NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Geography Chapter 5 - Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
Q1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below:
(i) To which one of the following types of vegetation does rubber belong to?
(a) Tundra
(b) Tidal
(c) Himalayan
(d) Tropical Evergreen
Ans: (d) Tropical Evergreen
Rubber trees are typically found in tropical evergreen forests. These forests are characterized by high rainfall and consistent temperatures throughout the year, which are ideal conditions for rubber cultivation.
(ii) Cinchona trees are found in the areas of rainfall more than
(a) 100 cm
(b) 50 cm
(c) 70 cm
(d) less than 50 cm
Ans: (a) 100 cm
Cinchona trees, which are used for extracting quinine, thrive in areas with rainfall of more than 100 cm annually. They are typically found in tropical regions with abundant rainfall.
(iii) In which of the following state is the Simlipal bio-reserve located?
(a) Punjab
(b) Delhi
(c) Odisha
(d) West Bengal
Ans: (c) Odisha
The Simlipal Biosphere Reserve is located in the state of Odisha. It is known for its rich biodiversity and is an important protected area in eastern India.
(iv) Which one of the following bio-reserves of India is not included in the world network of bioreserve?
(a) Manas
(b) Nilgiri
(c) Gulf of Mannar
(d) Panna
Ans: (d) Panna
The Panna Biosphere Reserve is not included in the World Network of Biosphere Reserves. However, the Nilgiri, Gulf of Mannar, and Manas are part of this network.
Q2. Answer the following questions briefly.
(i) What is a bio-reserve? Give two examples.
Ans: Bio-reserves are the large areas where vegetation, wildlife and the environment are conserved to preserve the biological diversity. In totality, there are 18 bio-reserves in India. Examples include Sunderbans Bio-reserve in West Bengal and Nanda Devi Bio-reserve in Uttaranchal.
(ii) Name two animals having a habitat in tropical and montane type of vegetation.
Ans: The common animals found in the tropical forests are elephants and monkeys, and the common animals found in the montane forests are Kashmir stag and spotted deer.
Q3. Distinguish between
(i) Flora and Fauna
Ans: The word ‘flora’ is used to denote plants of a particular region or period and the species of animals are referred to as ‘fauna’.
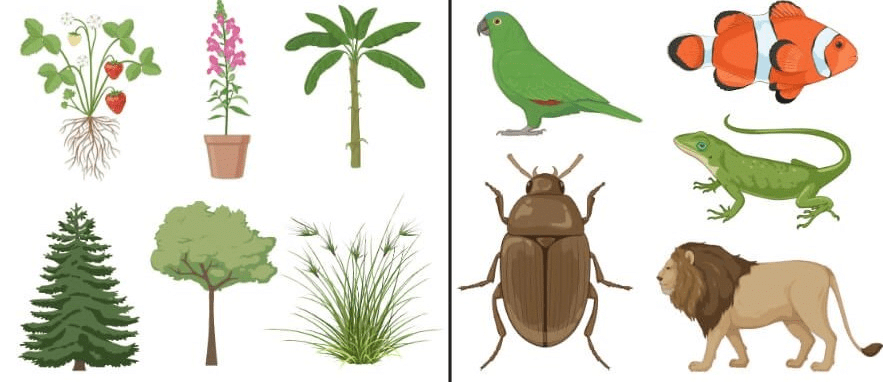 Flora and Fauna: Comparison
Flora and Fauna: Comparison
(ii) Tropical Evergreen and Deciduous Forests
Ans: Tropical Evergreen Forests:
- The rainfall is very heavy, over 200 cm of rain.
- Forests appear green all year round as the trees shed their leaves at different times of the year.
- Vegetation is luxuriant, multilayered, and of great variety.
- Commercially important trees are ebony, mahogany, rosewood, rubber, and cinchona.
- Trees are tall and have straight trunks.
Deciduous Forests:
- They are also known as Monsoon Forests.
- These are found where the rainfall is between 70 cm - 200 cm.
- Trees shed their leaves for about 6-8 weeks in the dry summer.
- These forests are divided into Dry and Wet Deciduous Forests.
- Wet Deciduous Forests are found in the northeast states, foothills of the Himalayas, Jharkhand, West Odisha, Chhattisgarh, and the eastern slopes of the Western Ghats. Important trees are bamboo, sal, shisham, Khair, Arjun, etc.
- Dry Deciduous Forests are found in the plains of Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and the rainier parts of the Deccan Plateau. Important trees are teak, sal, peepal, and neem. Trees have been cleared in some parts for cultivation and for grazing.
Q4. Name different types of vegetation found in India and describe the vegetation of high altitudes.
Ans: The different types of vegetation found in India are:
- Tropical Evergreen Forests
- Tropical Deciduous Forests
- Tropical Thorn Forests and Scrubs
- Mangrove Forests
In mountainous areas, the decrease in temperature with increasing altitude leads to the corresponding change in natural vegetation:
- The foothills of the Himalayas, the Shiwaliks, have tropical moist deciduous flora. Sal and bamboo are important trees.
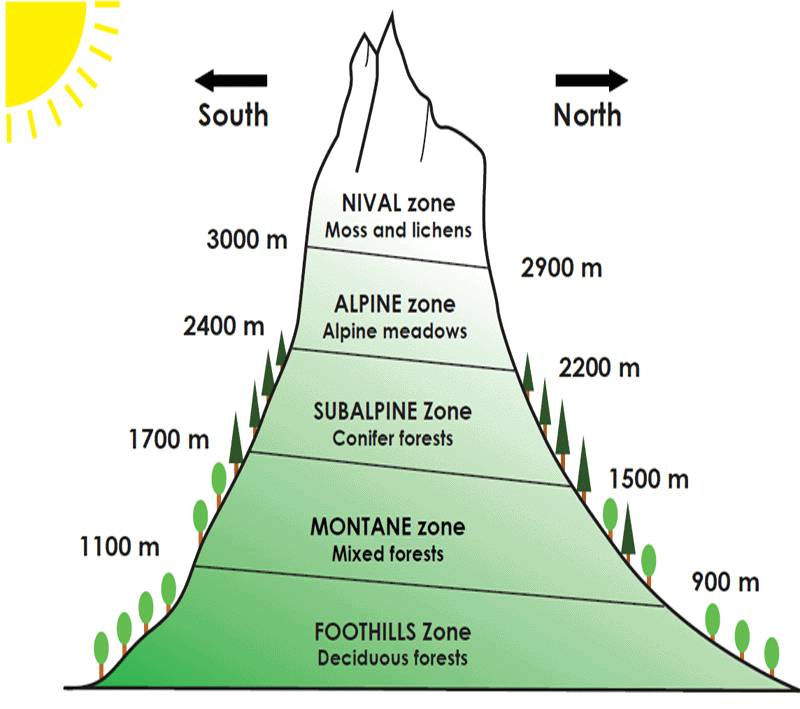
- They are followed by the wet hill forests. They lie between about 1,000 to 2,000 m. Important trees are oak, chestnut, ash, birch, etc.
- Between 1,500 and 3,300 m above sea level, there occur the well-known coniferous forests occur. Pine, deodar, silver fir, spruce, etc., are some dominant trees.
- Above the coniferous forests lie the alpine forests at an altitude of about 3,600 m. Important trees are silver fir, pine, birch, etc. Alpine vegetation is found at places over 3,600 m in height. The trees common to these are silver fir, junipers, pines, and birches.
- They get stunted as they approach the show line. Through shrubs and scrubs, they ultimately merge into the Alpine grasslands. Tundra vegetation is limited to lichens and mosses.
Q5. Quite a few species of plants and animals are endangered in India. Why?
Ans: Many plants and animals are endangered in India due to several reasons:
- Hunting of animals for commercial purposes.
- Pollution due to chemical and industrial waste, and acid deposits.
- Introduction of alien species.
- Reckless cutting of the forests to bring land under cultivation and inhabitation.
As a result of these activities, about 1300 plant species are endangered, and 20 plant species have become extinct. Quite a few animal species are also endangered.
Q6. Why has India a rich heritage of flora and fauna?
Ans: India has a rich heritage of flora and fauna due to the following reasons:
- India is a diverse country with various relief features (i.e. mountains, plateaus, plains, etc.) These regions consist of different types of vegetation that support different types of animals.
- There is the availability of different types of soil, which facilitates a base for different types of vegetation.
- There is variation in the climatic conditions of India (Temperature, humidity, etc.). It differs from north to south and east to west. Thus, supporting a large variety of flora and fauna.
- India has a monsoon type of climate where rainfall varies from 20 cm to 300 cm distributed throughout the year, supporting a large amount of flora and fauna.
- Variation in the duration of sunlight at different places due to differences in latitude and altitude.
Map Skills
Q. On an outline map of India, label the following.
(i) Areas of Evergreen Forests
(ii) Areas of Dry Deciduous Forests
(iii) Two national parks each in Northern, Southern, Eastern and Western parts of the Country
Ans: The outline of India’s map is given below with the labelling of the above-mentioned areas.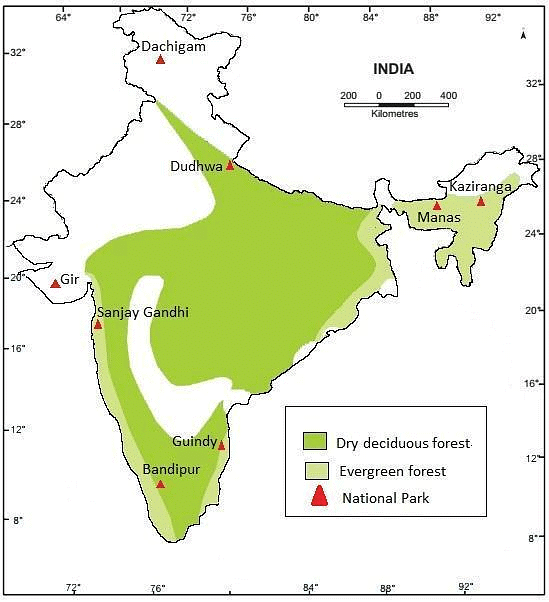
|
55 videos|637 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Geography Chapter 5 - Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
| 1. What are the main types of natural vegetation found in India? |  |
| 2. How does climate affect the distribution of natural vegetation in India? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of wildlife conservation in India? |  |
| 4. What are the threats to natural vegetation and wildlife in India? |  |
| 5. How can we promote the conservation of natural vegetation and wildlife? |  |

















