Mensuration: Volume, Surface Area & Solid Figures | Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) - CAT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Mensuration? |

|
| Prism |

|
| Pyramid |

|
| Quadrilateral |

|
| Circles |

|
| Triangles |

|
| Polygons |

|
| Cuboid, Cube and Cylinder |

|
| Cone |

|
| Sphere |

|
| Hemisphere |

|
| Practice Questions |

|
What is Mensuration?
A branch of mathematics that talks about the length, volume, or area of different geometric shapes is called Mensuration. These shapes exist in 2 dimensions or 3 dimensions. Mensuration deals with the measurement of 3D solids in terms of Total surface area, Lateral/Curved surface area, and volume.
2D and 3D Shapes

Important Terms
- Area (A)
The area is the amount of surface a closed shape covers. It is represented by the letter A and is measured in square units. - Perimeter (P)
The perimeter is the total length of the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. It is represented by the letter P and is measured in linear units. - Volume (V)
The volume is the amount of space a three-dimensional object occupies. It is represented by the letter V and is measured in cubic units. - Curved Surface Area (CSA)
The curved surface area refers to the area of only the curved part of a shape, excluding the base and top. It is abbreviated as CSA. - Lateral Surface Area (LSA)
The lateral surface area is the total area of all the sides of a shape, excluding the base and top. It is abbreviated as LSA. - Total Surface Area (TSA)
The total surface area is the sum of the areas of all surfaces of a closed shape. It is abbreviated as TSA. - Square Unit
A square unit is the area of a square with sides of one unit length. It is used to measure surface area. - Cubic Unit
A cubic unit is the volume of a cube with sides of one unit length. It is used to measure volume. - Tools Required for Mensuration
Caliper: A tool used for measuring diameters.
Try Square: A tool used to check the squareness and flatness of a surface.
Meter Stick: A measuring tool that is one meter long.
Compass: A tool used for drawing arcs and circles.
Some Important Formulas of Mensuration
| SOLID | Total Surface Area | Lateral/ Curved Surface area | Volume | Length of Leading Diagonal/ Slant Height |
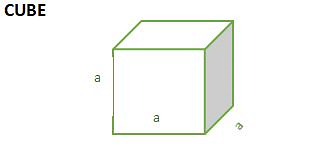
| 6a2 | 4a2 | a3 | √3a |
 | 2(LB+ BH+ HL) | 2H (L + B) | LBH | √ (L2 + H2 + B2) |
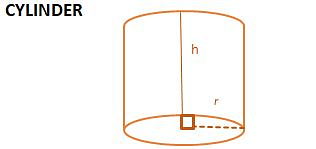 | 2Πr (r + h) | 2Πrh | Πr2h | No Slant height or diagonal |
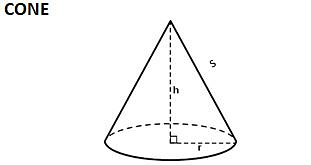
| Πr (r + l) | Πrl | ⅓Πr2h | √(h2 + r2) |
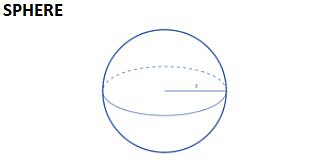
| 4Πr2 | 4Πr2 | 4/3Πr3 | No Slant height or diagonal |
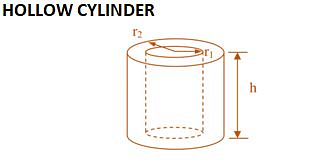
| 2Π(r₁+r₂) (r₂-r₁+h) | 2Πh(r₁+r₂) | Πh(r₂²-r₁²) | No Slant height or diagonal |
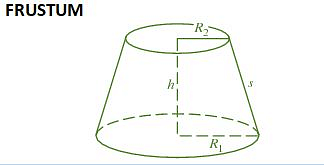
| Π(R1 + R2)s + (R12 + R22) | Π(R1 + R2)s | ⅓Πh(R12 + R22 + R1R2) | √(h2 + (R1 – R2)2) |
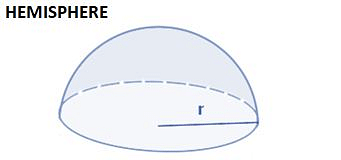
| 3Πr2 | 2Πr2 | 2/3Πr3 | No Slant height or diagonal |
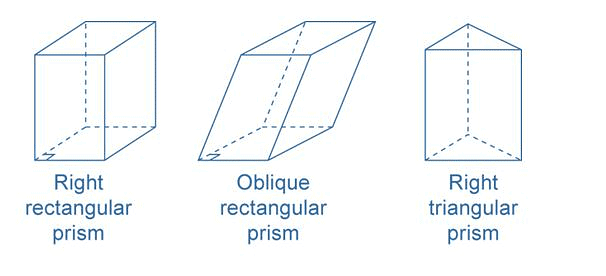
Prism
A Prism is a polyhedron comprising n-sided polygonal base congruent with a face parallel to it whose lateral faces are parallelogram and has a same cross section all along its length.
- Everyone must have heard the name Prism and might now a little about it through Physics or maybe some of you have don’t remember anything at all. Today, we’ll tell you the geometric properties of Prism.
- The number of lateral faces is equal to a number of sides in the polygonal base. Thus, the base could be triangular, quadrangular, hexagonal, etc.
- A prism is said to be right if the side edges are perpendicular to the ends. For example, cuboids and cubes.

Mensuration of Prism
- Curved Surface area of Prism: perimeter of the base x Height
- Total Surface area of Prism: Lateral surface area + (2 x base area)
- Volume of Prism: Base area x height
Pyramid
A pyramid is a polyhedron formed by connecting a polygonal base and a point called apex. The lateral surface of pyramids form triangles.
- With the word pyramid what first pops up in our mind are the pyramids of Egypt. And you are right, the pyramid is of similar in structure with the pyramids of Egypt. But it's just that the pyramids of Egypt are one kind of pyramids with a square base.
- A pyramid with an n-sided base has n+1 vertices, n+1 faces, and 2n edges.
- A right pyramid has its apex directly above the centroid of its base.

Mensuration of Pyramid
- Curved surface area of Pyramid: perimeter/2 x slant height
- Total surface area of Pyramid: curved surface area + area of the base
- Volume of the Pyramid: Base area x ⅓ x height
Quadrilateral
To find the area of any quadrilateral we can divide it into two triangles and then the area can be easily calculated by calculating the area of both the triangles separately.
- Area of ABCD = Area of ∆ABC + Area of ∆ACD
= (1/2) × AC × h1 + (1/2) × AC× h2
Area of Quadrilateral
 Where h1 and h2 are the height of both the triangles and d is the length of the common diagonal i.e.AC.
Where h1 and h2 are the height of both the triangles and d is the length of the common diagonal i.e.AC.
Rhombus
A rhombus is a quadrilateral with all the sides equal and parallel but not the right angle. Its two diagonals are perpendicular bisectors to each other.

In this also we can split the rhombus into two triangles and can find the area of the rhombus easily.
Area of Rhombus
Area of rhombus is half of the product of its two diagonals.
Mensuration of Quadrilaterals

Circles

- Circumference of circle= 2πr
- Area of circle= πr2
- Length of arc=

- Area of Sector=

- Area of Segment=

Triangles

- Formula of Perimeter of triangle (P) = a + b + c

- Some advance mensuration formulas for area of triangle are:

Polygons

Cuboid, Cube and Cylinder
- Surface Area
If we draw the net of the solid shape then we can see it’s all the faces clearly and if we add the areas of all the faces then we get the total surface area of that solid shape. The unit of surface area is a square unit. - Lateral or Curved Surface Area
If we leave the top and bottom faces of the solid shape then the area of the rest of the figure is the lateral surface of the shape. The unit of lateral surface area is a square unit.

- Volume
Volume is the space occupied by any solid figure i.e. the amount of capacity to carry something is the volume of that solid shape. The unit of volume is a cubic unit.
Cone

- Curved Surface Area of Cone= πrl, where l = slant height
- Total Surface Area of Cone= πr(r+l)
- Volume of Cone=1/3πr2h
Sphere
- Total Surface Area of Sphere = 4πr2
- Volume of Sphere= 4/3×πr3
Hemisphere
- Curved Surface Area of Hemisphere=2πr2
- Total Surface Area of Hemisphere = 3πr2
- Volume of Hemisphere= 2/3×πr3
Practice Questions
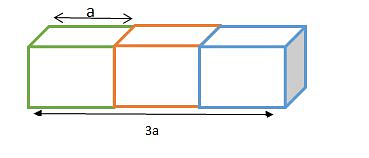
Problem 1: If three cubes are placed adjacently in a row, then the ratio of the total surface area of the new cuboid to the sum of the surface area of the three cubes will be
(1) 1:3
(2) 2:3
(3) 5:9
(4) 7:9
Correct Answer is Option (4)
We are given 3 cubes in the above question each with side a cm. When the cubes are placed adjacent in a row then the cuboid is formed with length 3a cm (a + a+ a) and height and breadth as a cm. Thus,
T.S.A of the cuboid = 2(3a*a + a*a + 3a*a)
= 14a2 cm2
T.S.A. of three cubes = 3*6a2
= 18a2 cm2
Thus, the ratio of T.S.A of cuboid to that of cube will be
14a2 cm2: 18a2 cm2
7 : 9
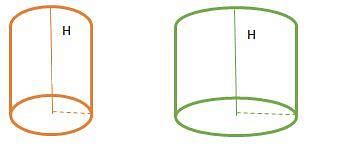
Problem 2: X and Y are two cylinders of the same height. The base of the X has diameter that is half the diameter of the base of Y. If the height of X is doubled, the volume of X becomes
(1) Equal to the volume of Y
(2) Double the volume of Y
(3) Half the volume of Y
(4) Greater than the volume of Y
Correct Answer is Option (3)
Original Solids
There are two cylinders X and Y each with height H and diameter of X is 1/2 of the diameter of Y. Thus, volume of each solid is
Volume of X = Πr²H
Volume of Y = Π(2r)² H = 4ΠrH
Now, if the height of X is doubled then,
Volume of X = Πr²2H = 2 Πr²H = ½ x 4ΠrH
Thus, the resultant cylinder has volume has volume ½ of Y.
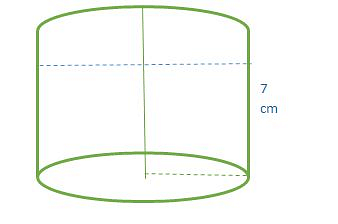
Problem 3: Water is poured into an empty cylindrical tank at a constant rate for 5 minutes. After the water has been poured into the tank, the depth of the water is 7 feet. The radius of the tank is 100 feet. Which of the following is the best approximation for the rate at which the water was poured into the tank
(1) 140 cubic feet/sec
(2) 440 cubic feet/sec
(3) 700 cubic feet/sec
(4) 2200 cubic feet/sec
Correct Answer is Option (3)
We need to find out the rate at which water is flown in tank. The volume of water flown in tank in 5 minutes = Πr²h= (22/7 * 100² * 7)
=220000 cm²
The rate at which water is flowing in the tank is = (220000/5*60) = 733.33 ft./sec
Problem 4: A conical cavity is drilled in a circular cylinder of 15 cm height and 16 cm base diameter. The height and base diameter of the cone is same as those of cylinder. Determine total surface area of the remaining solid?
(1) 215 Π cm2
(2) 376 Π cm2
(3) 440 Π cm2
(4) 542 Π cm
Correct Answer is Option (3)
In this question, we are given a cylinder out of which a cone is scraped out and we need to find out total surface area of the remaining solid given in the above figure.
Therefore, T.S.A of the remaining solid = C.S.A of cylinder + C.S.A of the cone + area of the base of cylinder
= 2Πrh + Πrl + Πr²
= Π(2*8*15 + 8*17 + 8²)
= Π(240 + 136 + 64)
= 440 cm²
Problem 5: Base of a right prism is a rectangle the ratio of whole length and breath is 3:2. If the height of the prism is 12 cm and total surface area is 288 cm2 then the volume of the prism is
(1) 291 cm3
(2) 288 cm3
(3) 290 cm3
(4) 286 cm3
Correct Answer is Option (2)
Since, the prism has rectangular base then the prism formed is cuboid with the ratio of length and breath is 3:2 and height is 12 cm. Therefore T.S.A of cuboid = 288 cm²
288 = 2(lb + bh + hl)
288 =2(3x*2x + 2x*12+ 12*3x)
288 = 2(6x² + 24x + 36x)
144 = 6x² + 60x
x² + 10x – 24 = 0
x² + 12x – 2x – 24 = 0
(x + 12) (x – 2) = 0
x = 2
Therefore, length is 6 cm and breadth is 4 cm. Thus, volume of cuboid = lbh = 6 x 4 x 12 = 288 cm3
Problem 6: Five marbles of various sizes are placed in a conical funnel. Each marble is in contact with the adjacent marble(s). Also, each marble is in contact all around the funnel wall. The smallest marble has a radius of 8 mm. The largest marble has a radius of 18 mm. What is the radius (in mm) of the middle marble?
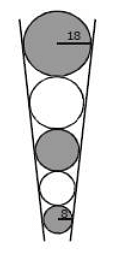 (1) 10
(1) 10
(2) 11
(3) 12
(4) 15
Correct Answer is Option (3)
Problem 7: Three identical cones with base radius r are placed on their base so that each is touching the other two. The radius of the circle drawn through their vertices is
(1) Smaller than r
(2) equal to r
(3) larger than r
(4) depends on the height of the cones
Correct Answer is Option (3)
The centres of the bases of the cones from a triangle of side 2r. The circumcircle of the circle will be identical to a circle drawn through the vertices of the cones and thus, it will have a radius of 2/√3 times r. which is greater than r.
|
191 videos|131 docs|110 tests
|
FAQs on Mensuration: Volume, Surface Area & Solid Figures - Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) - CAT
| 1. What is the formula to calculate the volume of a cylinder? |  |
| 2. How do you find the surface area of a cube? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between a prism and a pyramid? |  |
| 4. How do you calculate the area of a circle? |  |
| 5. How do you find the perimeter of a quadrilateral? |  |