance.
- Examples: Strategies like implementing lean manufacturing principles, reducing material waste, optimizing energy usage, and minimizing inventory carrying costs are used to achieve cost reduction.
Quality Enhancement
Kaizen costing also emphasizes improving product and service quality through incremental improvements in processes and systems. Enhancing quality results in higher customer satisfaction, fewer defects, and reduced rework or warranty costs. It also bolsters brand reputation and market competitiveness.
- Examples: Initiatives focused on quality enhancement include implementing Total Quality Management (TQM) principles, conducting root cause analysis for quality issues, applying error-proofing techniques (poka-yoke), and improving supplier quality.
Employee Engagement and Empowerment
Kaizen costing fosters a culture of continuous improvement by engaging employees at all levels within the organization. Empowered employees are encouraged to identify and implement improvements in their work areas, leading to increased satisfaction, motivation, and productivity.
- Examples: Promoting employee engagement involves establishing cross-functional Kaizen teams, encouraging open communication for idea sharing, providing training in Kaizen principles, and recognizing employee contributions through rewards and incentives.
Organizational Culture and Sustainability
Kaizen costing contributes to creating a culture of continuous improvement and sustainability within the organization. By embedding Kaizen principles into the organizational culture, companies promote long-term success, adaptability to change, and resilience in dynamic business environments.
- Examples: Encouraging lifelong learning and improvement, fostering innovation and creativity, promoting leadership commitment to Kaizen, and integrating Kaizen practices into strategic planning and performance management systems are key to ensuring sustainability.
Types of Kaizen Costing
Kaizen costing is a method that focuses on continuous improvement in processes, identifying waste, and making changes that enhance efficiency, improve product quality, and save money.
Asset-Oriented or Organization-Oriented Kaizen Costing:
This type of Kaizen costing helps businesses reduce expenses by improving how they use their assets. It involves analyzing processes to find inefficiencies and taking action to optimize asset usage. For example, if a machine is used only 60% of the time, Kaizen costing can identify ways to increase usage to 80%, resulting in a 25% reduction in asset costs.
Product-Oriented Kaizen Costing:
Product-oriented Kaizen costing aims to reduce the cost of producing a specific product by examining all aspects of its production, including materials, labor, and overhead. The goal is to find ways to reduce waste and inefficiencies without compromising quality. For instance, if a business uses too much material to make a product, Kaizen costing can help find ways to use less material while maintaining high quality.
Both asset-oriented and product-oriented Kaizen costing can work together to maximize cost reduction. For example, a company might identify inefficiencies in asset usage.
Standard Kaizen:
Standard Kaizen involves continuous improvement efforts focused on making incremental changes in processes, products, and systems. It applies across various departments and functions within the organization to enhance productivity, quality, and cost-effectiveness.
Value Stream Mapping (VSM):
VSM is a Kaizen costing technique that involves mapping the flow of materials and information needed to deliver a product or service to the customer. It identifies inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and waste in the value stream, enabling targeted improvements to streamline processes and reduce costs.
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM):
TPM integrates Kaizen principles with maintenance practices to optimize equipment effectiveness and minimize downtime. It focuses on proactive maintenance, autonomous maintenance by operators, and continuous improvement in equipment reliability and performance.
Just-In-Time (JIT):
JIT is a Kaizen costing approach that aims to minimize inventory levels and associated costs by producing goods or services just in time for delivery or use. It emphasizes reducing waste, lead times, and storage costs while improving responsiveness to customer demand and quality.
5S of Kaizen Costing
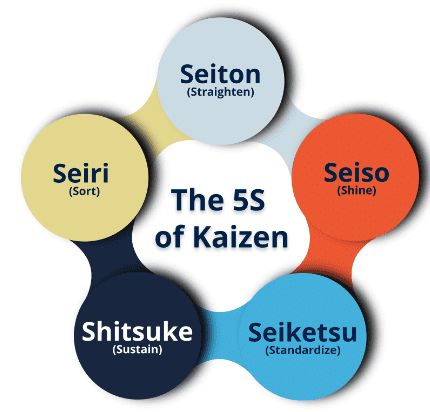
The 5S method in Kaizen Costing is a systematic approach designed to improve efficiency and reduce costs in the workplace. Originating in Japan, this technique has gained global recognition and consists of five key steps:
Seiri (Sort):
- The first step, "Sort," involves removing unnecessary items from the workspace. This step focuses on separating essential items from those that are not needed for current operations. By reducing clutter, the process becomes more efficient, leading to increased productivity and profitability.
Seiton (Set in Order):
- "Set in Order" is the second step, which involves arranging necessary items and tools in a structured and logical manner. This step categorizes similar objects and labels them for easy identification. An organized workspace saves time, increases productivity, and prevents errors.
Seiso (Shine):
- The third step, "Shine," emphasizes maintaining a clean and organized workspace. This involves cleaning machinery, equipment, and workstations to ensure they are neat, tidy, and free of dirt and debris. Keeping tools and materials in their designated locations is also crucial in this step.
Seiketsu (Standardize):
- "Standardize" is the fourth step, focusing on developing standard procedures to maintain the workspace. This involves establishing consistent practices for maintaining the first three S's (Sort, Set in Order, Shine). Creating routines for cleaning, organizing, and maintaining the workspace ensures long-term efficiency.
Shitsuke (Sustain):
- The fifth and final step, "Sustain," ensures that the 5S method becomes part of the organization's culture. This step involves fostering a culture of discipline, continuous improvement, and personal responsibility among employees. It ensures the long-term success of 5S initiatives by embedding these practices into the organization's culture. Training employees on the importance of 5S and including it in performance metrics are essential to sustaining the process.
Process of Kaizen Costing
Kaizen Costing is a cost management approach that focuses on continuous improvement in cost reduction and efficiency within an organization. Originating in Japan, it aligns with the principles of Kaizen, emphasizing continuous improvement and incremental changes. The process typically involves the following key steps:
Identification of Opportunities:
- The first step is to identify areas within the organization where cost reduction and efficiency improvements are possible. This can include manufacturing processes, administrative functions, supply chain management, and more. The process begins with analyzing current processes, workflows, and systems to pinpoint areas for improvement.
Formation of Kaizen Teams:
- Cross-functional teams consisting of employees from different departments are formed to implement Kaizen initiatives. These teams should include individuals with expertise in the areas targeted for improvement.
Setting Objectives:
- Specific and measurable cost reduction objectives are defined for each Kaizen project. These objectives should be realistic and achievable within a relatively short time frame, based on the identified areas for improvement.
Data Collection and Analysis:
- Relevant data on key performance metrics, such as production costs, cycle times, defect rates, and resource utilization, is gathered. Tools like process mapping, value stream mapping, Pareto analysis, and statistical process control (SPC) are used to identify areas for improvement.
Brainstorming and Idea Generation:
- Team members are encouraged to brainstorm and generate ideas for cost reduction and process improvement. Ideas can come from employee suggestions, benchmarking against industry best practices, or creative problem-solving.
Evaluation of Ideas:
- Each idea's feasibility and potential impact on cost reduction are evaluated. Ideas are prioritized based on their potential to achieve the cost reduction objectives. Criteria for evaluation may include feasibility, potential impact, and alignment with organizational goals.
Implementation:
- Selected Kaizen initiatives are implemented, which may include process redesign, workflow adjustments, equipment upgrades, or changes in work practices. Employees are trained and informed about the changes, and detailed action plans outline specific steps, responsibilities, timelines, and resources required.
Monitoring and Measurement:
- The progress of the Kaizen initiatives is continuously monitored using key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the impact of changes on costs and efficiency. The actual results are compared to the objectives set earlier.
Feedback and Adaptation:
- Feedback is gathered from employees and stakeholders involved in the process changes. Based on this feedback, adjustments and refinements are made to the initiatives, continuously adapting to changing conditions and requirements.
Documentation:
- Detailed records of all Kaizen initiatives are maintained, including objectives, actions taken, results achieved, and lessons learned. This documentation serves as a valuable reference for future initiatives and helps in sharing best practices.
Recognition and Reward:
- Employees and teams that significantly contribute to cost reduction and process improvement are recognized and rewarded. Incentives encourage continued engagement in Kaizen activities.
Communication:
- The results of Kaizen initiatives are communicated throughout the organization. Success stories and best practices are shared to inspire further improvement efforts. Open and transparent communication channels keep all stakeholders informed about progress, challenges, and outcomes.
Repeat the Process:
- Kaizen is an ongoing process. Once one set of initiatives is complete, the process begins again in a different area or with new objectives. The cyclical nature of Kaizen costing ensures continuous improvement and cost reduction.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Kaizen Costing
Kaizen Costing focuses on continuous improvement, identifying areas for enhancement, and finding ways to reduce costs while maintaining or improving quality. Here are some key advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages of Kaizen Costing
- Continuous Improvement Culture: Kaizen costing promotes a culture of continuous improvement within an organization. It encourages employees at all levels to identify inefficiencies, suggest improvements, and implement changes systematically. This culture fosters innovation, employee engagement, and teamwork.
- Cost Reductions: The primary objective of Kaizen costing is to reduce costs through incremental improvements in processes, products, and systems. Continuous optimization of processes and elimination of waste can lead to significant cost savings over time.
- Enhanced Quality: Kaizen principles emphasize the importance of quality improvement as part of the continuous improvement process. By eliminating defects, standardizing processes, and implementing quality control measures, organizations can deliver higher-quality products or services to customers.
- Increased Efficiency: Kaizen costing aims to streamline operations and improve efficiency through small, incremental changes. By optimizing workflows, reducing cycle times, and eliminating non-value-added activities, organizations can enhance operational efficiency.
- Employee Engagement and Empowerment: Kaizen costing encourages active participation and involvement of employees in the improvement process. When employees see their ideas for improvement being implemented, it boosts their morale and motivation.
Disadvantages of Kaizen Costing
- Time and Resource Intensive: Implementing Kaizen costing requires significant time and resources. Continuous monitoring, analysis, and improvement of processes can be demanding for organizations, especially those with limited resources or competing priorities.
- Resistance to Change: Kaizen costing relies heavily on employee involvement and a culture of continuous improvement. However, resistance to change among employees or management can hinder effective implementation. Employees may be skeptical or reluctant to adopt new practices or suggest changes due to concerns about job security, disruption of routines, or lack of trust in the process.
- Complexity in Measurement and Evaluation: Measuring the effectiveness and impact of incremental improvements in Kaizen costing can be challenging. Quantifying cost reductions or efficiency gains from small changes may require sophisticated measurement tools and accurate data tracking systems.
- Potential for Inconsistent Results: The effectiveness of Kaizen costing initiatives may vary across different departments, teams, or projects within an organization. Inconsistent results can arise due to uneven implementation efforts, varying levels of employee engagement, or differences in the complexity of processes targeted for improvement.
- Focus on Short-term Goals: Kaizen costing may sometimes have a short-term focus. While it can lead to immediate cost savings and quality improvements, it may not address larger, systemic issues that require more significant organizational change management.
Example of Kaizen Costing
Kaizen costing involves continuous improvement through incremental changes in the production process, making it an effective cost-reduction strategy. Here are five examples:
- Reducing Material Waste: By identifying and eliminating unnecessary materials that are not needed to make the product, Kaizen costing helps save money during production.
- Improving Efficiency: Kaizen costing can identify and eliminate bottlenecks and delays that slow down the manufacturing process, reducing costs for the company.
- Streamlining Inventory: Kaizen costing helps businesses save money by reducing excess inventory, which in turn lowers storage and management costs.
- Standardizing Processes: By creating standardized procedures for everything, Kaizen costing improves organizational efficiency, leading to better quality products or services and fewer errors.
- Employee Engagement: The Kaizen costing process involves all employees, leveraging their specialized knowledge and expertise to identify and implement cost-saving improvements.
Conclusion
Kaizen Costing is a cost-saving method that promotes continuous improvement by gradually enhancing processes, resources, and equipment. This approach not only saves money but also improves quality and efficiency, building a culture of progress that involves employees at all levels. Though it requires effort and dedication, Kaizen Costing is a smart investment for any business, helping organizations remain competitive in today's fast-paced business environment.
|
157 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Kaizen Costing - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What is Kaizen Costing? |  |
| 2. What are the principles of Kaizen Costing? |  |
| 3. What are the features of Kaizen Costing? |  |
| 4. What is the scope of Kaizen Costing? |  |
| 5. What are the types of Kaizen Costing? |  |















