Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Mass & Weight
Mass & Weight | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Mass |

|
| Weight |

|
| Gravitational Field Strength |

|
| Using a Balance |

|
Mass
- Mass represents the amount of matter an object possesses when observed while at rest.
- Mass is a scalar quantity.
- The kilogram (kg) is the standard International System of Units (SI) unit for mass.
- Mass is the property of an object that opposes alterations in its motion.
- Objects with greater mass exhibit increased resistance to changes in speed, deceleration, or alteration of trajectory.
- Mass might occasionally be expressed in grams (g).
- The conversion between grams and kilograms is: 1000 g equals 1 kg, and 1 g equals 0.001 kg.
- For Example:
- To convert from kilograms to grams, you multiply by 1000.
- If an object has a mass of 2.7 kg, it is equivalent to 2700 grams (g).
Weight
- Weight is the gravitational force exerted on an object with mass.
- Weight, being a force, is classified as a vector quantity.
- The standard units for force are newtons (N).
- Weight is the consequence of gravitational interaction with mass.
- Weight is described as the force applied to an object due to gravitational attraction.
- Planets possess potent gravitational fields, leading them to exert a strong gravitational force on nearby masses.
- Weight is accountable for various effects:
- Objects remain firmly grounded.
- Objects unfailingly descend towards the ground.
- Satellites are maintained in orbit.

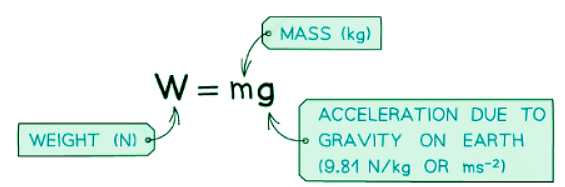
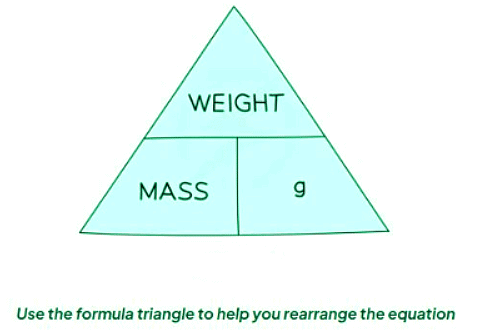
- The weight of an object equals the result of multiplying its mass (m) by the acceleration due to gravity (g).

- This equation can be rearranged using a formula triangle.

Question for Mass & WeightTry yourself: What is the SI unit for mass?View Solution
Gravitational Field Strength
- Gravitational field strength is the force per unit mass acting on an object in a gravitational field.
- On Earth, this value is 9.8 N/kg.
- It is also known as acceleration of free fall, with units in m/s2.
- The gravitational field strength g differs from one planet to another based on their mass and radius.
- Below are some examples illustrating the variability of gravitational field strength:

Mass v Weight
- The mass of an object remains constant, but its weight varies according to the gravitational field strength on different planets.
- For instance, on the Moon, where the gravitational field strength is 1.63 N/kg, an object's weight will be approximately six times less than on Earth.

Edurev Tip: You're not required to memorize the precise value of g (9.81 N/kg), but you should remember that g is approximately 9.8 N/kg and utilize it in calculations.
Using a Balance
- A balance can be utilized to compare the weight of two objects.
- Due to the consistent gravitational field strength across Earth, this enables the measurement of an object's mass.


The document Mass & Weight | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
127 videos|148 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Mass & Weight - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is the difference between mass and weight? |  |
Ans. Mass is the amount of matter in an object, while weight is the force exerted on an object due to gravity. Mass is constant, while weight can vary depending on the gravitational field strength.
| 2. How does a balance measure mass? |  |
Ans. A balance measures mass by comparing the gravitational force on an object to a standard mass. The balance will show when the two forces are equal, indicating the mass of the object.
| 3. What is gravitational field strength and how does it affect weight? |  |
Ans. Gravitational field strength is a measure of the gravitational force acting on an object per unit mass. It affects weight as weight is directly proportional to the gravitational field strength - the greater the field strength, the greater the weight.
| 4. Can an object have mass but no weight? |  |
Ans. Yes, an object can have mass but no weight when it is in a location with zero or negligible gravitational field strength, such as in outer space. The object still has mass but does not experience a gravitational force.
| 5. How does weight change on different planets? |  |
Ans. Weight changes on different planets due to variations in their gravitational field strength. An object will weigh more on a planet with a higher gravitational field strength and less on a planet with a lower gravitational field strength compared to Earth.

|
Explore Courses for Year 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches