Motion & it's types - Class 9 PDF Download
What is a Motion?
A body is said to be in motion when its position changes continuously with respect to a stationary object, taken as reference point.
For example:
- When a car changes its position with respect to a stationary object like a traffic signal, we say that the car is in motion.

- If we want to know how far the man is from his starting point
Distance Travelled and Displacement
Distance Travelled and Displacement
The concept of distance travelled and displacement of an object can be understood by an example.
Suppose a man lives at a place, say A and he has to reach his office located at C, but first, he has to take his medicine from the shop located at the place, say B. The path travelled by him is drawn in the figure

Distance from A to B = 5 km
Distance from B to C = 4 km
Length of the path ABC travelled by the man = 5 + 4 = 9 km.
Then the actual distance travelled by the man in reaching from A to C is given by, distance travelled, AB + BC = 9km.
- If we want to know how far the man is from his starting point A, then is, we have to find the shortest distance between point A and point C.
- To do this draw a straight line joining A and C whose length is 6km. This distance AC is called the displacement of the man from point A to point C.
This displacement is in the East direction
Thus,
Distance travelled – refers to the actual length of the path travelled by an object during motion.
Displacement – refers to the shortest path between the initial and the final position of an object
during motion.
 View Answer
View AnswerKey Note: Distance has only magnitude but displacement has magnitude as well as direction. Thus, Distance is a scalar quantity and displacement is a vector quantity.
Can the Displacement of a Body be Zero?
Yes, the displacement of a body can be zero, when it traces a closed loop path and its final and
initial position is at same point.
For example:
A boy takes a path along the border of a square park whose each side is 1km long, and reaches back to its starting position A.

He travelled along the path AB→BC→CD→DE, Distance travelled =1+1+1+1= 4 km Displacement (from A to A) = 0.
Types of motion
- Linear motion: The motion of an object along a straight line is called linear or rectilinear motion.
For example: a boy running on a 100 m straight track on the ground, the motion of a bus on a straight highway - Circular motion: The motion of an object on a circular path is called circular motion
For example: an athlete running on a circular path around the field. - Rotatory Motion: The motion of an object along its axis on a fixed point is called the rotatory motion.
For example: motion of a top, the motion of a globe, motion of a ceiling fan, etc. - Vibratory Motion: The to–and–from the motion of a body about the mean position along the same path is called vibratory motion.
For example: the motion of a pendulum in a clock.
Uniform Motion and Non-Uniform Motion
What is Uniform Motion?
A body moves in a uniform motion if it travels equal distances in equal intervals of time.
For example:
A car running at a speed of 15 meters per second will always cover 15 meters in every one second of its motion.
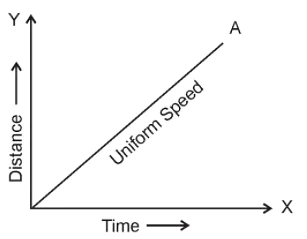
Note: The distance-time graph for uniform motion is a straight line.

From the above table, we observe that,
- An athlete runs a marathon 8 km long, starting at 9:00 AM.
- He covers 2 km every 1 hour, thus covering the whole distance in 4 hours.
What is Non–Uniform Motion?
A body moves in a non–uniform motion if it travels unequal distances in equal intervals of time.
For example,
A car travels at 15 km in one hour due to heavy traffic, but 25 km in the next one hour due to no traffic, and then 35 km on the road outside the city with no traffic at all. Thus, total distance covered is75 km in 3 hours.


 View Answer
View AnswerNote: The distance time graph for a body having non-uniform motion is a curved line. The non–uniform motion is also called accelerated motion.
Speed, Velocity and Acceleration
The motion of a body can be described in three terms: speed, velocity and acceleration.
What is Speed?
The distance travelled by an object in unit time is called speed. It can be measured by dividing the distance travelled by the time taken to travel this distance. It is a scalar quantity.
Speed= Distance travelled(in meters)/Time taken(in seconds)
If a body travels a distance d in time t, then its speed v is given by
v=d/t
The SI unit of speed is meters per second written as ms–1.
What is Average speed?
The average speed of a body is given by the total distance travelled divided by the time taken to cover this distance.
Average speed = Total distance travelled/Speed
What is Velocity?
Velocity of a moving body is the distance travelled by it per unit time in a given direction, denoted by the symbol V. Velocity is a vector quantity.
If a body travels a distance d in time t in a given direction, then its velocity v is given by,
V=d/t
d = distance travelled in a given direction = displacement, thus, the velocity of a body is the displacement produced per unit time.
The SI unit of velocity is the same as that of speed, namely m/s or ms–1.
 View Answer
View AnswerKey Note: The direction of velocity is same as the direction of displacement of the body.
Can the average velocity of an object be zero?
- In most cases, the bodies move in a single straight line without changing direction.
- The values of speed and velocity will be same in these cases.
- In case the body changes its direction at some point of time, then speed and velocity may be different.
- Though average speed of a moving body can never be zero, but the average velocity of a moving body can be zero.
What is Average velocity?
Average velocity can be calculated by taking the average of the initial velocity, represented by u and the final velocity, represented by v.
Average velocity= vav = (u+v)/2
Distance – time graph for uniform speed
The graph for an object moving at uniform speed (covering equal distances in equal time periods) is a linear graph.

Distance – time graph for a non–uniform speed

Case1: When the speed of a moving object increases with time, the graph will be curving upward.
Case2: When the speed of a moving object decreases with time, the graph will be curving downward.
What is Acceleration?
When an object starts, its velocity is zero. Gradually, it increases and then decreases to get halted. The rate at which the velocity of the object changes with time is called acceleration, it is denoted by a.
Acceleration = Change in velocity/Time taken
Change in velocity = Final velocity – Initial Velocity = v – u
[a=(v-u)/t]
Therefore, t is the time taken for the change in velocity.
The SI unit of acceleration is m/s2or ms–2 .
 View Answer
View AnswerKey Note: When a body is moving with uniform velocity, its acceleration will be zero as v = u i.e, change in velocity is zero.
What is Uniform acceleration?
If the body travels in a straight line and its velocity increases by equal amounts in equal intervals of time, the body is said to be in uniform acceleration .
The motion of a freely falling body or the motion of a ball rolling down on an inclined plane is an example of uniformly accelerated motion. The velocity-time graph of a body having uniformly accelerated motion is a straight line.
What is Non–uniform acceleration?
A body is said to be in non–uniform acceleration if its velocity increases by unequal amounts in equal intervals of time i,e its velocity changes at a non–uniform rate.
The velocity-time graph for a body having non–uniform acceleration is a curved line.
Retardation or negative acceleration
Acceleration takes place when the velocity of a body changes. This change can be increasing or
decreasing. Thus, acceleration can be classified into two groups.
- Positive acceleration: When a car runs down on an inclined plane, the velocity of car increases and it is said to be moving with positive acceleration, which we usually called acceleration.
- Negative acceleration: When a car runs upward on an inclined plane, the velocity of car decreases and it is said to be running with negative acceleration, which we generally called retardation or deceleration. A ball thrown vertically upwards is also an example of negative acceleration. A parachute is also an example of deceleration.
- Zero acceleration: A bus standing at the bus stop and a bus moving on a straight road with a
constant speed of 40 km/hr are examples of zero acceleration. In both cases, velocity is constant i.e; ∆v = 0.
Equations of uniformly accelerated motion
There are equations for the motion of those bodies which travel with a uniform acceleration these equations give the relationship between initial velocity (u), final velocity (v), time taken (t), acceleration (a) and distance travelled (s) by the bodies.
1. First equation of motion: It gives the velocity acquired by a body in time t moving with acceleration a.
Let, the initial velocity = u.Final velocity = v.
Time = t
Acceleration = a
thus,
[v=u+at]
2. Second equation of motion: It gives the distance travelled (s) by a body, moving at an initial speed of u, in time t
[s=ut+(1/2)at2]
3. Third equation of motion: It gives the velocity (v) acquired by a body in
travelling a distance (s)
[v2=u2+2as]
 View Answer
View AnswerKey Point:
1. If a body starts from rest, initial velocity, u = 0
2. If a body comes to rest, its final velocity, v = 0
3. If a body moves moves with uniform velocity, its acceleration, a = 0
Circular Motion
When a body moves in a circular path with uniform speed (constant speed), its motion is called uniform circular motion.
Examples:
- Artificial satellites move in their orbits in space.
- Moon moving around the earth.
- Toy train moving on a circular track.
- Tip of the needle of a clock.
Speed of a body in a uniform circular motion: When a body takes one round of a circular path,
then it travels a distance of 2πr, where r is the radius of the circular path.
Speed v = Distance travelled (circumference)/Time taken
[v =2πr/t]
where, π=22/7=3.14
FAQs on Motion & it's types - Class 9
| 1. What is the difference between distance travelled and displacement? |  |
| 2. What are the types of motion? |  |
| 3. What is uniform motion? |  |
| 4. What is average velocity? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between speed, velocity, and acceleration? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|


















