Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Geography for GCSE/IGCSE > Maps
Maps | Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Maps
Questions in the exam will be based on topographical maps.
- The maps can be from anywhere in the world.
- Maps will have a key, scale, northings, and eastings.
- These elements must be utilized to answer the questions.
Grid references
4-Figure Grid References
- 4-figure references are utilized to identify specific grid squares on a map.
- First two figures: Eastings - show east or west position on the map.
- Second two figures: Northings - indicate north or south position on the map.
6-Figure Grid References
- 6-figure references are employed to pinpoint exact points within grid squares.
- First three figures: Eastings - specify east or west location on the map.
- Last three figures: Northings - determine north or south location on the map.
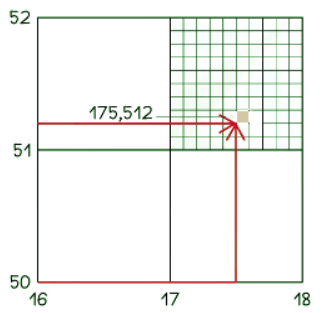
To find a 4 and 6 figure grid reference
- To determine a 4-figure grid reference, provide the number from the bottom of the map first, followed by the number from the side of the map.

- In the image above, the 4-figure grid reference would be 17, 51. To give the 6-figure grid reference, you need to imagine that the grid square is divided into 100 smaller squares.

Scale
- Maps in the exam will either be scale 1:25,000 where 1cm on the map = 25,000cm (250m) in real life or 1:50,000 where 1cm = 50,000cm (500m) in real life
- When the distance is straight or almost straight, it can be measured using a ruler or the edge of a straight piece of paper
- Using the scale at the bottom of the map, mark distances on a piece of paper
- This marked paper can then be laid from the first point to the second point to calculate the distance

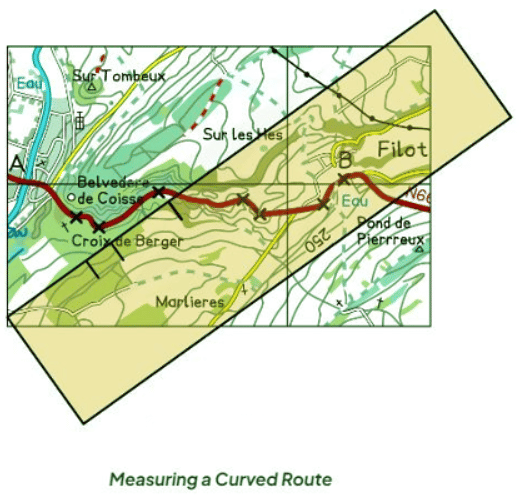
- A distance along a curved route can be divided; the paper can be rotated and marked in stages to calculate the full distance
- To measure from point A to point B following the road on the map, the route can be divided into a series of straight sections using crosses
- The plain piece of paper can then be used to measure from point A to the first cross, and then rotated at the cross to mark the second cross

Question for MapsTry yourself: What do the first two figures in a 4-figure grid reference represent?View Solution
Bearings
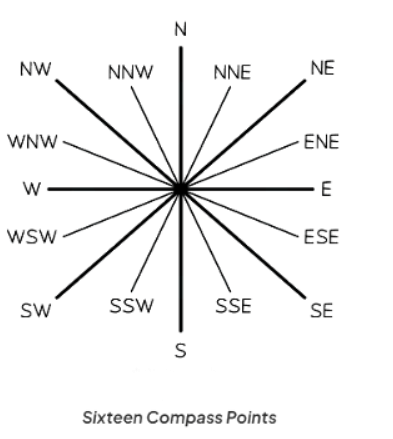
- Directions on a map should always be provided using compass points.
- There are a total of 16 compass points.

- A grid bearing is measured from grid north at 0 degrees. East corresponds to 90 degrees, South to 180 degrees, and West to 270 degrees.
- Grid bearings are determined using a protractor where 0 degrees should align with north. The center of the protractor indicates the direction from which the bearing is given.

- On the map, location B lies to the South West of point A, indicated by a bearing of 280 degrees.
Heights
- Height representation on maps can be achieved through three primary methods:
- Spot Heights
- Contour Lines
- Trigonometrical Stations
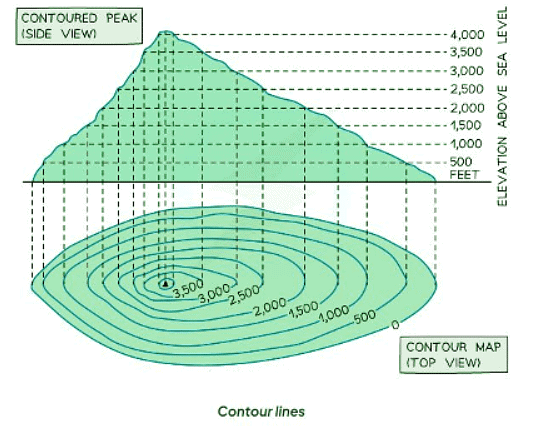
- Spot Heights: These indicate the height at a specific point, with the measurement provided next to it.
- Contour Lines: These are isolines connecting points of equal height, typically at 5 or 10-meter intervals. The spacing between contour lines signifies an increase in land height by 5 or 10 meters.
- Trigonometrical Stations: Represented by small black triangles with accompanying height measurements.
Topography
- Contour lines play a crucial role in representing the shape and slope of the land or topography.
- When contour lines are closely packed together, it signifies steep terrain, whereas lines that are spaced far apart indicate gently sloping or flat land, depending on the distance between them.
- V-shaped valleys are characterized by a set of V-shaped contours, providing insight into the landscape's features.
- A hill's presence is depicted by circular contour lines encircling it.
Cross-sections
- A cross-section serves as a slice through the landscape, aiding in understanding land features.
- On maps, cross-sections are represented by labeled lines, such as A and B, utilizing contour lines to assess land elevation.

- To determine height accurately, a paper is placed along the line, marking points A and B, with contour lines being noted each time they intersect the paper.

- These figures can then be used to create the cross-section

Key
- Maps are effective tools for recognizing various landscape characteristics.
- These features encompass both physical and human aspects.
- Each map includes a legend or key to explain the symbols used and their meanings.

Question for MapsTry yourself: Which method is used to represent the height at a specific point on a map?View Solution
The document Maps | Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Geography for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
57 videos|70 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Maps - Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is a grid reference on a map? |  |
Ans. A grid reference on a map is a numerical way of identifying a specific location on a map using a grid system. It consists of two numbers representing the easting and northing coordinates.
| 2. How do you read a grid reference on a map? |  |
Ans. To read a grid reference on a map, start by looking at the bottom left-hand corner of the map to find the grid lines. Then, locate the easting coordinate first followed by the northing coordinate to pinpoint the exact location on the map.
| 3. Why are grid references important when using maps? |  |
Ans. Grid references are important when using maps because they provide a precise way of communicating and locating specific points on a map. They help in navigation, search and rescue operations, and accurately sharing locations with others.
| 4. What are the different types of grid references used on maps? |  |
Ans. The two main types of grid references used on maps are 4-figure grid references and 6-figure grid references. 4-figure references give a general location within a 1 km square, while 6-figure references provide a more precise location within a 100 m square.
| 5. How can grid references be used in orienteering or navigation activities? |  |
Ans. Grid references are crucial in orienteering or navigation activities as they help participants locate checkpoints or specific locations accurately on a map. By understanding how to read and use grid references, individuals can navigate through unfamiliar terrain with ease.
Related Searches