UGC NET Exam > UGC NET Notes > Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for UGC NET > Notes: List of General Abbreviations & Terminology
List of General Abbreviations & Terminology - Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Notes
General Terminology in ICT
A
- Abort: To stop a program or function before it has finished.
- Algorithm: A set of instructions that provide a solution to a given problem.
- Animation: A simulation of movement created by displaying a series of pictures or frames, such as cartoons on television.
- ANSI: American National Standards Institute, a powerful industry association in the USA that promotes programming language standards.
- Antivirus Program: A utility that searches a hard disk for viruses and removes any that are found.
- Architecture: The design of a system, which can refer to hardware, software, or a combination of both. It defines the broad outlines of the system.
- ASCII: American Standard Code for Information Interchange, a seven/eight-bit code widely used in computers for data transfer.
B
- Bandwidth: The amount of data that can be transmitted in a fixed amount of time, usually expressed in bits per second (bps) or bytes per second.
- Bit: The smallest unit of information in a computer system, short for binary digit, which is either a “1” or a “0”.
- Boot: The process of getting the computer started.
- Byte: Made up of 8 bits, the amount of memory it takes to store a single character.
C
- Cache: A separate area of primary memory (RAM) where the computer stores a copy of frequently used information for quick access, speeding up operations.
- CD-ROM: Compact Disk-Read Only Memory, a permanent storage device used to store large quantities of information that need not be changed.
- CGA: Color Graphics Adapter, a low-resolution screen (640×200 pixels) with color capability.
- Character: A number, letter, symbol, or punctuation mark.
- Chip: A small piece of silicon containing thousands or millions of electrical elements, also known as an Integrated Circuit (IC).
- Compatible: The ability of one device or program to work with another device or program, such as a printer and a computer being able to connect and function together.
- Conventional Memory: The first 640K of electronic memory (RAM) in a computer used to run the operating system and applications.
D
- Debug: Fixing software-related problems.
- Digitize: To scan a piece of artwork in fine detail and store it in a form that a computer understands.
- DOS: Disk Operating System, a single-user operating system.
- DVD: Digital Versatile Disc or Digital Video Disc.
- Dynamic: Refers to actions that take place at the moment they are needed rather than in advance.
E
- EDP: Electronic Data Processing.
- E-Mail: Electronic Mail, a facility to send electronic messages over a computer network.
- End-User: The individual who uses a product after it has been fully developed and marketed.
- EPROM: Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory, a type of ROM that can be programmed or reprogrammed by exposing a sector to UV light.
- Extended Memory: Memory in addition to conventional memory, used to run and manage applications, allowing PCs to address increased amounts of data in memory.
F
- Fax/Facsimile: A way of transmitting copies of documents over telephone lines.
G
- Gigabyte (GB): Approximately 1,024 megabytes (MB).
- GUI: Graphical User Interface, a user interface that is visually based and involves selecting actions using a mouse or similar pointing device to click on icons or pick options from menus.
H
- Hertz: A unit of frequency meaning cycles per second.
- High Density: The amount of information a disk can hold. High-density disks hold more information than double-density disks.
- Hypertext: A method of presenting information so the user can view it in a non-sequential way, allowing flexible access to information in large documents.
- HTML: HyperText Markup Language, a markup language used to describe web and intranet documents.
I
- IBM: International Business Machines, a USA-based multinational company.
- Icon: A graphical screen element that executes one or more commands when selected with a mouse or other pointing device.
- IDE: Integrated Device Electronics, a standard for connecting hard drives to a computer.
- Intel: The manufacturer of the most popular microprocessors or CPUs.
- Intelligent Printer: A printer that combines laser, computer, and photocopying technology.
- Internet: The world’s largest computer network, linking many scientific, research, and educational computers, as well as commercial networks.
K
- Kilobyte (KB): Approximately one thousand bytes, actually 1,024 bytes.
L
- LAN: Local Area Network, a system of PCs located relatively near each other and connected by wire to share information and resources.
- Laptop Computer: A portable computer small enough to be held on a lap but larger than a notebook computer.
- LED: Light Emitting Diode, an electronic device that lights up when electricity is passed through it.
- Light Pen: An input device that allows a user to write on or point to a special pad or screen.
M
- Macintosh: A PC based on a Motorola microprocessor employing a GUI.
- Macro: A symbol, name, or key that represents a list of commands, actions, or keystrokes.
- Math Co-processor: A companion chip designed to perform complex calculations.
- Megabyte (MB): Approximately one million bytes, actually 1,048,576 bytes.
- Megahertz (MHz): A measure of processing speed; the higher the value, the faster a computer can work.
- Microprocessor: A single chip containing all the elements of a computer’s CPU.
- MIPS: Million Instructions Per Second, a unit for measuring the speed of a computer.
- Motherboard: The main circuit board of a computer.
- Multimedia: A computer system that combines text, graphics, animation, music, voice, and video.
- Multiprocessing: A computer system's ability to support more than one process at the same time, also known as multitasking.
N
- Nibble: Half a byte, i.e., 4 bits.
- Non-Volatile Memory: Data storage that does not lose its contents when power is off, such as ROM.
- Notebook Computer: A portable computer, approximately 8½ by 11 inches, that fits inside a briefcase.
- Numeric Keypad: The part of a keyboard that looks like an adding machine, with 10 digits and mathematical operators, usually located on the right side of the keyboard.
O
- Office-Automation: The use of computer systems to execute a variety of office operations.
- Parallel Port: An outlet on a computer used to attach devices such as a printer, sending data (bits) down the wire side by side (parallel to each other).
- Pentium: The fifth generation of microprocessors, faster than the fourth generation 80486 microprocessors.
- Peripheral: Any piece of hardware attached to the outside of a computer, such as printers and modems.
- Pixel: Short for "Picture Element", the smallest dot the computer can control on the screen.
- Portable Computer: A small computer that usually runs on batteries, including laptops, notebooks, sub-notebooks, and palmtops.
- Protocol: The formal specification that defines procedures for transmitting and receiving data in networking and communications.
R
- Resolution: The size and quantity of dots that make up a printed page, screen, or scanned image.
- Runtime Error: An error that occurs during the execution of a program.
S
- Scanner: An input device used to copy a printed document into a computer’s memory in digital form.
- SCSI: Small Computer System Interface, a standard for connecting hard drives to a computer.
- Serial Port: An outlet on a computer used to attach a device, sending data (bits) down the wire one at a time (in a series).
- Service Pack: An update to a software version that fixes problems or provides enhancements.
T
- TCP/IP: Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol, a set of communication protocols used on the Internet.
- Troubleshoot: To isolate and fix a problem, usually hardware-related.
U
- UNIX: A multiuser operating system.
- Upgrade: A new version of a software or hardware product designed to replace an older version.
- UPS: Uninterruptible Power Supply, a power supply that includes a battery to maintain power in the event of a power cut.
- Utility: A program that performs a very specific task related to managing system resources.
V
- Vector Graphic: A method of creating graphic images by drawing lines in particular positions, which can be resized without loss of quality.
- Video Card: An electronic circuit board inside a computer that controls the display on the monitor.
- Videoconferencing: A computer-based communications system that allows users at different locations to conduct a virtual conference.
- Videodisc: A now-obsolete optical disc used mainly to store still images or video clips, replaced by CD-ROMs and DVDs.
- Virtual Learning Environment (VLE): A system for delivering learning materials to students via the web.
- Virtual Memory: Using hard disk space to extend the apparent size of RAM.
- Virus: A self-replicating program that spreads by inserting copies of itself into other executable code or documents.
- Voice Recognition: A system that allows a computer to recognize and respond to spoken commands.
W
- WAN: Wide Area Network, a network that extends over a large geographical area.
- Web Browser: A software application used to locate, retrieve, and display content on the World Wide Web.
- Windows: A series of graphical operating systems developed by Microsoft.
- Workstation: A powerful single-user computer, often used for tasks like computer-aided design (CAD) or software development.
- Word Processor: A software application used for creating, formatting, and editing text documents.
Z
- Zip Drive: A removable disk storage system introduced by Iomega.
- Zipped File: A file compressed using a utility such as WinZip.
This comprehensive explanation of the terminology and abbreviations should provide clarity and better understanding of the concepts in ICT.
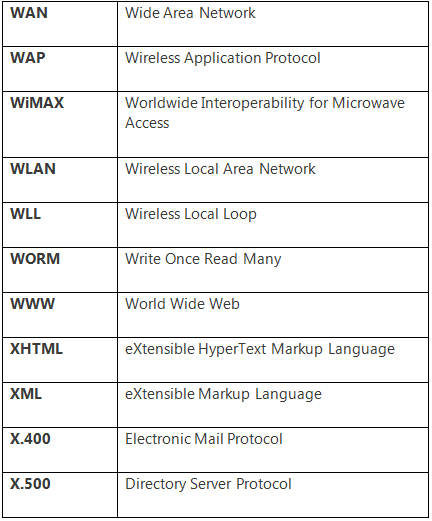
General Abbreviations and Terminology in ICT
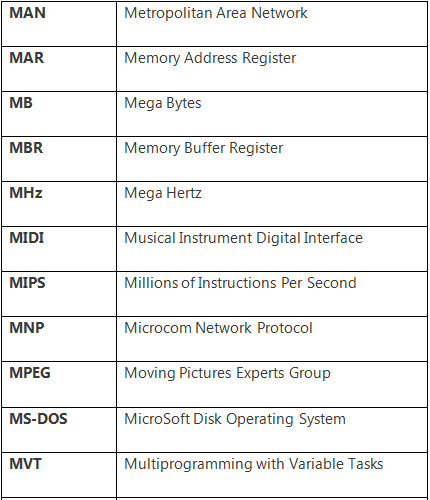
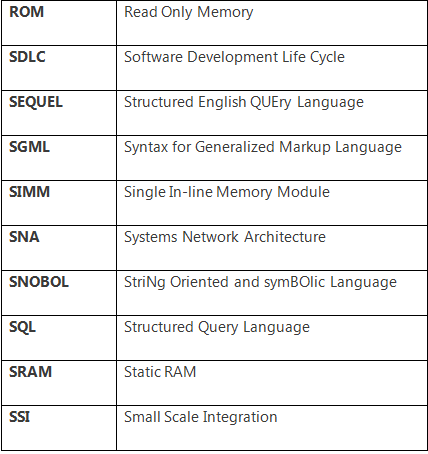
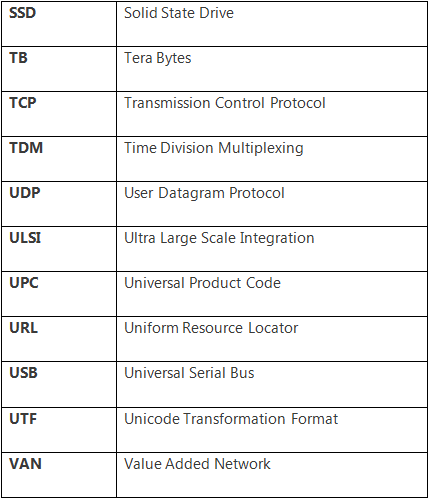
There is a number of abbreviations in the computer or ICT domain. Some useful and important abbreviations are the following: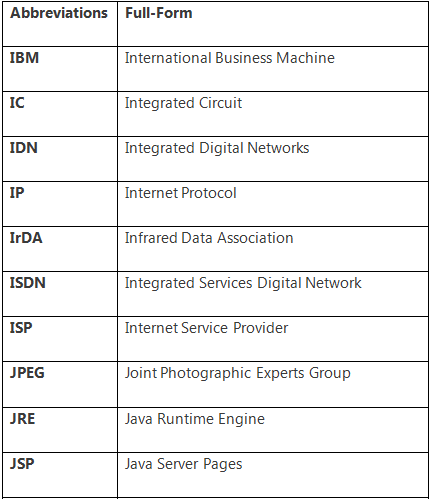




The document List of General Abbreviations & Terminology - Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Notes is a part of the UGC NET Course Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for UGC NET.
All you need of UGC NET at this link: UGC NET
|
30 videos|17 docs|8 tests
|
FAQs on List of General Abbreviations & Terminology - Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Notes
| 1. What does UGC NET stand for? |  |
Ans. UGC NET stands for University Grants Commission National Eligibility Test.
| 2. What are some common abbreviations used in the context of UGC NET? |  |
Ans. Some common abbreviations used in UGC NET are UGC (University Grants Commission), NET (National Eligibility Test), etc.
| 3. How is UGC NET different from other competitive exams? |  |
Ans. UGC NET is specifically designed for determining the eligibility for Assistant Professor and/or Junior Research Fellowship in Indian universities and colleges, while other competitive exams may have different purposes and criteria.
| 4. What is the significance of knowing the general abbreviations and terminology related to UGC NET? |  |
Ans. Knowing the general abbreviations and terminology related to UGC NET can help candidates better understand the exam guidelines, syllabus, and instructions, which can ultimately enhance their preparation and performance.
| 5. Is it important to stay updated with the changes in UGC NET abbreviations and terminology? |  |
Ans. Yes, it is important to stay updated with the changes in UGC NET abbreviations and terminology as it ensures that candidates are well-informed and can navigate the exam process effectively.
|
30 videos|17 docs|8 tests
|
Download as PDF

|
Explore Courses for UGC NET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches

















