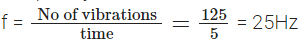Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur: Sound- 1 | Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur Solutions: Class 8 Science PDF Download
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q.1. How is sound produced?
Sound is produced by vibrating objects.
Q.2. What should an object do to produce sound?
An object should vibrate in order to be table to produce sound.
Q.3. How does a sound making object differ from one that is silent?
A sound making object vibrates while a silent does not. You can feel the vibrations by touching them.
Q.4. Name the part which vibrates to produce sound in the following:
(a) Drums
(b) Sitar
(c) Flute
(a) Its stretched membrane
(b) It’s strings.
(c) Its long hollow pipe.
Q.5. What brings the sound of a ringing telephone bell to our ears?
The vibration of our eardrums brings us the sound of a ringing telephone bell.
Q.6. What is the length of vocal cords in a man?
The male vocal chords are between 17 mm and 25 mm in length.
Q.7. Out of a man and a woman:
(a) who has shorter vocal cords?
(b) who produces sound of higher pitch?
(a) Woman has short vocal chords. The male vocal chords are between 17 mm and 25 mm in length whereas of a woman are between 12.5 mm and 17.5 mm long.
(b) Woman produces sound of higher pitch.
Q.8. Give any four sources of sound in a market place.
The four sources of sound in a market place are:
- Vendors selling eatables or other things.
- Shopkeepers selling their things.
- Vehicles in the market area, example, autorickshaw, car, etc.
- Machines or generators noise.
Q.9. Name the sound producing organ in humans.
Vocal chords are the sound producing organ in humans.
Q.10. Which part of our body vibrates when we speak?
Vocal chords vibrates when we speak.
Q.11. What does the working of a toy telephone tell us about sound?
The working of a toy telephone tells us that vibrating objects produce sound and it is carried in all directions in a medium.
Q.12. Name one solid, one liquid and one gas through which sound can travel.
Solid: Metal- Iron, Aluminium etc.
Liquid: Water
Gas: Air
Q.13. Which of the following cannot transmit sound?
Water, Vacuum, Aluminium, Oxygen gas
Vacuum cannot transmit sound because sound needs a material medium to travel.
Q.14. Is the speed of sound more in water or in steel?
The speed of sound is faster in solid as compared to liquid. Thus, the speed of sound is more in steel.
Q.15. Where would sound travel faster-in wood or in water?
The speed of sound is faster in solid as compared to liquid. Thus, the speed of sound is more in wood.
Q.16. In which medium sound travels faster : air or iron?
The speed of sound is faster in solid as compared to gas. Thus, the speed of sound is more in iron.
Q.17. In which medium sound travels fastest : air, water or steel?
The speed of sound is faster in solid as compared to liquid, and then slowest in gases. Thus, the speed of sound is more in steel, then water and then air.
Q.18. Out of solids, liquids and gases :
(a) in which medium sound travels slowest?
(b) in which medium sound travels fastest?
(a) Sound travels slowest in gas medium
(b) Sound travels fastest in solid medium.
Q.19. What is the speed of sound in air?
The speed of sound in air is 343m/s.
Q.20. Which of the following is the speed of sound in water and which in steel?
(a) 5000 m/s
(b) 1500 m/s
(c) 340 m/s
The speed of sound is faster in solid as compared to liquid, and then slowest in gases. Thus, the speed of sound is more in steel, then water and then air.
(a) 5000 m/s – Speed of sound in steel.
(b) 1500 m/s – Speed of sound in water.
(c) 340 m/s – Speed of sound in air.
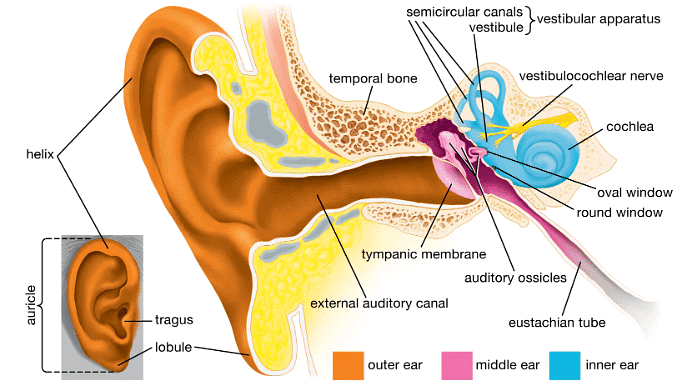
Q.21. Name the organs of hearing in our body.
Our ears are the organs of hearing in our body.
Q.22. Name that part of ear which vibrates when outside sound falls on it.
Eardrum vibrates when outside sound falls on it.
Q.23. Name the three tiny bones present in the middle part of ear.
The three tiny bones – the malleus, incus, and stapes – are found in the middle ear. Each bone is named in Latin for its shape.
Q.24. What is the function of three tiny bones in the ear?
The three bones help in transmitting the sound into the middle ear.
Q.25. Name the nerve which carries electrical impulses from the cochlea of ear to the brain.
The auditory nerve carries electrical impulses from the cochlea of ear to the brain
Q.26. What is the name of passage in outer ear which carries sound waves to the eardrum?
As seen from the figure given below, the sound is carried through the Ear canal.
Q.27. Name the quantity whose unit is ‘hertz’.
The unit of frequency is called “hertz”.
Q.28. What is the relation between ‘time-period’ and ‘frequency’ of an oscillating body?
Time Period given by the inverse of the frequency.
Time period = 1/frequency
Q.29. Name three characteristics which are used to describe oscillations (or vibrations).
Frequency, amplitude and Phase are the three characteristics which are used to describe oscillations (or vibrations).
Q.30. What is the scientific name for the following?
Frequency is the term used for number of vibrations made per second.
Q.31. What name is given to the maximum displacement of a vibrating body from its central position?
Amplitude is called as the maximum displacement of a vibrating body from its central position.
Q.32. If 125 oscillations are produced in 5 seconds, what is the frequency in hertz?
Frequency is
Q.33. How does loudness depend on the amplitude of vibrations?
Loudness is directly related to amplitude. If amplitude is high, then loudness is high. But if amplitude is low, then the loudness is low.
Q.34. By how much will the loudness of a sound change when the amplitude of vibrations is:
(a) doubled?
(b) halved?
(a) Loudness is also doubled.
(b) Loudness is halved.
Q.35. Name the unit used to measure the loudness of sound. Also, write its symbol.
Decibel is the unit used to measure the loudness of sound. Its symbol is dB.
FAQs on Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur: Sound- 1 - Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur Solutions: Class 8 Science
| 1. What is sound and how is it produced? |  |
| 2. How does sound travel through different mediums? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between pitch and loudness of sound? |  |
| 4. How does the human ear perceive sound? |  |
| 5. What are echoes and how are they formed? |  |