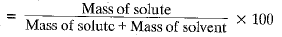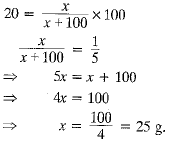Q.12. You are given two samples of water labelled as ‘A’ and ‘B’. Sample ‘A’ boils at 100 °C and sample ‘B’ boils at 102 °C. Which sample of water will not freeze at 0 °C? Comment.
Ans. Sample 'B' will not freeze at 0°C as it is impure water because it boils at 102°C. Therefore, it will freeze below 0°C.
Q.13. What are the favourable qualities given to gold when it is alloyed with copper or silver for the purpose of making ornaments?
Ans. Pure gold is soft metal and can change its shape with a little force. Therefore, it is not suitable for making ornaments. When it is alloyed with copper or silver it becomes hard and suitable for making ornaments. Thus, it provides strength to gold.
Q.14. An element is sonorous and highly ductile. Under which category would you classify this element? What other characteristics do you expect the element to possess
Ans. The element is a metal.
Characteristics:
(i) It has metallic lustre.
(ii) It is malleable.
(iii) It is good conductor of heat and electricity.
(iv) It is hard and has high tensile strength.
Q.15. Give an example each for the mixture having the following characteristics. Suggest a suitable method to separate the components of these mixtures:
(a) A volatile and a non-volatile component.
(b) Two volatile components with appreciable difference in boiling points.
(c) Two immiscible liquids.
(d) One of the components changes directly from solid to gaseous state.
(e) Two or more coloured constituents soluble in some solvent.
Ans. (a) Iodine is separated from sand by sublimation.
(b) Acetone is separated from water by distillation.
(c) Kerosene oil and water are separated by separating funnel.
(d) Camphor by the process of sublimation.
(e) Mixture of inks can be separated by chromatography.
16. Fill in the blanks:
(a) A colloid is a ________ mixture and its components can be separated by the technique known as _______ .
(b) Ice, water and water vapour look different and display different _______ properties but they are_______the same.
(c) A mixture of chloroform and water taken in a separating funnel is mixed and left undisturbed for some time. The upper layer in the separating funnel will be of _______ and the lower layer will be that of .
(d) A mixture of two or more miscible liquids, for which the difference in the boiling points is less than 25 K can be separated by the process called _______.
(e) When light is passed through water containing a few drops of milk, it shows a bluish tinge. This is due to the ______ of light by milk and the phenomenon is called_______. This indicates that milk is a _______solution.
Ans. (a) heterogeneous, centrifugation
(b) physical, chemically
(c) water, chloroform; because water is lighter than chloroform
(d) fractional distillation
(e) scattering, Tyndall effect, colloidal
Q.17. Sucrose (sugar) crystals obtained from sugarcane and beet root are mixed together. Will it be a pure substance or a mixture? Give reasons for the same.
Ans. It will be pure substance because sugar obtained by different sources will have same composition.
Q.18. Give some examples of Tyndall effect observed in your surroundings?
Ans. When a beam of light enters a dark room, its path can easily be seen due to Tyndall effect which is due to scattering light by dust particle present in air.
 Q.19. Can we separate alcohol dissolved in water by using a separating funnel? If yes, then describe the procedure. If not, explain.
Q.19. Can we separate alcohol dissolved in water by using a separating funnel? If yes, then describe the procedure. If not, explain.
Ans. No, because alcohol and water form miscible liquids. Separating funnel is used to separate immiscible liquids. Miscible liquids can be separated by the process of distillation. Alcohol and water are best separated by fractional distillation as difference in boiling point is large.
Q.20. On heating calcium carbonate gets converted into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
(a) Is this a physical or a chemical change?
(b) Can you prepare one acidic and one basic solution by using the products formed in the above process? If so, write the chemical equation involved.
Ans. (a) It is a chemical change.
(b) Yes. CaO dissolves in water forming calcium hydroxide which is basic solution.
CaO (s) + H2O (l) → Ca(OH)2 (aq)
CO2(g) dissolves in water forming carbonic acid which is acidic solution.
CO2(g) + H2O (l) → H2CO3 (aq)
Q.21. Non-metals are usually poor conductors of heat and electricity. They are non-lustrous, nonsonorous, non-malleable and are coloured.
(a) Name a lustrous non-metal.
(b) Name a non-metal which exists as a liquid at room temperature.
(c) The allotropic form of a non-metal which is a good conductor of electricity. Name the allotrope.
(d) Name a non-metal which is known to form the largest number of compounds.
(e) Name a non-metal other than carbon which shows allotropy.
(f) Name a non-metal which is required for combustion.
Ans. (a)Diamond
(b) Bromine
(c) Graphite
(d) Carbon
(e) Sulphur/phosphorus
(f) Oxygen
Q.22. Classify the substances given in figure into elements and compounds
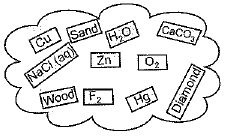
Ans. Elements: Cu, Zn, O2, F2, and Hg, Diamond (carbon)
Compounds: H2O, CaCO3
Q.23. Which of the following are not compounds?
(a) Chlorine gas
(b) Potassium chloride
(c) Iron
(d) Iron sulphide
(e) Aluminium
(f) Iodine
(g) Carbon
(h) Carbon monoxide
(i) Sulphur powder
Ans. (a) Chlorine gas
(c) Iron
(e) Aluminium
(f) Iodine
(g) Carbon
(z) Sulphur powder
are elements and not compounds.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q.1. Fractional distillation is suitable for separation of miscible liquids with a boiling point difference of about 25 K or less. What part of fractional distillation apparatus makes it efficient and possess an advantage over a simple distillation process. Explain using a diagram.
Ans. Fractionating column packed with glass beads gives the effect of repeated distillation. It provides surface for vapours to come in contact with glass beads and lose energy so that they can condense easily and get distilled. The effectiveness increases with increase in length and number of glass beads in the fractionating column.
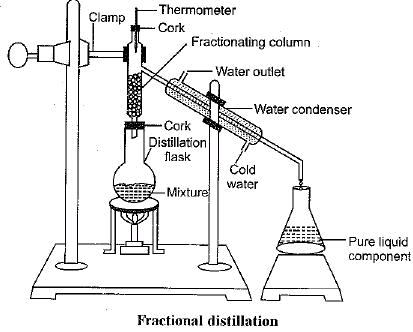 Q.2. (a) Under which category of mixtures will you classify alloys and why?
Q.2. (a) Under which category of mixtures will you classify alloys and why?
(b) A solution is always a liquid. Comment.
(c) Can a solution be heterogeneous?
Ans. (a) Homogeneous mixture because they have same composition throughout.
(b) No, solution may involve solids and gases also, e.g. alloys are solution of solid in solid. Air is solution of gases in gases.
(c) No, solution cannot be heterogeneous. It is homogeneous mixture of two or more substances.
Q.3. Iron filings and sulphur were mixed together and divided into two parts, ‘A’ and ‘B’. Part ‘A’ was heated strongly while Part ‘B’ was not heated. Dilute hydrochloric acid was added to both the parts and evolution of gas was seen in both the cases. How will you identify the gases evolved?
Ans. In A compound formed FeS will react with dilute acid to form H2S gas which has smell of rotten eggs and will turn lead acetate paper black.
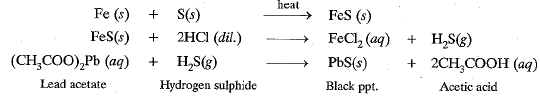 ‘B’ is a mixture of iron filings and sulphur powder. Iron filing reacts with dil. HCl to form H2(g) which bums with a ‘pop’ sound if burning matchstick is brought near it
‘B’ is a mixture of iron filings and sulphur powder. Iron filing reacts with dil. HCl to form H2(g) which bums with a ‘pop’ sound if burning matchstick is brought near it
Fe(s) + 2HCl (dil.)→ FeCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Q.4. A child wanted to separate the mixture of dyes constituting a sample of ink. He marked a line by the ink on the filter paper and placed the filter paper in a glass containing water as shown in figure. The filter paper was removed when the water moved near the top of the filter paper
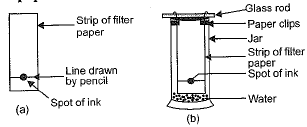 Separation of dyes in black ink using chromatography(i) What would you expect to see, if the ink contains three different coloured components ?(ii) Name the technique used by the child.
Separation of dyes in black ink using chromatography(i) What would you expect to see, if the ink contains three different coloured components ?(ii) Name the technique used by the child.
(iii) Suggest one more application of this technique
 Ans. (i) Three different coloured bands will be formed.
Ans. (i) Three different coloured bands will be formed.
(ii) Chromatography
(iii) To separate the pigments present in coloured flowers, ink and chlorophyll.
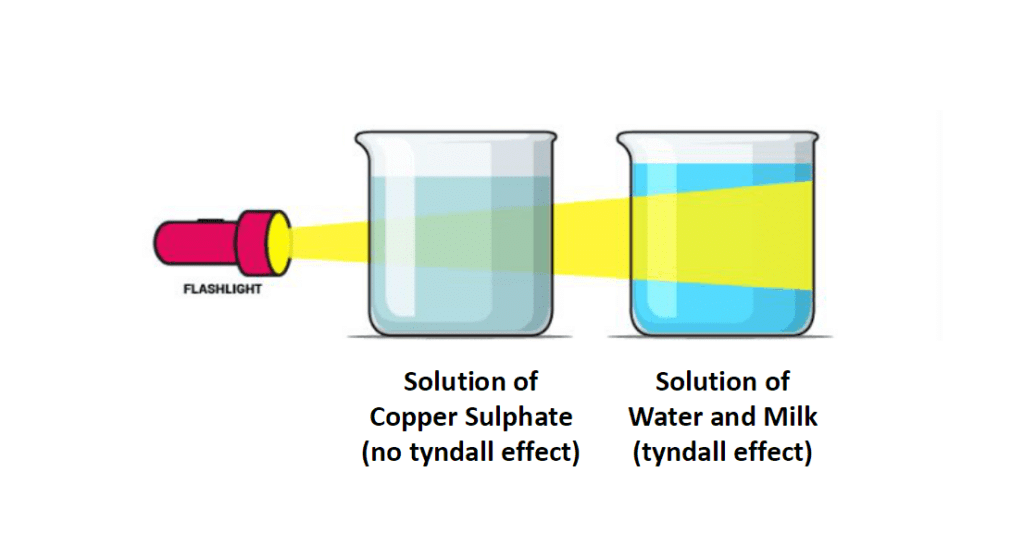
Q.5. A group of students took an old shoe box and covered it with a black paper from all sides.They fixed a source of light (a torch) at one end of the box by making a hole in it and made another hole on the other side to view the light. They placed a milk sample contained in a beaker/tumbler in the box as shown in the figure. They were amazed to see that milk taken in the tumbler was illuminated. They tried the same activity by taking a salt solution but found that light simply passed through it?
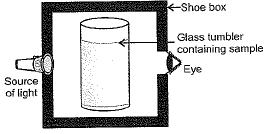 (a) Explain why the milk sample was illuminated. Name the phenomenon involved.(b) Same results were not observed with a salt solution. Explain.(c) Can you suggest two more solutions which would show the same effect as shown by the milk solution ?
(a) Explain why the milk sample was illuminated. Name the phenomenon involved.(b) Same results were not observed with a salt solution. Explain.(c) Can you suggest two more solutions which would show the same effect as shown by the milk solution ?
Ans. (a) Milk is colloidal solution and its particles scatter light and cause Tyndall effect, therefore it gets illuminated.
(b) It is because salt solution is true solution, particles are small and do not scatter light and do not show Tyndall effect.
(c) Blood, soap solution, egg-albumin in water, sulphur sol, etc
Q.6. Classify each of the following, as a physical or a chemical change. Give reasons.
(a) Drying of a shirt in the sun.
(b) Rising of hot air over a radiator.
(c) Burning of kerosene in a lantern.
(d) Change in the colour of black tea on adding lemon juice to it.
(e) Churning of milk cream to get butter.
Ans. (a) Physical change
(b) Physical change
(c) Chemical change
(d) Chemical change
(e) Physical change
Q.7. During an experiment the students were asked to prepare a 10% (Mass/Mass) solution of sugar in water. Ramesh dissolved 10 g of sugar in 100 g of water while Sarika prepared it by dissolving 10 g of sugar in water to make 100 g of the solution.
(a) Are the two solutions of the same concentration.
(b) Compare the mass % of the two solutions.
Ans. (a) No, two solutions do not have the same concentration.
(b) Mass percentage of solutions prepared by
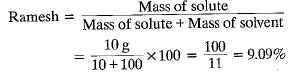 Mass percentage of solution prepared by Sarika
Mass percentage of solution prepared by Sarika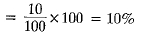 The solution prepared by Sarika has more percentage by mass than that of Ramesh.
The solution prepared by Sarika has more percentage by mass than that of Ramesh.
Q.8. You are provided with a mixture containing sand, iron filings, ammonium chloride and sodium chloride. Describe the procedures you would use to separate these constituents from the mixture?
Ans. (a) Remove iron filings with the help of magnet.
(b) Sand and ammonium chloride can be separated by sublimation. Ammonium chloride will get vapourised and change into vapours and on condensation will form NH4l(s), sand and sodium chloride will be left in china dish.
(c) Dissolve the sand and sodium chloride in water. Sodium chloride will dissolve. Filter the solution. Sand will be left as residue.
(d) Evaporate the filtrate to dryness to get sodium chloride back or use crystallization.
Q.9. Arun has prepared 0.01% (by mass) solution of sodium chloride in water. Which of the following correctly represents the composition of the solutions?
(a) 1.00 g of NaCI + 100 g of water
(b) 0.11 g of NaCI + 100 g of water
(c) 0.01 g of NaCI + 99.99 g of water
(d) 0.10 g of NaCI + 99.90 g of water
Ans. (c) 0.01 g of NaCI will be dissolved in 99.99 g of water so as to get 100 g of solution. It will have 0.01% by mass.
Q.10. Calculate the mass of sodium sulphate required to prepare its 20% (mass per cent) solution in 100 g of water?
Ans. % of solute
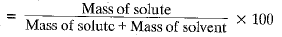
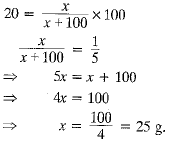
 Q.19. Can we separate alcohol dissolved in water by using a separating funnel? If yes, then describe the procedure. If not, explain.
Q.19. Can we separate alcohol dissolved in water by using a separating funnel? If yes, then describe the procedure. If not, explain.
 Q.2. (a) Under which category of mixtures will you classify alloys and why?
Q.2. (a) Under which category of mixtures will you classify alloys and why?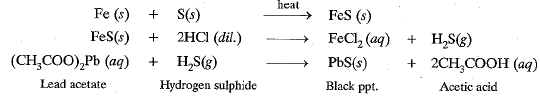 ‘B’ is a mixture of iron filings and sulphur powder. Iron filing reacts with dil. HCl to form H2(g) which bums with a ‘pop’ sound if burning matchstick is brought near it
‘B’ is a mixture of iron filings and sulphur powder. Iron filing reacts with dil. HCl to form H2(g) which bums with a ‘pop’ sound if burning matchstick is brought near it Separation of dyes in black ink using chromatography(i) What would you expect to see, if the ink contains three different coloured components ?(ii) Name the technique used by the child.
Separation of dyes in black ink using chromatography(i) What would you expect to see, if the ink contains three different coloured components ?(ii) Name the technique used by the child. Ans. (i) Three different coloured bands will be formed.
Ans. (i) Three different coloured bands will be formed. (a) Explain why the milk sample was illuminated. Name the phenomenon involved.(b) Same results were not observed with a salt solution. Explain.(c) Can you suggest two more solutions which would show the same effect as shown by the milk solution ?
(a) Explain why the milk sample was illuminated. Name the phenomenon involved.(b) Same results were not observed with a salt solution. Explain.(c) Can you suggest two more solutions which would show the same effect as shown by the milk solution ?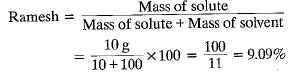 Mass percentage of solution prepared by Sarika
Mass percentage of solution prepared by Sarika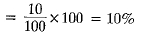 The solution prepared by Sarika has more percentage by mass than that of Ramesh.
The solution prepared by Sarika has more percentage by mass than that of Ramesh.