Motion and Measurement of Distances Class 6 Worksheet Science Chapter 7
Q1. Fill in the blanks:
i. Measurement is the comparison of an unknown quantity with some quantity.
Ans. fixed
ii. 1 km = m.
Ans. 1000
iii. Standard unit of length is .
Ans. metre
iv. The length of curved line can be measured using a .
Ans. thread
v. is the distance between two points or ends of an object.
Ans. Length
vi. means the change in position of an object with time.
Ans. Motion
Q2. True/False:
i. The choice of device used for the measurement depends on the type of measurement to be made.
Ans. True
ii. Our senses are reliable for accurate measurement.
Ans. False
iii. 1m = 100cm.
Ans. True
iv. 5km = 5000cm.
Ans. False
v. Motion of a child on a swing is periodic motion.
Ans. True
vi. Motion of a wheel of a cycle is random motion.
Ans. False
Q3. Which measuring device can be used to measure the girth of a tree?
Ans. Measuring tape
Q4. Write the type of motion in which a body moves along a straight path.
Ans. Rectilinear or linear motion
Q5. Which unit of length is used to measure a large distance?
Ans. Kilometre
Q6. Write one example of circular motion.
Ans. Motion of hands of a clock
Q7. Write one example of rectilinear motion.
Ans. Motion of an apple falling from a tree
Q8. Write one example of periodic motion.
Ans. A bouncing ball
Q9. Name the type of motion in which a body moves along a curved path.
Ans. Circular or Rotational motion
Q10. Name the type of motion in which motion repeats after equal time interval.
Ans. Periodic motion
Q11. The distance between Ria’s house and temple is 1340 m. Express this distance in kilometre.
Ans. 1 km = 1000m
1340/1000 = 1.340 km
Q12. Find the length of square in mm.
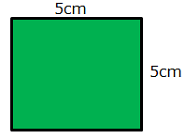
Ans. Each side = 5 x 10 = 50mm (All sides of square are equal)
Q13. Define ‘unit’.
Ans. The fixed quantity with which we compare an unknown quantity is called unit.
Q14. When object is said to be in rest?
Ans. If the position of an object does not change with time, it is said to be at rest.
Q15. What do you understand by ‘measurement’?
Ans. Measurement means the comparison of some unknown quantity with a known fixed quantity of same kind.
Q16. What is the common in between hand span, pace, angul and fist?
Ans. All of these are non-standard units of measurement that changes from person to person.
Q17. When object is said to be in motion?
Ans. When an object changes its position with time with respect to another object, it is said to be in motion.
Q18. Why is the hand span not considered as a reliable unit for measuring the length?
Ans. Hand span is not considered as a reliable unit for measuring the length because length of hand span varies from person to person.
Q19. What do you understand by standard unit of measurement?
Ans.The unit which is acceptable to the majority of people as a basic unit of measurement is called standard unit of measurement.
Assertion and Reason Questions
Q20. Assertion (A): Motion of moon around the earth is a circular motion.
Reason (R): In a circular motion, the distance of object from a fixed point remains the same.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (a)
Q21. Assertion (A): In ancient times bullock cart was used as a means of transport.
Reason (R): Aeroplanes were developed only in 1800 AD.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (c)
Q22. Assertion (A): The motion of a ball rolling on the ground is nothing but a rectilinear motion.
Reason (R): The motion of ball rolling on the ground is a combination of different types of motion.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (d)
Q23. Assertion (A): If an object travels in such a way that it comes back to the starting position, then the displacement is zero but, the distance travelled is not zero.
Reason (R): The displacement is the shortest distance between the initial and final position of the body whereas, distance is the actual path length covered by an object.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (a)
Q24. Assertion (A): While measuring the length, the eye of the observer should be exactly above that point of measurement to avoid the parallax error.
Reason (R): The scale used to measure the length of the object must be greater than the length of the object.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (c)
|
100 videos|261 docs|49 tests
|
FAQs on Motion and Measurement of Distances Class 6 Worksheet Science Chapter 7
| 1. What is motion and why is it important to study? |  |
| 2. How can we measure the distance traveled by an object? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between distance and displacement? |  |
| 4. How can we calculate the average speed of an object? |  |
| 5. What are some examples of objects in motion? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|


















