Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Moments
Moments | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Moments
- Forces can not only make objects speed up, slow down, change direction, and deform but also induce rotation.
- An instance of such rotational motion is when a force acts on one side of a pivot, causing the object to rotate either clockwise or anticlockwise.
- The rotation direction can be clockwise or anticlockwise.

- A moment is described as:
The rotational influence or torque produced by a force in relation to a pivot point. - The size of a moment (M) is given by the formula:
M = F × d - Here,
M represents the moment in newton metres (Nm),
F is the force in newtons (N), and
d is the perpendicular distance of the force to the pivot in meters (m).

- The door handle is typically placed opposite the hinge to increase the perpendicular distance from the pivot point.
- This larger distance results in a greater moment or turning effect when force is applied, making it easier to open the door.
- Conversely, having a handle close to the pivot would require much more force to open the door.
- Examples involving moments:
- Using a crowbar to pry open something.
- Turning a tap on or off.
- Operating a wheelbarrow.
- Using scissors.
Question for MomentsTry yourself: Which of the following situations involves the use of moments?View Solution
Principle of Moments (Core)
- The concept of moments:
If an object is in balance, the total clockwise moment around a pivot point equals the total counterclockwise moment around the same pivot point. - Key points to remember:
- The formula for moment is force multiplied by the distance from a pivot. The forces must act perpendicular to the distance from the pivot. For instance, on a horizontal beam, only forces directed upwards or downwards will create a moment.
- Illustrative example: On a horizontal beam, forces causing a moment are those directed either upwards or downwards.
Principle of Moments (Extended)
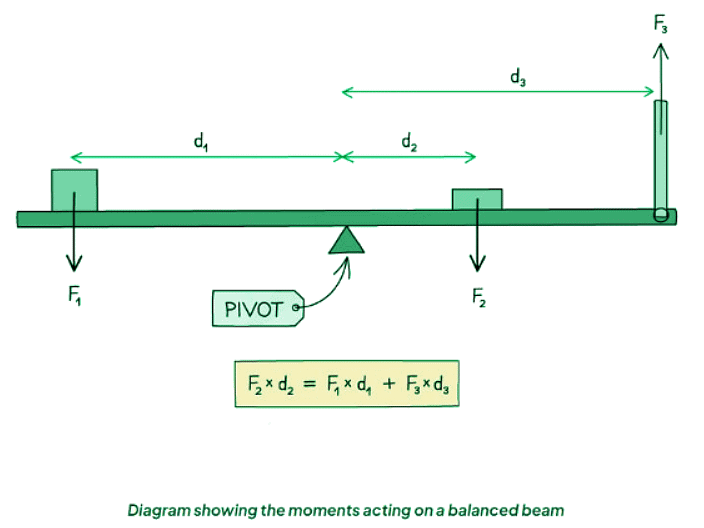
- In the above diagram, Force F2 is supplying a clockwise moment; Forces F1 and F3 are supplying anticlockwise moments.
- The mathematical representation of the principle of moments is F2 x d2 = (F1 x d1) - (F3 x d3).
The document Moments | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
127 videos|148 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Moments - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is the turning effect of a force? |  |
Ans. The turning effect of a force, also known as a moment, is the tendency of a force to rotate an object around a pivot point.
| 2. How can moments be calculated in physics? |  |
Ans. Moments can be calculated by multiplying the force applied by the distance from the pivot point at which the force is applied.
| 3. What is the principle of moments in physics? |  |
Ans. The principle of moments states that for an object to be in equilibrium, the sum of the clockwise moments about a pivot point must equal the sum of the anticlockwise moments about the same point.
| 4. How can the pivot point be determined in a moment calculation? |  |
Ans. The pivot point in a moment calculation is typically the point where the object or system is not moving or rotating.
| 5. Why is understanding moments important in physics? |  |
Ans. Understanding moments is important in physics as it allows us to analyze and predict the behavior of objects under the influence of forces, helping us solve practical problems and design structures.

|
Explore Courses for Year 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches
















