NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Getting to know plants | Science for Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
| Short Answer Questions |

|
| Long Answer Questions |

|
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: Which of the following combination of features would you observe in the grass?
(a) Parallel venation and fibrous root
(b) Parallel venation and taproot
(c) Reticulate venation and fibrous root
(d) Reticulate venation and taproot
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Parallel venation and fibrous roots are usually found in grass, maize, wheat etc.
In parallel venation, veins run parallel to one another in the leaf.
Fibrous roots are thin fibre like roots which arise in groups from the base of the stem.
Q2: Which of the following is the correct match between the characteristics of the stem and the category of a plant?
(a) The weak stem which cannot stand upright: Creeper
(b) Green tender stem: Shrub
(c) Thick, hard stem with branching near the base: Tree
(d) Thick, hard stem with branches high on the plant: Herb
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Herbs are plants which are small in size with a green and tender stem which cannot stand upright.
Shrubs are the medium-sized plants having a thick, hard stem with branches near the base. Trees are the tall plants having a thick, hard stem with branches high on the plant.
Q3: Which of the following is not the primary function of the stem?
(a) Conduction of water
(b) Photosynthesis
(c) Formation of branches
(d) Bears flowers and fruits
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
The primary function of the leaf is Photosynthesis.
The main function of stem: it holds the plant upright, forms branches, bear flowers and fruits, helps in transporting water from roots to the leaves.
Q4: Which of the following is not a correct match?
(a) Petiole: attaches the leaf to stem
(b) Lamina: green flat part of the leaf
(c) Margin: gives shape to the leaf
(d) Veins: transpiration
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Veins transport water, minerals and food in the leaf, and provide support to the leaf. In transpiration, water evaporates which is done by stomata of the leaves.
Q5: Read the following sentences about photosynthesis.
(i) Sunlight, carbon dioxide, chlorophyll and water are necessary.
(ii) Oxygen is absorbed.
(iii) Leaves carry out photosynthesis.
(iv) Proteins are made during photosynthesis.
Choose the correct pair of sentences that are true to photosynthesis.
(a) (iii) and (iv)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Oxygen is released during photosynthesis. Carbohydrates (glucose) are made during photosynthesis not proteins.
Q6: Which of the following terms constitute the female part of the flower?
(a) Sepals, petal and stamen
(b) Stigma, style and ovary
(c) Ovary, stamen and stigma
(d) Ovary, style and stamen
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
The female reproductive part of a flower is the Carpel (pistil). It consists of stigma, style and ovary.
Sepals and petals are accessory parts.
Stamens are male reproductive parts of a flower.
Very Short Answer Questions
Q7: Fill in the blanks.
(a) The small green leaves at the base of flowers are known as ______.
(b) The swollen basal part of the pistil is the ______which bears the ______.
(c) Stamen has two parts called ______and ______.
(d) The young unopened flower is termed as ______.
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) sepals
(b) ovary, ovules
(c) filament, anther
(d) bud.
Q8: Solve the riddles given below.
(a) “I have a green tender stem and I am much shorter than you. Who am I?”
(b) I come out first from the seed when it is soaked in water. I provide anchorage to plants. Who am I? Write another function that I perform.
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) I am a ‘Herb’. Herbs are small plants with green and tender stems.
(b) I am ‘Root’. The root comes out first from the seed when it is soaked in water.
Another function of the root is to absorb water and minerals from the soil.
Short Answer Questions
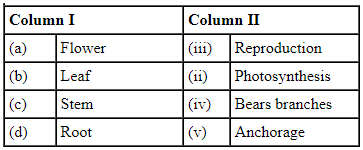
Q9: Match the parts of the plant given in column I with their function in column II.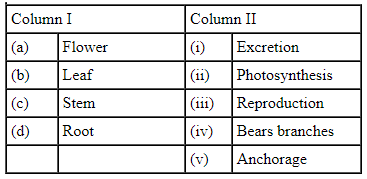
Q10: Boojho wanted to test the presence of starch in leaves. He performed the following steps.
(1) He took a leaf and boiled it in water.
(2) He placed the leaf in a petri dish and poured some iodine over it.
He did not get the expected result. Which step did he miss? Explain.
 View Answer
View Answer 
To remove the green colour of the leaf, firstly the leaf has to be boiled in the water next it has to be boiled in alcohol so that chlorophyll comes out.
Boojho missed the step of not boiling the leaf in the alcohol which removes the chlorophyll and therefore, he did not get the expected result (i.e. change in the colour of the leaf).
Q11: Will a leaf taken from a potted plant kept in a dark room for a few days turn blue-black when tested for starch? Give reasons for your answer.
 View Answer
View Answer 
No, it will not turn blue-black because all the starch present in the leaf would have been used up by the plant. And due to the non-availability of sunlight, no starch would be synthesized in the leaves.
Q12: Can the stem of a plant be compared with a street with two-way traffic? Give reason.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Yes, the stem of a plant can be compared with a street with two-way traffic. It is because in the stem, water and minerals move in an upward direction and food moves in a downward direction.
The stem transports water and minerals from the root to leaves and other parts of the plant (upward).
The food prepared by the leaves travels through the stem to different parts of the plant and roots (downward).
Long Answer Questions
Q13: Read the function of parts of a plant given below.
(a) Fixes plant to the soil
(b) Prepares starch
(c) Takes part in reproduction
(d) Supports branches and bears flowers
In the diagram given in Fig. 7.1, write the names of the parts whose functions you have just read at the appropriate space.
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) Fixes plant to the soil – Root
(b) Prepares starch – Leaf
(c) Takes part in reproduction – Flower
(d) Supports branches and bears flowers – Stem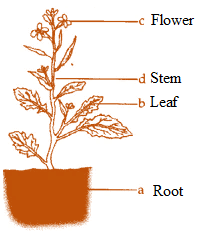
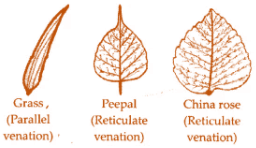
Q14: Draw the veins of leaves given in Fig 7.2 below and write the type of venation.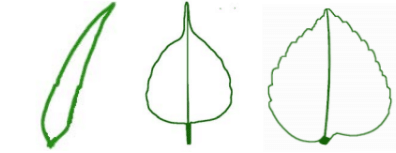 Grass, Peepal, China Rose
Grass, Peepal, China Rose
Q15: Observe Fig. 7.3 and attempt the questions that follow it.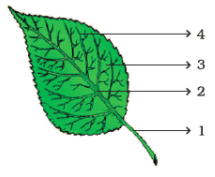 (a) Label the parts 1, 2, 3 and 4 in the diagram.
(a) Label the parts 1, 2, 3 and 4 in the diagram.
(b) What type of venation does the leaf have?
(c) What type of venation is seen in grass leaves?
 View Answer
View Answer 
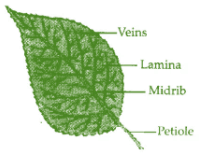
(a)
Part 1 – Petiole
Part 2 – Midrib
Part 3 – Lamina
Part 4 – Veins
(b) The leaf has reticulate venation. In reticulate venation, veins form a network-like appearance.
(c) In grass leaves, parallel venation is seen.
Q16: Observe the picture of an activity given as Fig. 7.4 carried out with leaves of plants and polythene bag. Now answer the following:
Now answer the following:
(a) Which process is demonstrated in the activity?
(b) When will this activity show better results on a bright sunny day or a cloudy day?
(c) What will you observe in the polythene bag after a few hours of setting up the activity?
(d) Mention any one precaution you must take while performing this activity.
 View Answer
View Answer 
(b) This activity shows better results on a bright sunny day because the rate of transpiration increases in the presence of strong sunlight.
(c) After a few hours, small drops of water will be seen inside the polythene cover.
(d) Precautions to be taken while performing the activity:
- The set-up must be airtight.
- The polythene bag should be dry.
- The twig or the leaves must be fresh with 10-12 leaves.
Q17: Identify the wrong statements and correct them.
(a) Anther is a part of the pistil.
(b) The visible parts of a bud are the petals.
(c) Lateral roots are present in a taproot.
(d) Leaves perform the function of transpiration only.
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) The statement is wrong
The anther is not part of the pistil. The anther is part of the stamen, which is the male part of a flower. The pistil is the female part of the flower and includes the stigma, style, and ovary.
(b) The statement is wrong
When you see a bud on a plant, the parts you see are called sepals, not petals. Sepals protect the flower before it opens. Petals are the colorful parts of the flower that are visible after the bud opens.
(c) The statement is correct.
Lateral roots can be found in a taproot system. A taproot is a big, main root that grows down into the soil. From this main root, smaller roots called lateral roots spread out to help the plant get more water and nutrients.
(d) The statement is wrong
Leaves perform various functions other than transpiration, such as gaseous exchange through tiny pores called stomata, photosynthesis etc.
Q18: Solve the crossword given in Fig. 7.5 as per the clues given below it.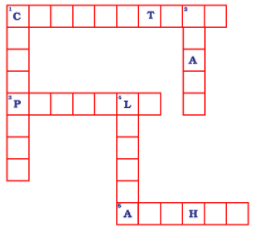
1. The term that describes the upward movement of water in a stem.
3. The part of the leaf which is attached to the stem.
5. This part is attached to the tip of the filament.
Down
1. Plants that are weak and spread on the ground.
2. Ovules are present in this part of the flower.
4. Is the broad part of a leaf?
 View Answer
View Answer 
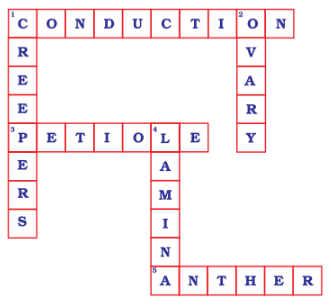
Across
1. Conduction
3. Petiole
5. Anther
Down
1. Creepers
2. Ovary
4. Lamina
Q19: Fill in the blanks with the terms that are listed below.
Anther, male, ovary, ovule, petals, pistil, stamen, filament.
Sepals, (a) ______, stamens and (b) ______ are the parts of a flower. Stamen is made up of (c) ______ and (d) ______ and it represents the (e) ______ part of the flower. The female part of the flower is called the (f) ______. The basal, swollen part of the pistil is called the (g) ______ which contains the (h) ______.
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) petals
(b) pistil
(c) anther
(d) filament
(e) male
(f) pistil
(g) ovary
(h) ovules
|
69 videos|288 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Getting to know plants - Science for Class 6
| 1. What are the different parts of a plant and their functions? |  |
| 2. How do plants reproduce? |  |
| 3. What is photosynthesis and why is it important for plants? |  |
| 4. How do plants adapt to their environment? |  |
| 5. What role do flowers play in the life cycle of a plant? |  |