Multidimensional Array | Programming and Data Structures - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
A multi-dimensional array is an array of arrays. 2-dimensional arrays are the most commonly used. They are used to store data in a tabular manner.
Consider the following 2D array, which is of size 3 x 5. For an array of size , the rows and columns are numbered from to and columns are numbered from to , respectively. Any element of the array can be accessed by arr[i][j] where and . For example, in the following array, the value stored at arr[1][3] is 14.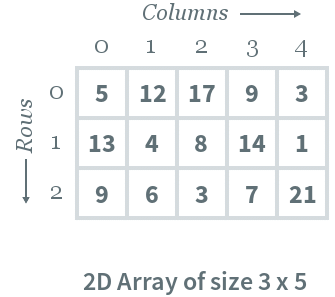
2D array declaration
To declare a 2D array, you must specify the following:
- Row-size: Defines the number of rows
- Column-size: Defines the number of columns
- Type of array: Defines the type of elements to be stored in the array, i.e., either a number, character, or other such datatype.
A sample form of declaration is as follows:type arr[row_size][column_size];
A sample C array is declared as follows:
cint arr[3][5];
2D array initialization
An array can either be initialized during or after declaration.
The format of initializing an array during declaration is as follows:type arr[row_size][column_size] = {{elements}, {elements} ... };
An example in C is given below:
cint arr[3][5] = {{5, 12, 17, 9, 3}, {13, 4, 8, 14, 1}, {9, 6, 3, 7, 21}};
Initializing an array after declaration can be done by assigning values to each cell of the 2D array, as follows:
ctype arr[row_size][column_size]; arr[i][j] = 14;
A C example of initializing an array after declaration by assigning values to each cell of a 2D array is as follows:
cint arr[3][5]; arr[0][0] = 5; arr[1][3] = 14;
This is quite naive and not usually used. Instead, the array elements are read from stdin.
Processing 2D arrays
The most basic form of processing is to loop over the array and print all its elements, which can be done as follows:
ctype arr[row_size][column_size] = {{elements}, {elements} ... }; for(i = 0; i < row_size; i++) for(j = 0; j < column_size; j++) print arr[i][j];
A C example of looping over the array and printing all its elements is as follows:
c#include <stdio.h> int main() { // Array declaration and initialization int arr[3][5] = {{5, 12, 17, 9, 3}, {13, 4, 8, 14, 1}, {9, 6, 3, 7, 21}}; // Iterate over the array for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) { // Print out each element printf("%d ", arr[i][j]); } // Print new line character after the row is printed in the above loop printf("\n"); } return 0; }
These methods of declaration, initialization, and processing can be extended to 3D or higher-dimensional arrays.
|
158 docs|31 tests
|
FAQs on Multidimensional Array - Programming and Data Structures - Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
| 1. What is a multidimensional array in programming? |  |
| 2. How do you declare a multidimensional array in C or C++? |  |
| 3. What are the common use cases of multidimensional arrays? |  |
| 4. How can you access elements in a multidimensional array? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between a one-dimensional array and a multidimensional array? |  |
















