Land Use, Deforestation & Global warming | Biology for Grade 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Land Use |

|
| Peat Bogs |

|
| Deforestation |

|
| Global Warming |

|
| The Greenhouse Effect |

|
Land Use
- The increasing human population of the planet means an increasing amount of land is required for activities such as building, quarrying, farming and dumping waste
- This is causing the destruction of many habitats, such as rainforests and woodlands
- This reduces the biodiversity of these areas and interrupts food chains and webs, meaning that more species may die because their prey is gone
- The main reasons for habitat destruction include:
Increasing human land use table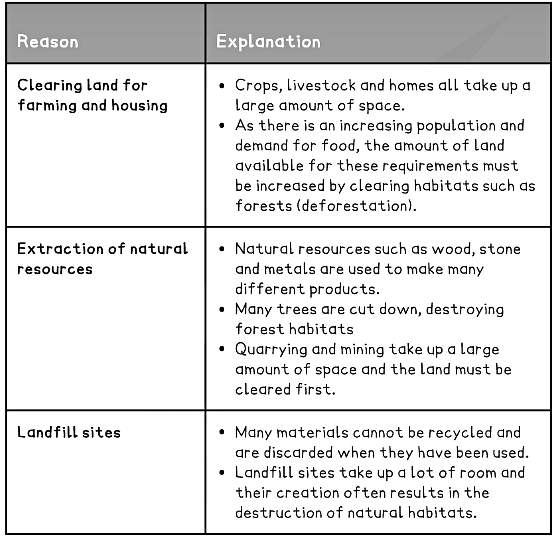
Peat Bogs
- Bogs are areas of land that are waterlogged and acidic – plants living in bogs do not decay fully when they die due to a lack of oxygen
- The partly decomposed plant matter accumulates over very long periods of time and forms peat
- The carbon that would have been released into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide (if the plants had been able to fully decompose) is instead stored in the peat
- Peat bogs are also important habitats for many species (eg. migrating birds)
Why they are being destroyed
- Peat bogs are drained so that the area can be used for farming
- Peat can be dried and used as a fuel
- Peat can be used to produce compost for gardens or farms to increase food production
Negative impacts
- Carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere when peat is burned as a fuel – this contributes to global warming
- Similarly to fossil fuels, peat bogs take so long to form that peat is effectively a non-renewable energy source
- The available peat bog habitat area for many species of animals, plants and microorganism is decreasing, reducing biodiversity
- Peat bogs are being destroyed faster than they can form – they are being used unsustainably
Exam Tip
Be careful – some students think that destroying peat bogs releases methane into the atmosphere. This is wrong. The destruction of peat bogs releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere (especially if the peat is burned as a fuel).
Deforestation
- Deforestation is the clearing of trees (usually on a large scale)
- If trees are replaced by replanting it can be a sustainable practise
- Unfortunately, this is not often the case and unsustainable deforestation is occurring in many places (forests are being cut down faster than they can regenerate)
- Unsustainable deforestation is occurring on a large scale in the rainforests of tropical areas for various reasons including:
- To provide more land for farming (eg. cattle and rice fields)
- To grow crops from which ethanol-based biofuels can be produced
- As the amount of the Earth’s surface covered by trees decreases, it causes increasingly negative effects on the environment and is a particularly severe example of habitat destruction
- Undesirable effects of deforestation include:
- Extinction of species
- Loss of soil
- Flooding
- Increase of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
Consequences of deforestation table
Exam Tip
The two main reasons deforestation occurs in tropical areas is for farming and growing biofuel crops. However, you may be asked why deforestation takes place more generally (not specifically in tropical areas). For this question, the following answers are acceptable:
- To provide land for farming/agriculture
- To provide land for quarrying
- To provide land for building
- To provide wood for building materials
- To provide fuel
- To provide paper
Global Warming
Greenhouse gases
- A greenhouse gas is a gas that absorbs infrared radiation from the Sun so it remains trapped in the Earth’s atmosphere
- This is important to ensure Earth is warm enough for life, however if levels of these gases in the atmosphere increase it leads to an increase in the greenhouse effect which causes the Earth’s average temperature to rise
- There are many greenhouse gases, the most important are:
- Water vapour
- Carbon dioxide
- Methane
- Nitrous oxides
- CFCs
- Human activities have led to increasing levels of carbon dioxide and methane in the atmosphere:
- Carbon dioxide is produced during the combustion of fossil fuel
- Methane is produced by cattle as they digest grass and released by rice paddy fields
The Greenhouse Effect
- The Sun emits rays that enter the Earth’s atmosphere
- The heat bounces back from the Earth’s surface
- Some heat is reflected back out into space
- Some heat is absorbed by greenhouse gases and is trapped within the Earth’s atmosphere – this is normal
- However, as the levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere rise due to human activities the Earth’s average temperature rises beyond normal (an enhanced greenhouse effect), causing global warming
 How the greenhouse effect works
How the greenhouse effect works
The consequences of global warming
- The consequences of global warming due to an enhanced greenhouse effect include:
- Ocean temperatures increasing, causing melting of polar ice caps / rising sea levels / flooding / coral bleaching
- Increasing temperatures causing extreme weather like super storms, flooding, droughts
- Changes in or loss of habitats due to these extreme weather events
- Decreases in biodiversity as food chains are disrupted and extinction rates increase
- Increases in migration of species to new places, including increased spread of pests and disease
The evidence for global warming
- There is scientific consensus (almost all scientists agree) that global warming is happening and that human activities are largely responsible for the most recent warming
- This scientific consensus is based on systematic reviews of thousands of scientific research papers that have been ‘peer reviewed’ by other scientists (the method used by scientists to check each other’s work in order to ensure that research findings are valid)
- Although they can make good predictions, it is difficult for scientists to say for certain what the consequences of global warming will be
Exam Tip
Describing the consequences of global warming is a common exam question and so it is worth learning at least three effects of increasing global temperatures.
|
110 videos|93 docs|9 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Grade 10 exam
|

|
















