Meaning and Scope of Business Economics | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Business Economics Overview |

|
| Nature of Business Economics |

|
| Scope of Business Economics |

|
| Objectives of Business Economics |

|
| Types of Business Economics |

|
Business Economics Overview
Business economics delves into the realm of business decisions, leveraging quantitative techniques and economic theory to provide solutions. It is centered around the application of economic theories and tools in practical business scenarios to bolster organizational and corporate decision-making processes. The primary aim of business economics is to enhance resource allocation and operational efficiency to achieve organizational objectives such as profit maximization, cost reduction, revenue optimization, and market share expansion.
Key Insights
- It provides valuable insights into various aspects of company management, including market analysis, pricing strategies, production scheduling, investment decisions, and risk management.
- Business economics furnishes a framework for comprehending and addressing the opportunities and financial challenges encountered by enterprises.
- Through the application of analytical tools and economic principles, organizations can achieve sustainable growth, enhance their competitiveness, and make informed decisions.
Nature of Business Economics
Managerial Orientation: Often referred to as managerial economics, this field aids managers in decision-making by providing frameworks and tools for strategic planning, risk management, policy development, and resource allocation.
Microeconomic Perspective: Business economics focuses on the study of individual firms, consumers, and markets, emphasizing microeconomic concepts such as supply, demand, pricing, and market structure.
Interdisciplinary Approach: To thoroughly analyze complex business issues, this field integrates knowledge from economics, finance, accounting, statistics, and operations research.
Dynamic and Evolving Field: Business economics adapts to the latest research findings and methodologies, as well as changes in the business environment, technological advancements, and market dynamics.
Decision Support Function: Within organizations, business economics serves as a decision support function by providing managers with relevant data, analysis, and insights to make informed decisions.
Scope of Business Economics
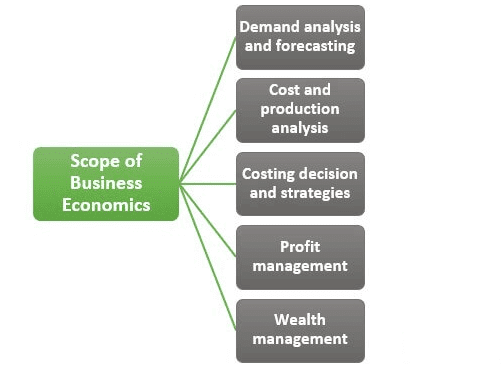
Demand Analysis: Business economists study market demand for products and services, along with consumer behavior. They assess factors influencing demand, such as price elasticity, consumer preferences, income levels, and market trends, to inform pricing strategies and marketing decisions.
Supply Analysis: Understanding the supply side of the industry is crucial for organizations. Business economists analyze factors affecting supplier behavior, including technology, resource availability, and production costs, to optimize inventory levels, streamline production processes, and manage supply chains effectively.
International Business: In a globalized economy, business economists examine international trade, foreign investment, exchange rates, and geopolitical factors that impact cross-border operations. They help organizations develop global expansion strategies, manage currency risks, and evaluate foreign market opportunities.
Investment Decisions: Companies face various investment decisions, including capital expenditures, expansion projects, acquisitions, and new ventures. Business economists assess investment opportunities, evaluate risks, project returns, and conduct feasibility studies to guide strategic investment decisions and ensure the efficient allocation of financial resources.
Planning and Forecasting: Business economists use economic indicators, statistical models, and forecasting techniques to predict future market conditions, demand patterns, and industry performance. Their accurate forecasts and scenario analyses help organizations with strategic planning, budgeting, and decision-making, allowing them to anticipate opportunities and risks.
Objectives of Business Economics
Enhancing Productivity and Efficiency: Business economics aims to improve productivity and efficiency by identifying inefficiencies in corporate processes, streamlining workflows, and implementing best practices. This includes boosting overall performance, minimizing waste, and optimizing operations.
Maximizing Profitability: One of the key objectives of business economics is to increase a company's profitability by reducing costs and maximizing revenue. This involves making strategic decisions related to pricing, production levels, cost management, and revenue generation.
Maintaining Market Competitiveness: Business economics helps organizations remain competitive in the marketplace by analyzing market trends, understanding consumer behavior, and identifying opportunities for growth and expansion.
Adapting to Changing Market Conditions: Business economics enables organizations to adapt to changes in regulations, technological advancements, and shifting market conditions. By proactively adjusting strategies based on market trends and future developments, businesses can stay ahead of the curve.
Promoting Sustainable Growth: Business economics focuses on achieving sustainable growth by balancing immediate needs with long-term sustainability goals. This involves making strategic decisions that foster growth while considering environmental, social, and ethical factors.
Types of Business Economics
Microeconomics: Microeconomics studies the behavior and decision-making processes of individual businesses, consumers, and markets. It examines how companies allocate resources, set prices, aim for profit maximization, and respond to changes in supply and demand.
Macroeconomics: This branch of business economics looks at the broader economic environment, including aggregate measures like GDP, inflation, unemployment, and interest rates. Businesses use macroeconomic analysis to understand the overall economic landscape in which they operate and to anticipate large-scale trends that could affect their operations.
Financial Economics: Financial economics focuses on the behavior of financial markets, institutions, and instruments. It covers topics such as capital budgeting, portfolio theory, asset pricing, risk management, and corporate finance. Businesses use financial economics to manage financial risks, make investment decisions, and raise capital.
International Economics: This field examines the economic interactions between different countries, including trade, investment, exchange rates, and global finance. For businesses operating in foreign markets, a solid understanding of international economics is essential for managing currency risks, conducting cross-border transactions, and capitalizing on global opportunities.
Managerial Economics: Managerial economics applies economic principles and concepts to managerial decision-making within organizations. It helps managers optimize resource allocation, pricing strategies, production decisions, investment choices, and other business processes to maximize profits and achieve organizational goals.
Uses of Business Economics
Demand Analysis: Companies use business economics to study consumer demand for their products and services. This helps them understand factors that influence demand, such as income levels, price elasticity, consumer preferences, and competitor actions.
Production Analysis: Businesses apply economic principles to determine the most efficient methods of producing goods and services. This involves analyzing production capabilities, input-output relationships, economies of scale, and technological advancements.
Market Structure Analysis: Business economics helps organizations understand the various market structures in which they operate, such as oligopoly, perfect competition, monopoly, and monopolistic competition. This knowledge aids in developing effective strategies, including pricing and marketing approaches.
Risk Analysis: Business economics assists in identifying, assessing, and managing the various risks that organizations face, including operational, financial, market, and regulatory risks. By measuring and evaluating risks, businesses can develop strategies to mitigate risks and improve decision-making under uncertainty.
Cost Analysis: Understanding costs is crucial for businesses to allocate resources efficiently, set prices, and produce goods effectively. Business economics helps analyze different types of costs, such as marginal, variable, and fixed costs, and optimize cost structures for better financial performance.
Career in Business Economics
Management Consultant: Management consultants provide companies with advice on organizational changes, operational improvements, and strategic issues. Professionals with a background in business economics are especially valuable in areas such as performance optimization, market analysis, and cost evaluation.
Financial Analyst: Financial analysts assess the overall financial performance of companies, organizations, and investment opportunities. They analyze risks, evaluate factors influencing financial markets, and offer investment recommendations based on economic analysis.
Academic Researcher: Business economists can pursue careers as academic researchers or professors in fields like business administration, economics, or related disciplines. Through research and scholarly publications, they contribute to the advancement of economic knowledge.
Entrepreneurship: Individuals with a background in business economics may choose to start their own businesses or work as independent consultants, applying their skills to solve business challenges and capitalize on opportunities.
Market Research Analyst: Market research analysts study consumer behavior, market trends, and competitive dynamics to help companies understand their target markets and develop effective marketing strategies. A solid understanding of business economics is crucial for analyzing pricing strategies, market segmentation, and demand trends.
Conclusion
In conclusion, business economics plays a crucial role in fostering sustainable growth, enhancing competitiveness, and supporting better decision-making by applying analytical tools and economic principles. It encompasses areas such as microeconomics, macroeconomics, international economics, financial economics, and managerial economics to provide a comprehensive framework for understanding and addressing business opportunities and financial challenges.
|
157 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Meaning and Scope of Business Economics - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What are the main objectives of Business Economics? |  |
| 2. What is the meaning and scope of Business Economics in the context of UGC NET? |  |
| 3. What are some key concepts covered in Business Economics for the UGC NET exam? |  |
| 4. How does Business Economics help businesses in making effective decisions? |  |
| 5. What role does Business Economics play in the overall success of a business organization? |  |















