Miscellaneous Periodic Properties | Inorganic Chemistry PDF Download
Miscellaneous Chemical Properties
1. Periodicity of oxy acids:
(a) Acidic character of oxy acid increases from left to right in a period.
H2CO3 < HNO3 < H2SO4 < HClO4
(b) Acidic character of oxy acid decreases from top to bottom in a group.
HN03 > H3PO3
2. Periodicity of nature of oxide:
(a) On moving from left to right in a period, acidic nature of oxide generally increases.
e.g. CO2 < P2O3 < SO2 < CIO2
(b) On moving from top to bottom in a group, acidic nature of oxide generally decreases.
N02 > P2O3> As2O3
3. Periodicity of nature of hydroxide:
(a) On moving from left to right in a period, basic nature of hydroxide generally decreases.
e.g. KOH > Ca(OH)2 > Fe(OH)2 > Zn(OH)2
(b) On moving from top to bottom in a group, basic nature of hydroxide generally decreases.
LiOH < NaOH < KOH < RbOH
4. Solubility of salt in water:
- The hydration energy exhibits a decreasing trend when moving along a group.
- A decrease in lattice energy is observed along a group.
Trends In Physical Properties
- Physical properties are generally influenced by atomic weight, but exceptions can be observed, leading to irregular trends in the graph.
- Exceptions in the graph indicate deviations from the expected pattern.
- Understanding the reasons behind these exceptions is crucial for a comprehensive analysis of physical properties.
- It implies that factors beyond atomic weight play a significant role in determining certain physical properties.
- Identifying and explaining these exceptions is essential for a more nuanced understanding of the relationships between atomic properties and physical behavior.
Some Commonly Used Terms:
Noble Gases:
- Group 18 elements are referred to as noble gases.
- Also known as inert gases due to the complete filling of their outermost ns and np orbitals, making them non-reactive under ordinary conditions.
- Exceptions include Helium (He) and the first element in the 1s orbital.
Representative Elements:
- All s and p block elements, excluding the zero group, are classified as representative elements.
Transition Elements:
- Elements in the d-block, excluding the 11B group, are termed transition elements.
- These elements span the 4th, 5th, 6th, and 7th periods, residing between s and p block elements.
Inner Transition Elements:
- F-block elements, specifically 4f and 5f block elements, are known as inner transition elements.
- Comprising a total of 28 elements, they are situated in the 111B group and occupy the lower portion of the periodic table.
Typical Elements:
- Elements belonging to the second and third periods are categorized as typical elements.
Diagonal Relationship:
- Properties of elements in the second period share similarities with those in the third period.
- This type of relation between two periods, where properties resemble each other, is termed a diagonal relationship.
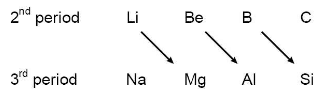
(i) Resemblance between Li and Mg :
- Lithium, unlike other group members, reacts with N2 to form a nitride, mirroring the behavior of magnesium.
- When heated, lithium hydroxide, carbonate, and nitrate undergo decomposition, yielding Li2O, similar to magnesium. However, unlike other alkali hydroxides and carbonates, lithium nitrate decomposes to form nitrite.
- Lithium hydroxide, carbonate, and fluoride exhibit higher solubility compared to their sodium and potassium counterparts. The solubilities are akin to the corresponding magnesium compounds.
ii) Resemblance between Be and Al:
- Ionic radius of Be2+ is comparable to that of Al3+ ions.
- Similar to aluminum, beryllium remains resistant to acid attacks due to the presence of a protective oxide film.
- Beryllium, like aluminum, forms a beryllate ion [Be(OH)4]2− when dissolved in alkali.
- BeO and Al2O3 are hard, high-melting, insoluble solids. Both oxides and their hydroxides exhibit amphoteric behavior, dissolving in sodium hydroxide solution.
- Beryllium and aluminum form stable fluoro complexes (BeF42- and AlF63-) in solution, while other Group 2 metals do not.
- Beryllium chloride (BeCl2) and aluminum trichloride (Al2Cl6) are essentially covalent with bridged polymeric structures. Both chlorides are soluble in organic solvents and act as strong Lewis acids.
(iii) Resemblance between B and Si :
- Boron and silicon hydrides spontaneously catch fire when exposed to air and are easily hydrolyzed.
- Boron halides, like silicon halides, undergo hydrolysis in water, while aluminum halides are only partially hydrolyzed.
- Boron forms binary compounds with various metals called borides, similar to silicon forming metal silicides. Some borides and silicides undergo hydrolysis, yielding boron and silicon, respectively.
- B2O3 and SiO2 exhibit acidic properties. Borates and silicates have tetrahedral B04 and Si04 structural units. Borosilicates are known where boron can replace silicon in a three-dimensional lattice. However, boron can also form planar BO3 units.
- Both boron (B) and aluminum (Al) are semiconductors.
SUMMARY OF PERIODICITY
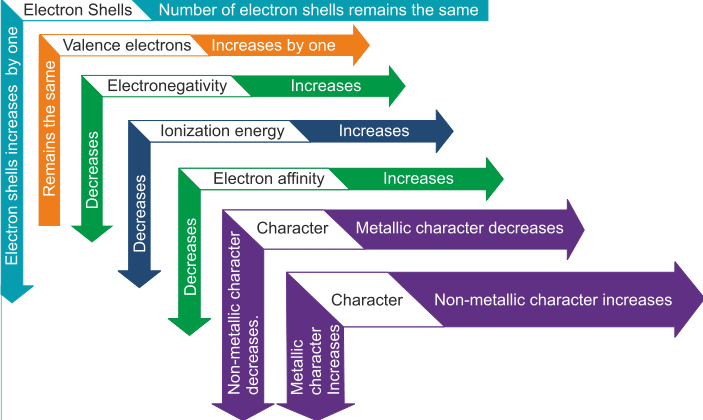
- Electron shells - Along the group, number of electrons remains the same and along the period, shells are increased by 1
- Valence electrons- Along the group, valence electrons increases by one and along the period, remains the same
- Electronegativity- Increases along the group and decreases along the period
- Ionization energy- Along the group, it increases and decreases along the period
- Electron Affinity- Along the group it increases and along the period decreases
- Metallic characteristics- Along the group, non-metallic characteristic increases and along the period metallic characteristics increases.
- Acidic nature of oxides increases along the group and decreases along the period
- Reducing nature of hydride increases in a period and decreases in a group.
|
50 videos|92 docs|41 tests
|
FAQs on Miscellaneous Periodic Properties - Inorganic Chemistry
| 1. What are some examples of miscellaneous periodic properties? |  |
| 2. How is atomic radius defined? |  |
| 3. What is ionization energy? |  |
| 4. How does electron affinity affect an element's properties? |  |
| 5. What is metallic character? |  |

















