Motivation & Leadership | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Motivation-Meaning |

|
| Importance of Motivation |

|
| Theories of Motivation |

|
| Leadership-Meaning |

|
| Importance of Leadership |

|
| Theories of Leadership |

|
| Difference Between Motivation and Leadership |

|
Motivation-Meaning
Motivation can be defined as the inner drive that compels individuals to take action in order to achieve their goals and aspirations. This driving force can originate from both internal sources, such as personal desires and values, as well as external factors like rewards and recognition. It encompasses the understanding and manipulation of elements that encourage individuals to remain actively involved, efficient, and dedicated to their tasks.
Importance of Motivation
Motivation plays a crucial role in human resource management for various reasons which are detailed below:
- Rewards and recognition: Offering rewards, incentives, and recognition schemes that acknowledge and value employees' hard work and accomplishments can significantly enhance motivation.
- Clear communication: Effectively communicating organizational goals, expectations, and performance feedback helps employees comprehend their roles and how their contributions contribute to the overall objectives, thereby fostering motivation.
- Training and development: Providing opportunities for skill enhancement and career progression through training programs and professional development initiatives can boost employees' motivation to learn and advance.
- Empowerment and autonomy: Granting employees autonomy, decision-making responsibilities, and involvement in meaningful tasks can increase motivation by instilling a sense of ownership and accountability.
- Supportive leadership: Encouraging supportive leadership styles that include guidance, feedback, and mentorship can nurture motivation by cultivating a positive and nurturing work environment.
Theories of Motivation
Motivation has been a subject of extensive study, leading to the development of various theories by researchers and observers. Let's delve into some prominent theories of motivation:
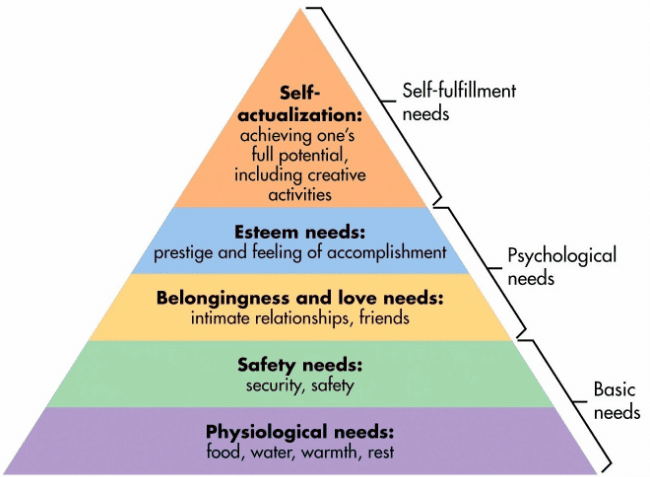
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs is a psychological theory proposed by Abraham Maslow, which categorizes human needs into five levels. According to Maslow, individuals are motivated to fulfill these needs in a hierarchical order, starting from the most basic to the highest level of personal growth and fulfillment.
Physiological Needs:
- This is the foundational level of needs, encompassing basic biological requirements such as food, water, shelter, and sleep, essential for survival.
Safety Needs:
- After physiological needs are met, individuals seek safety and security, including personal security, financial stability, a safe environment, employment, health, and protection from harm.
Social Needs:
- Social needs involve the desire for love, affection, and a sense of belongingness. This includes forming meaningful relationships with family, friends, and community.
Esteem Needs:
- Esteem needs relate to the desire for recognition, respect, and self-worth. It includes aspects like confidence, competence, status, and reputation.
Self-Actualization Needs:
- At the pinnacle of the hierarchy, self-actualization needs entail realizing one's full potential, pursuing personal goals, and engaging in activities aligned with one's values and interests.
According to Maslow, individuals typically progress from fulfilling lower-level needs to higher ones, with self-actualization representing the peak of motivation and personal development.
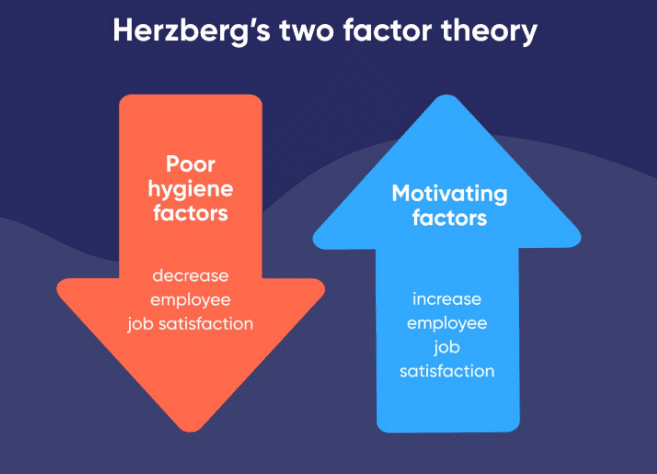
Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory
According to Herzberg, there are two types of factors affecting motivation and job satisfaction in the workplace: hygiene factors and motivational factors.
Hygiene Factors:
- These factors, when fulfilled, help prevent job dissatisfaction.
- However, their presence alone does not lead to motivation or satisfaction.
Motivational Factors:
- These factors are crucial in fostering motivation and job satisfaction.
- Includes providing challenging work, recognition, growth opportunities, and intrinsic rewards.
Herzberg emphasized that organizations should focus on both types of factors to enhance motivation and create a positive work environment.
Expectancy Theory
Expectancy theory of motivation is a psychological framework that focuses on how individuals make decisions regarding their behaviors based on the belief that effort leads to performance and performance leads to rewards. This theory consists of three key components:
Expectancy (Effort-Performance Link):
- Expectancy is an individual's belief that their effort will result in the desired performance. It involves evaluating the likelihood of achieving a specific outcome based on the effort put in. When people believe that their efforts will lead to successful performance, they are more likely to be motivated to engage in the task.
Instrumentality (Performance-Reward Link):
- Instrumentality refers to the belief that successful performance will bring about desired outcomes or rewards. It is the perception of the connection between performance and rewards. When individuals believe that their performance will be acknowledged and rewarded, they are more inclined to invest effort into the task.
Valence (Value of Outcomes):
- Valence represents the value or desirability that individuals associate with anticipated outcomes or rewards. It reflects the personal significance or importance placed on the rewards. The more individuals value the expected outcomes, the more motivated they are to participate in the activity.
According to expectancy theory, motivation can be calculated using the formula: Motivation = Expectancy × Instrumentality × Valence. This means that individuals are motivated when they believe that their efforts will lead to successful performance, which will, in turn, result in desired rewards, and when they value those rewards.
Managers can enhance motivation by ensuring that employees perceive a strong connection between effort, performance, and rewards. This can be achieved by providing clear performance expectations, offering rewards that are meaningful and aligned with employee preferences, and fostering a work environment where individuals believe that their efforts will lead to desired outcomes.
Goal-Setting Theory
- Goal Specificity: Goals should be specific and well-defined rather than vague or general. Clear goals provide individuals with a clear direction and focus, enabling them to understand what needs to be accomplished.
- Goal Difficulty: Goals should be challenging but achievable. A moderate level of difficulty encourages individuals to exert effort and engage in strategic planning to accomplish the goals.
- Goal Acceptance: For goals to be effective, individuals must accept and commit to them willingly. When individuals are involved in the goal-setting process and have a sense of ownership, they are more likely to be motivated to achieve those goals.
- Goal Feedback: Feedback plays a crucial role in goal setting. Regular feedback on progress and performance helps individuals track their advancement, make adjustments, and maintain motivation. It provides information on whether individuals are moving in the right direction towards goal attainment.
- Goal Complexity: Goals should be set in a way that takes into account the complexity of the task or objective. Complex goals may need to be broken down into smaller, manageable sub-goals to maintain motivation and provide a sense of achievement along the way.
Application of Goal-Setting Theory
Goal-Setting Theory suggests that setting specific, challenging, and accepted goals leads to increased motivation, task engagement, and performance. By establishing clear goals, providing feedback, and involving individuals in the goal-setting process, organizations and individuals can enhance motivation and improve performance. This theory has been widely applied in various fields, such as education, sports, and business, to drive success and accomplishment.
Leadership-Meaning
Leadership is incredibly significant in human resource management (HRM) as it shapes the organizational culture, provides guidance to employees, and propels performance. Effective leadership within HRM is vital for establishing a positive work environment, attracting and retaining top talent, and nurturing employee engagement and productivity.
Importance of Leadership
Strategic Alignment:
- HR leaders provide strategic direction by aligning HR initiatives with organizational goals to ensure sustainable growth.
Talent Acquisition and Retention:
- Effective HR leadership fosters talent acquisition and retention through attracting high-potential candidates and implementing fair recruitment processes.
- Leaders also focus on creating a positive employer brand and establishing employee development programs to retain valuable employees.
Employee Engagement:
- HR leaders inspire and motivate employees, nurturing engagement and commitment within the workforce.
- They cultivate a supportive work environment, encourage open communication, and provide avenues for personal growth and development.
Performance Management:
- HR leaders are instrumental in setting up performance management systems that include clear expectations, regular feedback, and performance incentives.
- By implementing transparent evaluation processes, leaders encourage optimal performance and acknowledge outstanding contributions.
Change Management:
- During organizational transitions, HR leaders guide employees through change by facilitating effective communication and necessary training to aid adaptation.
- Efficient change management ensures seamless transitions and minimizes resistance within the organization.
Employee Well-being:
- Leaders prioritize employee well-being and work-life balance, promoting a culture of integration and providing wellness initiatives.
- By focusing on mental health and satisfaction, HR leaders create a positive workplace environment.
Conflict Resolution:
- Skilled in conflict resolution, HR leaders mediate workplace conflicts, promote effective communication, and foster a harmonious work environment.
- Addressing conflicts promptly and fairly helps maintain a cohesive and productive workforce.
Theories of Leadership
- Leadership theories offer different viewpoints on what makes a good leader and help us grasp the various elements that contribute to effective leadership. While no single theory can fully explain leadership, they provide valuable insights into the qualities, behaviors, and situations that impact leadership success. Effective leaders often combine ideas from various theories and adjust their approach based on their followers' needs and specific circumstances.
Trait Theory
- The trait theory of leadership suggests that certain inherent qualities and characteristics play a role in effective leadership. Traits like confidence, intelligence, determination, and integrity are thought to be linked to successful leadership. However, this theory has been criticized for oversimplifying leadership by concentrating only on individual traits without considering the context or behaviors.
Behavioral Theory
- Behavioral theories aim to identify specific behaviors demonstrated by effective leaders. The two primary behavioral theories are:
The Ohio State Studies and the University of Michigan Studies
- These studies pinpointed two types of leader behaviors: consideration (fostering relationships, displaying care for subordinates) and initiating structure (establishing clear objectives, organizing tasks). Both behaviors were deemed crucial for effective leadership.
Managerial Grid Theory
The Managerial Grid Theory, developed by Blake and Mouton, illustrates leadership behavior by plotting it on a grid with two dimensions: concern for people and concern for production. It outlines five leadership styles:
- Impoverished: Characterized by low concern for both people and production.
- Country Club: Demonstrates high concern for people but low concern for production.
- Authority-Compliance: Shows high concern for production but low concern for people.
- Middle-of-the-Road: Balances concern for both people and production.
- Team: Reflects high concern for both people and production.
Contingency Theories
- Contingency theories suggest that effective leadership hinges on the interplay among leaders, followers, and the situation at hand.
Fiedler's Contingency Model
- Fiedler's model posits that leadership effectiveness is influenced by the leader's style and the favorability of the situation. The leader's style is categorized as task-oriented or relationship-oriented, while situational favorableness is determined by leader-member relations, task structure, and position power.
Hersey and Blanchard's Situational Leadership Theory
- This theory proposes that effective leaders should adjust their leadership style based on the readiness level of their followers. Readiness is evaluated through followers' competence and commitment levels. The theory outlines four leadership styles: directing, coaching, supporting, and delegating.
Transformational Leadership
- Transformational leadership theory highlights the capacity of leaders to inspire and motivate their followers towards exceptional performance.
- Leaders in this model are charismatic, visionary, and focus on nurturing and empowering their followers.
- They encourage followers to surpass personal interests and align with the organizational objectives.
Servant Leadership
- Servant leadership theory underscores leaders' dedication to serving and supporting their followers.
- These leaders prioritize the needs of their followers, fostering a sense of community and individual growth.
- By prioritizing others' needs, servant leaders strive to enhance the well-being and success of both followers and the organization.
Difference Between Motivation and Leadership
The distinction between motivation and leadership lies in their unique characteristics and roles within a team or organization.
Definition
- Leadership: Leadership involves the capacity of an individual to direct and influence others towards a shared vision or objective. It encompasses taking control, making decisions, and motivating others to achieve common goals.
- Motivation: Motivation pertains to the internal drive, passion, or excitement that propels individuals to initiate and maintain actions towards attaining personal or professional objectives. It acts as a catalyst for individuals to excel.
Key Characteristics
Leadership:
- Involves establishing direction and offering guidance.
- Requires strong communication and decision-making skills.
- Emphasizes the growth and empowerment of others.
- Focuses on long-term vision and strategic planning.
Involves setting direction and providing guidance:
- This aspect of the role entails establishing the course of action and offering advice to ensure everyone is aligned towards common goals.
Requires effective communication and decision-making skills:
- Effective communication and the ability to make sound decisions are crucial in this role to convey ideas clearly and make choices that benefit the team.
Emphasizes the development and empowerment of others:
- This responsibility involves focusing on nurturing the growth and confidence of team members, empowering them to reach their full potential.
Focuses on long-term vision and strategic planning:
- Strategic planning and envisioning future outcomes are key components, requiring a focus on the bigger picture and long-term objectives.
Motivation:
- Motivation involves inspiring and encouraging individuals by understanding their unique needs and aspirations, utilizing both intrinsic and extrinsic factors to enhance engagement, productivity, and satisfaction.
Roles and Responsibilities
Leadership:
- Sets clear goals and objectives to provide a sense of direction and purpose.
- Develops and communicates a compelling vision to inspire and align the team towards a common goal.
- Establishes strategies and plans to achieve targets effectively.
- Provides guidance and support to team members to foster growth and success.
- Evaluates performance and provides constructive feedback to drive improvement.
Motivation:
- Identifies individual needs and aspirations
- Recognizes and rewards achievements
- Creates a positive work environment
- Encourages personal and professional growth
- Fosters teamwork and collaboration
Impact on Individuals and Teams
Leadership:
- Builds trust and respect among team members
- Enhances individual and collective performance
- Promotes innovation and creativity
- Cultivates a positive organizational culture
- Develops future leaders
Motivation:
- Increases job satisfaction and morale
- Enhances productivity and efficiency
- Boosts creativity and problem-solving abilities
- Reduces absenteeism and turnover rates
- Improves overall employee engagement
Importance of Motivation in the Workplace
- Increases job satisfaction and morale
- Enhances productivity and efficiency
- Boosts creativity and problem-solving abilities
- Reduces absenteeism and turnover rates
- Improves overall employee engagement
Strategies for Effective Leadership and Motivation
Leadership:
- Lead by example and exhibit integrity
- Encourage open communication and active listening
- Delegate responsibilities and empower team members
- Provide regular feedback and recognition
- Invest in professional development opportunities
Motivation:
- Understand individual needs and aspirations
- Offer meaningful rewards and recognition
- Foster a supportive and inclusive work environment
- Promote work-life balance and flexibility
- Encourage autonomy and ownership of tasks
Strategies for Motivating Employees
- Understand individual needs and aspirations
- Offer meaningful rewards and recognition
- Foster a supportive and inclusive work environment
- Promote work-life balance and flexibility
- Encourage autonomy and ownership of tasks
Conclusion
Leadership and motivation are crucial aspects for any organization, guiding individuals towards achieving goals and influencing decision-making processes. While new motivators and leadership styles emerge, the fundamental principles remain constant.
|
157 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Motivation & Leadership - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What is the importance of motivation in an organization? |  |
| 2. Can you explain the difference between motivation and leadership? |  |
| 3. How does motivation play a role in effective leadership? |  |
| 4. What are some popular theories of motivation and leadership? |  |
| 5. How can organizations benefit from implementing effective motivation and leadership strategies? |  |















