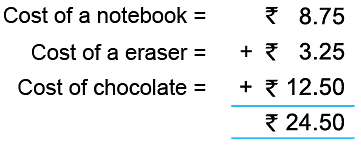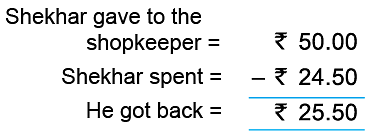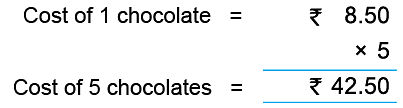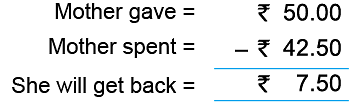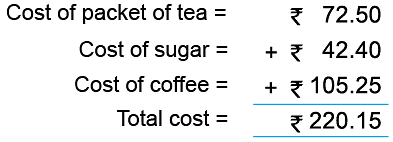Money Class 5 Notes Maths
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What is Money? |

|
| Understanding Indian Currency |

|
| Addition and Subtraction of Money |

|
| Multiplication of Money |

|
| Division of Money |

|
Introduction
- Imagine this: You walk into a toy shop and see your favorite game on the shelf.
- But wait—how will you buy it?
- You need money to make the purchase!
- From buying snacks to saving for a new bicycle, money plays an important role in our everyday life.
- Let’s explore what money is and how it's used.

What is Money?
- Money is what we use to buy things, pay bills, or save for the future.
- It can take different forms like coins, paper notes (currency), or digital money (used online).
- Money has value, which means each coin or note can be exchanged for goods or services.
Understanding Indian Currency
- The symbol for the Indian rupee is ₹.
- Common coins: ₹1, ₹2, ₹5, and ₹10.
- Common notes: ₹10, ₹20, ₹50, ₹100, ₹200, ₹500, and ₹2,000.
- Each coin and note is marked with its value, making it easy to know how much it is worth.
Addition and Subtraction of Money
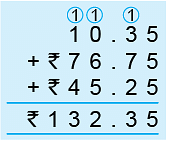
Example 1: Add ₹ 10.35, ₹ 76.75 and ₹ 45.25.
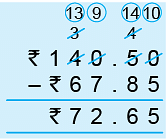
Example 2: Subtract ₹ 67.85 from ₹ 140.50.
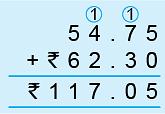
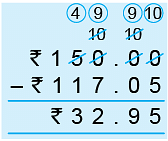
Example 3: Add ₹ 54.75 to ₹ 62.30 and subtract the sum from ₹ 150.
Multiplication of Money
- Multiplication in rupees and paise is done like multiplication of whole numbers.
- To multiply a sum of money with decimals with a whole number, ignore the decimal point during this process.
- In the product, place the decimal point after two places from the right.
- This separates paise from rupees.
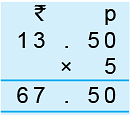
Example 4: Solve ₹ 13.50 × 5.
Method: Multiply 1350 b 5.
Put decimal point (.) from the right leaving two digits 50.
Digits on the right of decimal point indicate paise and digits on the left of decimal point represent rupees.
So, ₹ 13.50 × 5 = ₹ 67.50.
Division of Money
- Division of money is done in the same way as we divide numbers.
- Always remember to put the decimal point after two digits from the right in the quotient.
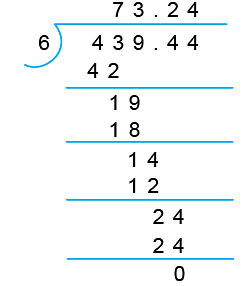
Example 5: Divide ₹ 439.44 by 6
So, ₹ 439.44 6 = ₹ 73.24.
Making a Bill
Let us make bills for the following purchases.
A notebook ₹ 16.50, A pen ₹ 7.50, A story book ₹ 12.50,
A pack of sketch pens ₹ 21.00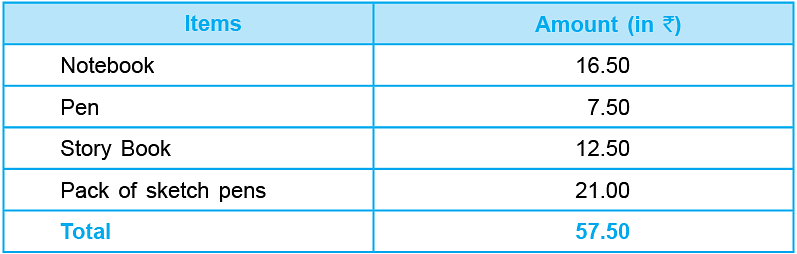
Rice ₹ 24.00, Moong Daal ₹ 36.50, Salt ₹ 9.50,
Shampoo ₹ 18.50, Hair Oil ₹ 28.50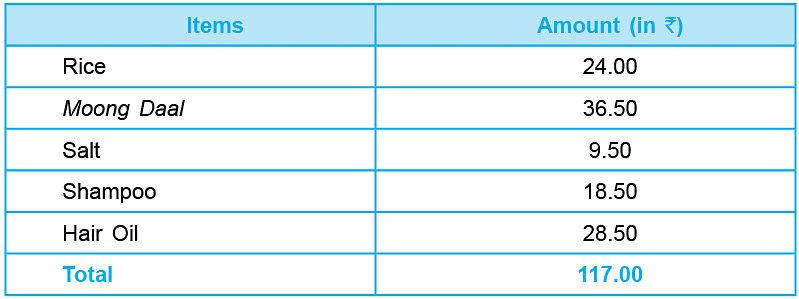
Shopping
Example 6: Shekhar bought a notebook for ₹ 8.75, an eraser for ₹ 3.25 and a chocolate for ₹ 12.50. He gave a 50-rupee note to the shopkeeper. How much did he get back?
So, Shekhar will get back ₹ 25.50.
Example 7: The cost of 1 chocolate is ₹ 8.50. Mother bought 5 chocolates and paid with a 50-rupee note. How much will she get back?
Hence, Mother will get back ₹ 7.50.
Example 8: Mrs. Shukla bought the following items from a shop.
1 packet of tea for ₹ 72.50
2 kg of sugar for ₹ 42.40
1 packet of coffee for ₹ 105.25
She gave a 500-rupee note to the shopkeeper. How much mone did the shopkeeper return?
Hence, the shopkeeper will return ₹ 279.85 to Mrs. Shukla.
|
32 videos|57 docs|45 tests
|
FAQs on Money Class 5 Notes Maths
| 1. What is the definition of money? |  |
| 2. What are the different denominations of Indian currency? |  |
| 3. How do you add and subtract money in transactions? |  |
| 4. How do you multiply and divide money in real-life situations? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to understand money management in daily life? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 5 exam
|

|