Methods of Calculating National Income | SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| How is National Income Calculated? |

|
| Methods of Calculating National Income |

|
| What is Value Added Method? |

|
Introduction
The National Income stands as a pivotal gauge of a nation's economic well-being and advancement. It measures the aggregate value of all goods and services generated within the country's confines over a defined timeframe. To precisely assess this economic metric, economists utilize diverse methods, each providing a distinct vantage point on economic activity.
How is National Income Calculated?
After depreciation, the total value of final products and services produced by normal residents throughout an accounting year is termed national income.
Goods and services are generally produced by production units, utilizing four factors of production: land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship.
These four factors work together to create goods and services, adding value to existing products.
The additional value, or net domestic product, is dispersed among the owners of the four production components, who receive rent, employee compensation, interest, and profit for their contribution.
Profits earned by the owners of the factors of production are used to acquire goods and services from the production units for consumption and investment.
In essence, manufacturing generates revenue, and income is utilized to fund spending. Subsequently, spending fuels more production.
The circular flow of national income encompasses three phases: Production, Income, and Expenditure.
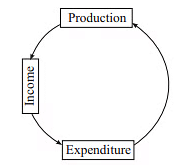
Methods of Calculating National Income
- The three methods of calculating national income are:
- Value Added Method
- Income Method
- Expenditure Method
- To enhance accuracy and comprehensiveness, economists often combine two or more methods to calculate National Income.
- This triangulation helps mitigate the limitations of individual methods and provides a more accurate depiction of an economy's performance.
What is Value Added Method?
The Value Added Method assesses the difference between a firm's output value and the value of intermediate goods and services utilized in production.
It signifies the net contribution of a firm or sector to the overall economy.
This method involves segmenting the economy into sectors like agriculture, industry, and services.
For each sector, value added is computed by subtracting the value of intermediate consumption (inputs used in production) from the value of output (goods or services produced). This ensures consideration only of the additional value created at each stage.
Double counting is a significant challenge in National Income calculation, where the value of intermediate goods and services is erroneously included multiple times.
The Value Added Method mitigates this issue by excluding intermediate consumption, focusing solely on the value added at each stage.
|
1335 videos|1437 docs|834 tests
|















