Measurements of Area & Volume | Geomatics Engineering (Surveying) - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Introduction
The main objective of the surveying is to compute the areas and volumes.
Generally, the lands will be of irregular shaped polygons.
There are formulae readily available for regular polygons like, triangle, rectangle, square and other polygons.
But for determining the areas of irregular polygons, different methods are used.
Earthwork computation is involved in the excavation of channels, digging of trenches for laying underground pipelines, formation of bunds, earthen embankments, digging farm ponds, land levelling and smoothening. In most of the computation the cross sectional areas at different interval along the length of the channels and embankments are first calculated and the volume of the prismoids are obtained between successive cross section either by trapezoidal or prismoidal formula.
Calculation of area is carried out by any one of the following methods:
a) Mid-ordinate method
b) Average ordinate method
c) Trapezoidal rule
d) Simpson’s rule
The mid-ordinate rule
Let O1, O2, O3, O4……….On = ordinates at equal intervals
l = length of base line
d = common distance between ordinates
h1, h2,…….. hn = mid-ordinates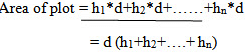
Area = common distance* sum of mid-ordinates
Average ordinate method
Let O1, O2, …..On = ordinates or offsets at regular intervals
l = length of base line
n = number of divisions
n+1 = number of ordinates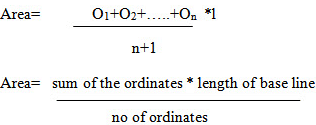
The Trapezoidal Rule
While applying the trapezoidal rule, boundaries between the ends of ordinates are assumed to be straight. Thus the areas enclosed between the base line and the irregular boundary line are considered as trapezoids.
Let O1, O2, ….. On = ordinate at equal intervals, and d = common distance between two ordinates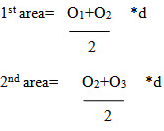
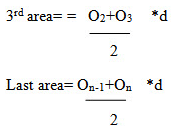
Total area = d/2{O1+ 2O2 + 2O3 +…….+2On-1+On}
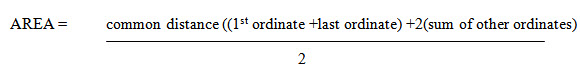
Thus the trapezoidal rule may be stated as follows:
To the sum of the first and last ordinate, twice the sum of intermediate ordinates is added. This total sum is multiplied by the common distance. Half of this product is the required area.
Limitation: There is no limitation for this rule. This rule can be applied for any number of ordinates
Simpson’s Rule
In this rule, the boundaries between the ends of ordinates are assumed to form an arc of parabola. Hence simpson’s rule is some times called as parabolic rule. Refer to figure:
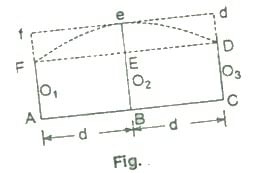
Let
O1, O2, O3 = three consecutive ordinates
d = common distance between the ordinates
area AFeDC = area of trapezium AFDC+ area of segment FeDEF
Here,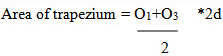
Area of segment= 2/3* area of parallelogram FfdD
= 2/3* eE*2d
= 2/3 *{O2- O1 + O3 /2}*2d
So, the area between the first two divisions,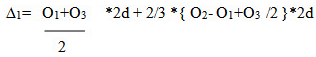
= d/3(O1 + 4O2 + O3)
Similarly, the area of next two divisions
∆2 = d/3(O1+4O2+O3) and so on
Total area = d/3[O1+On+4(O2+O4+……) + 2(O3+O5)]
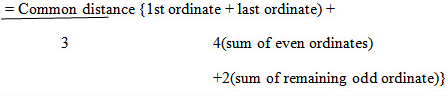
Thus the rule may be stated as the follows
To the sum of the first and the last ordinate, four times the sum of even ordinates and twice the sum of the remaining odd ordinates are added. This total sum is multiplied by the common distance. One third of this product is the required area.
Limitation: This rule is applicable only when the number divisions is even i.e. the number of ordinates is odd.
The trapezoidal rule may be compared in the following manner: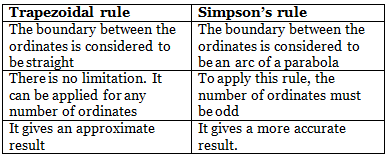
Note: sometimes one or both the end of the ordinates may be zero. However they must be taken into account while applying these rules.
Worked- out problems
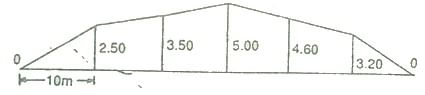
Problem 1: The following offsets were taken from a chain line to an irregular boundary line at an interval of 10 m:
0, 2.50, 3.50, 5.00, 4.60, 3.20, 0 m
Compute the area between the chain line, the irregular boundary line and the end of offsets by:
a) mid ordinate rule
b) the average –ordinate rule
c) the trapezoidal rule
d) Simpson’s rule
Solution:
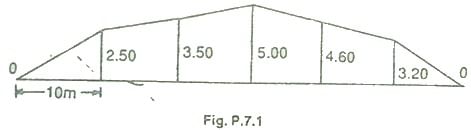
Mid-ordinate rule: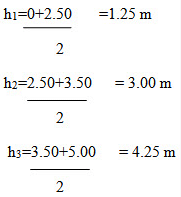
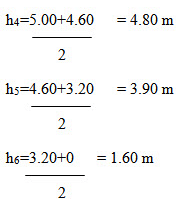
Required area = 10(1.25+3.00+4.25+3.90+1.60)
= 10*18.80 =188 m2
By average-ordinate rule:
Here d =10 m and n = 6(no of devices)
Base length = 10*6 = 60 m
Number of ordinates = 7
Required area = 10((1.25+3.00+5.00+4.60+3.20+0)/7)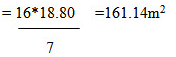
By trapezoidal rule:
Here d = 10m
Required area = 10/2{0+0+2(2.50+3.50+5.00+4.60+3.20+)}
= 5*37.60=188 m2
By Simpson’s rule:
d =10m
required area = 10/3{0+0+4(2.50+5.00+3.20)+2(3.50+4.60)}
= 10/3{ 42.80+16.20} =10/3*59.00
10/3*59= 196.66m2
Problem 2: The following offsets were taken at 15 m intervals from a survey line to an irregular boundary line
3.50,4.30, 6.75, 5.25, 7.50, 8.80, 7.90, 6.40, 4.40, 3.25 m
Calculate the area enclosed between the survey line, the irregular boundary line, and the offsets, by:
a) the trapezoidal rule
b) simpson’s rule
Solution: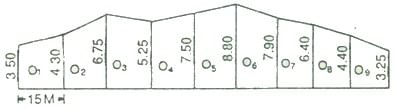
a) the trapezoidal rule
required area =15/2{3.50+3.25+2(4.30+6.75+5.25+7.50+8.80+7.90+6.40+4.40)}
= 15/2{6.75+102.60} = 820.125 m2
b) simpson’s rule
If this rule is to be applied, the number of ordinates must be odd. But here the number of ordinates must be odd. But here the number of ordinate is even(ten).
So, simpson’s rule is applied from O1 to O9 and the area between O9 and O10 is found out by the trapezoidal rule.
A1 = 15/3{3.50+4.40+4(4.30+5.25+8.80+6.40)}+2(6.75+7.50+7.90)
= 15/3(7.90+99.00+44.30)= 756.00 m2
A2 = 15/2(4.40+3.25)= 57.38 m2
Total area= A1+ A2 =756.00+57.38 = 813.38 m2
Problem 3: the following offsets are taken from a survey line to a curves boundary line, and the first and the last offsets by:
a) the trapezoidal rule
b) simpson’s rule
Solution:
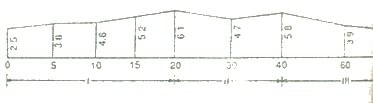
Here the intervals between the offsets are not reglar through out the length.
So, the section is divided into three compartments
Let
∆I = area of the first section
∆II = area of 2nd section
∆III = area of 3rd section
Here
d1 = 5 m
d2 =10 m
d3 = 20 m
a) by trapezoidal rule
∆I = 5/2{2.50+6.10+2(3.80+4.60+5.20)} = 89.50 m2
∆II = 10/2{6.10+5.80+2(4.70)} =106.50 m2
∆III = 20/2{5.80+2.20+2(3.90)} = 158.00 m2
Total area = 89.50+106.50+158.00 = 354.00 m2
b) by simpson’s rule
∆I = 5/3{2.50+6.10+4(3.8+5.20) + 2(4.60)} = 89.66 m2
∆II = 10/3{6.10+5.80+4(4.70)} =102.33 m2
∆III = 20/3{5.80+2.20+4(3.90)} = 157.33 m2
Total area= 89.66+102.33+157.33 = 349.32 m2
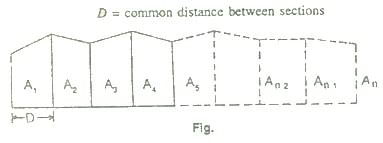
Formula For Calculation of Volume:
D = common distance between the sections
A. trapezoidal rule
volume (cutting or filling), V = D/2(A1+An+2(A2+A3+….+An-1))
Prismoidal formula
Volume( cutting or filling), V= D/3{A1+ An +4(A2+ A4+ An-1)+ 2(A3+ A5+….+ Ann-1)}

Note: the prismoidal formula is applicable whrn there is an odd number of sections. If the number of sections is even, the end strip is treated separately and the area is calculated according to the trapezoidal rule. The volume of the remaining strips is calculated in the usual manner by the prismoidal formula. Then both the results are added to obtain the total volume.
Works out problems
Problem 1: an embankment of width 10 m and side slopes 1 ½:1 is required to be made on a ground which is level in a direction transverseto the centre line. The central heights at 40 m intervals are as follows:
0.90,1.25,2.15,2.50,1.85,1.35, and 0.85
Calculate the volume of earth work according to
i) Trapezoidal formula
ii) Prismoidal formula
Solution: the c/s areas are calculated by
∆= (b+sh)*h
∆1 = (10+1.5*0.90)*0.90 = 10.22 m2
∆2 = (10+1.5*1.25)*0.90 = 14.84 m2
∆3 = (10+1.5*1.25)*2.15 = 28.43 m2
∆4 = (10+1.5*2.50)*2.50 = 34.38 m2
∆5 = (10+1.5*1.85)*1.85 = 23.63 m2
∆6 =(10+1.5*1.35)*1.35 = 16.23 m2
∆7 =(10+1.5*0.85)*0.85= 9.58 m2
(a) Volume according to trapezoidal formula:
V = 40/2{10.22+ 9.58+2(14.84+28.43+34.38+23.63+16.23)}
= 20{19.80+235.02} = 5096.4 m2
(b) Volume calculated in prismoidal formula:
V = 40/3 {10.22+9.58+4(14.84+34.38+16.23)+2(28.43+23.63)}
= 40/3 (19.80+ 261.80+104.12) = 5142.9 m2
Problem the areas enclosed by the contours in the lake are as follows:
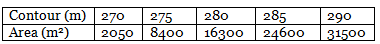
Calculate the volume of water between the contours 270 m and 290 m by:
i) Trapezoidal formula
ii) Prismoidal formula
Volume according to trapezoidal formula:
= 5/2{2050+31500+2(8400+16300+24600)}
= 330,250 m3
|
19 videos|31 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Measurements of Area & Volume - Geomatics Engineering (Surveying) - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What are the common units of measurement used for area in civil engineering? |  |
| 2. How can I calculate the area of an irregular shape in civil engineering? |  |
| 3. What is the formula to calculate the volume of a rectangular prism in civil engineering? |  |
| 4. How do I convert cubic meters (m^3) to cubic feet (ft^3) for volume calculations in civil engineering? |  |
| 5. Is there a specific formula to calculate the volume of a irregular shape in civil engineering? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|