NCERT Solution (Part - 3) - Bills of Exchange | Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
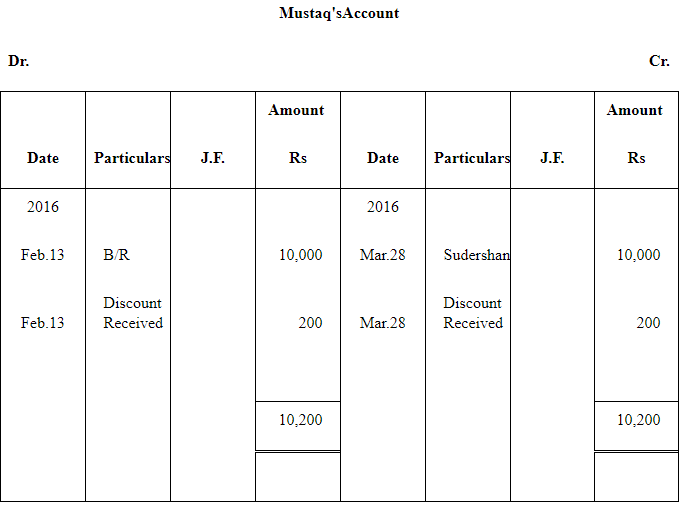
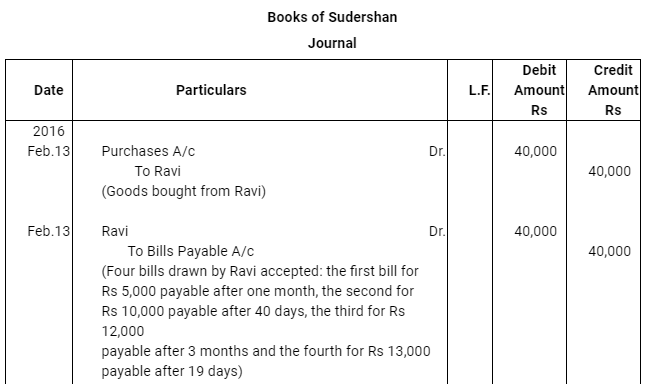
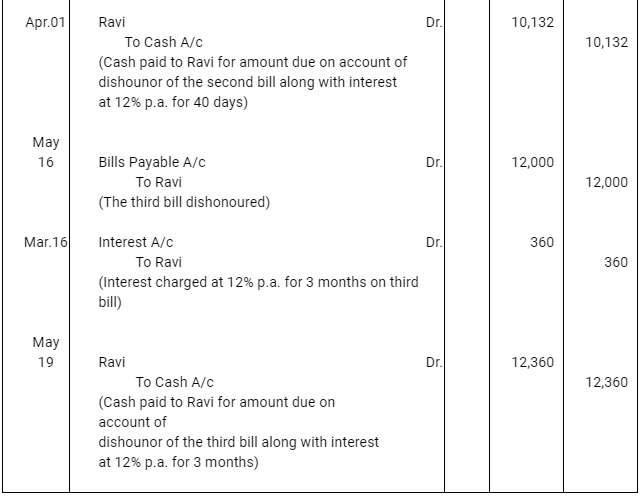
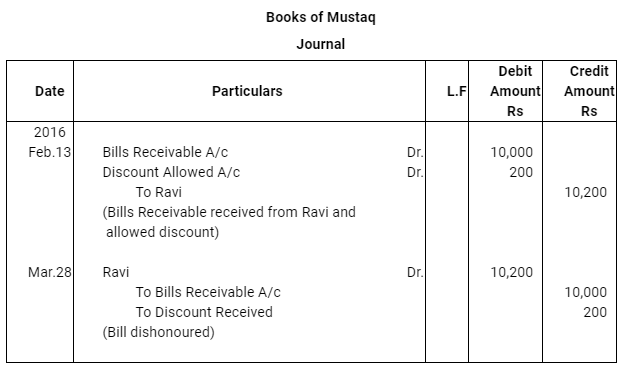
Q10 : Ravi sold goods for Rs 40,000 to Sudershan on Feb 13, 2016. He drew four bills of exchange upon Sudershan. The first bill was for Rs 5,000 payable after one month. The second bill was for Rs 10,000 payable after 40 days; the third bill was for Rs 12,000 payable after three months and fourth bill was for the balance amount payable after 19 days. Sudershan accepted all the bills and returned the same to Ravi. Ravi discounted the first bill with his bank at 6% p.a. He endorsed the second bill to his creditor Mustaq for the full settlement of a debt of Rs 10,200. The third bill was kept by Ravi with him till the date of maturity. Five days before the maturity of the fourth bill, Ravi sent the bill to his bank for collection. All the four bills were dishounoured by Sudarshan on maturity. Sudershan settled Ravi’s claim in cash three days after the dishonour of each bill along with interest @ 12% p.a. for the terms of the bills. You are requested to record the necessary journal entries in the books to Ravi, Sudershan, Mustaq and bank for the above transaction. Also prepare Sudershan’s account and Mustaq’s account in the books of Ravi.
Answer :
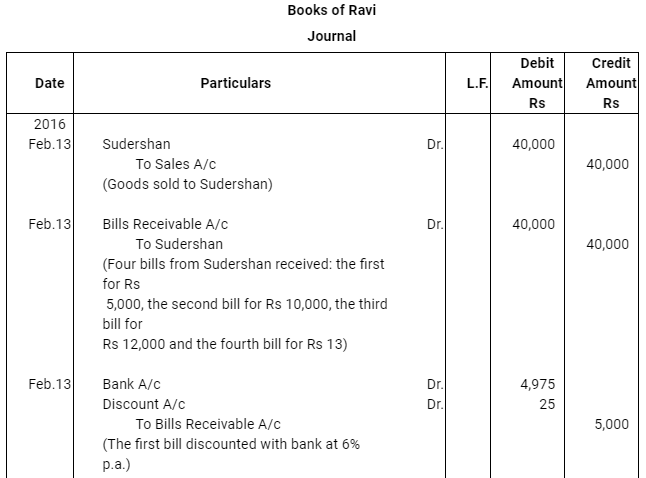


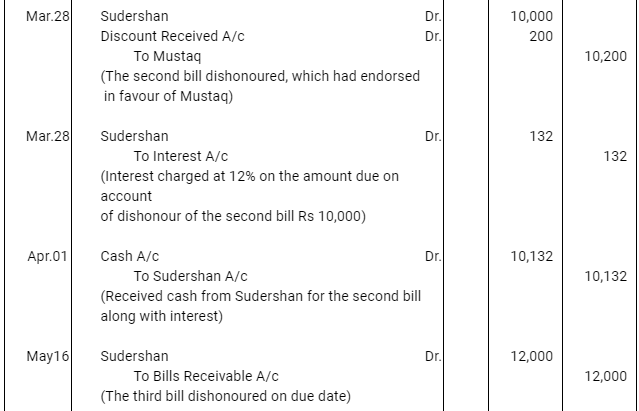
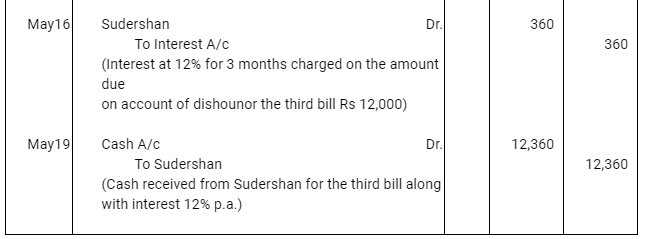
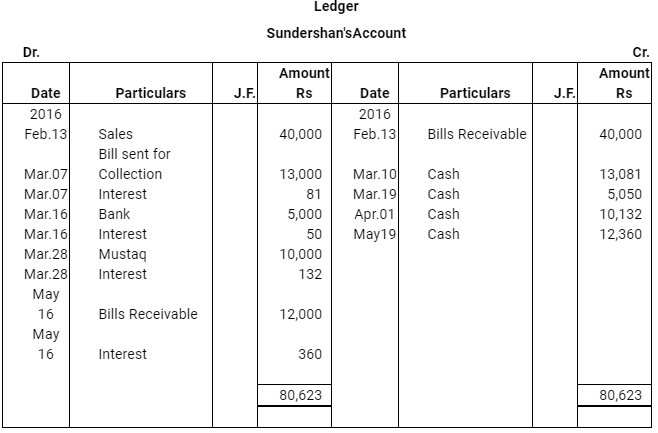


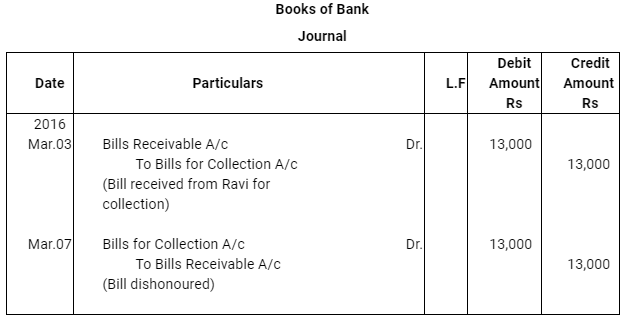
Q11 : On Jan 01, 2016 Neha sold goods for Rs 20,000 to Muskan and drew upon her a bill of exchange payable after two months. One month before the maturity of the bill Muskan approached Neha to accept the payment against the bill at a rebate @ 12% p.a. Neha agreed to the request of Muskan and Muskan retired the bill under the agreed rate of rebate. Journalise the above transaction in the books of Neha and Muskan.
Answer :
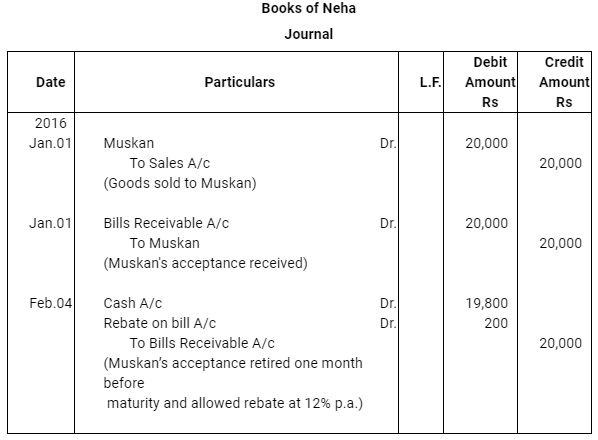
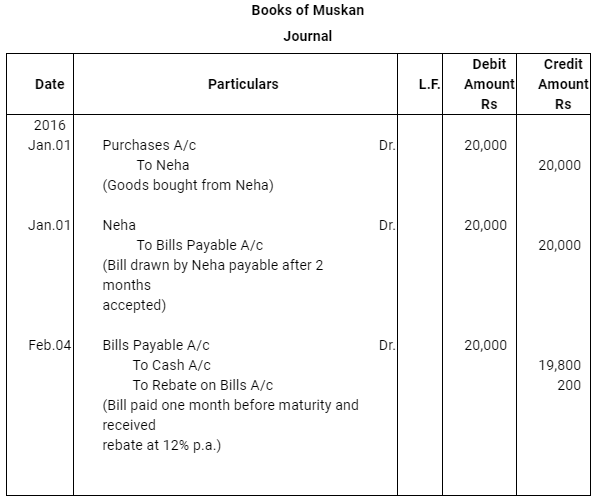
Q12 :On Jan 15, 2016 Raghu sold goods worth Rs 35,000 to Devendra and drew up to the latter three bills of exchanges. The first bill was for Rs 5,000 payable after one month, the second bill was for Rs 20,000 payable after three months and third bill for balance amount for 4 months. Raghu endorsed the first bill in favour of his creditor Dewan in full settlement of a debt of Rs 5,200. The second bill was discounted by Raghu @ 6 % p.a. and the third bill was retained by Raghu till the date of maturity. Devendra dishonoured the bill on maturity and the bank paid Rs 30 as noting charges. Four days before the maturity of the third bill Raghu, sent the same for collection to his bank. The third bill was also dishonoured by Devendra and the bank paid Rs 200 as noting charges. Five days after the dishonour of the bill Devendra paid the entire amount due to Raghu along with interest Rs 1,000 for this purpose Devendra obtained a short term loan from his bank. You are requested to record the necessary journal entries in the books of Raghu Devendra and Dewan and also prepare Devendra’s account in Raghu’s books and Raghu’s account in Devendra’s account.
Answer :
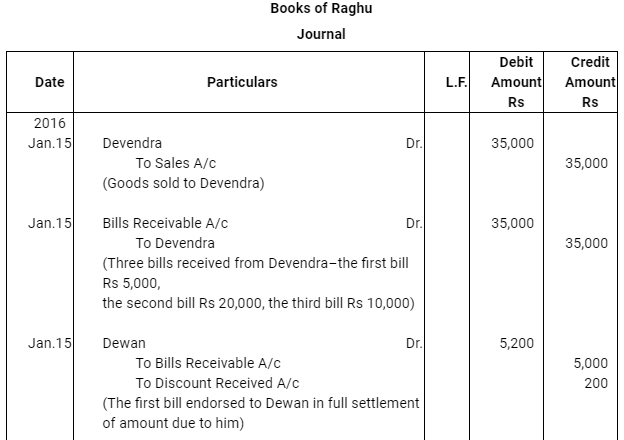
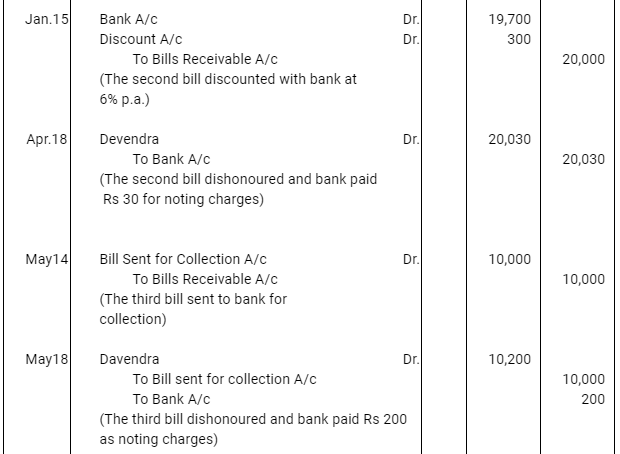
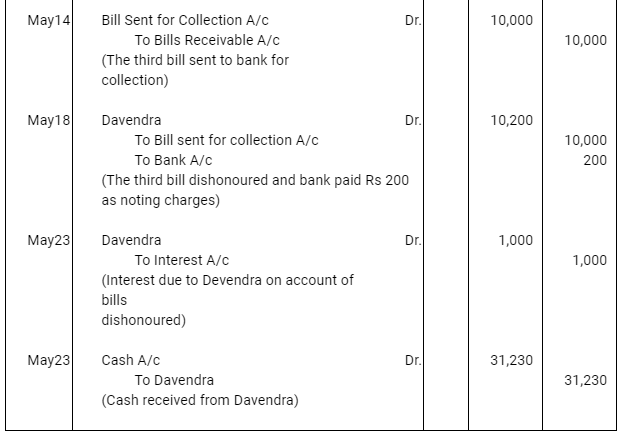
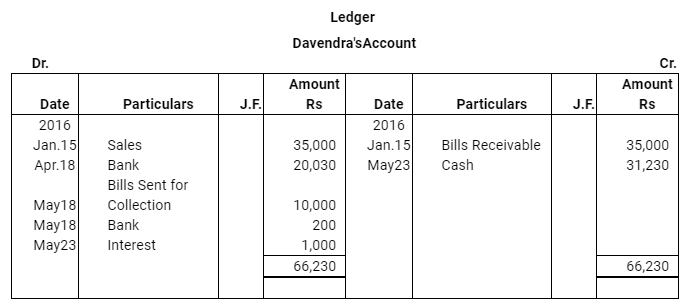
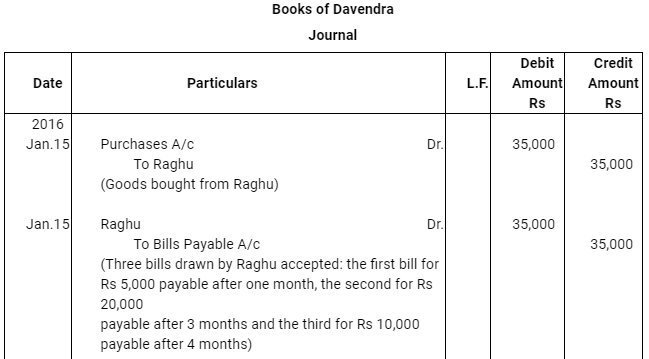
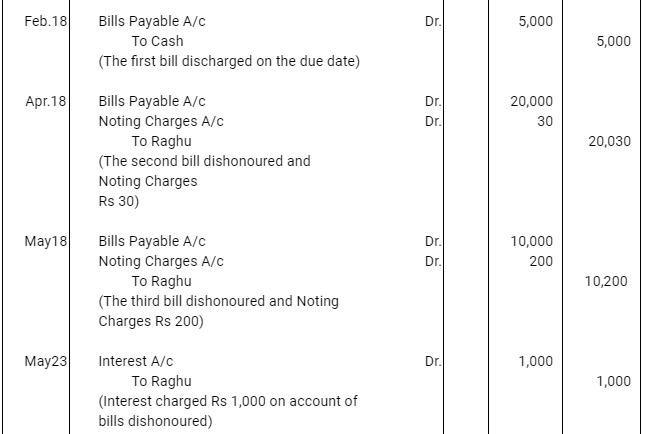
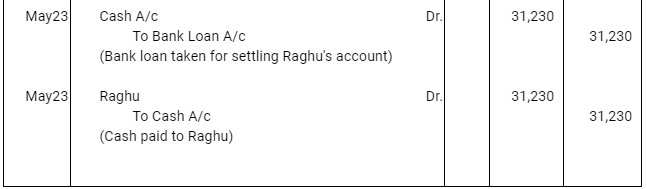
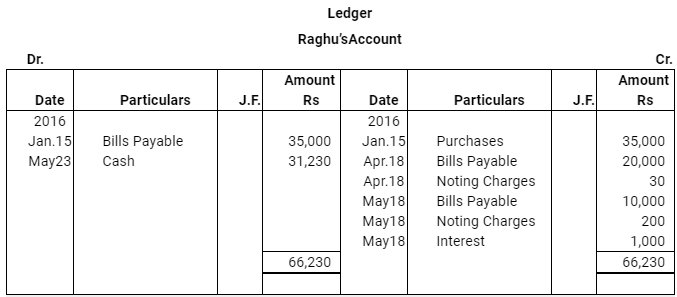
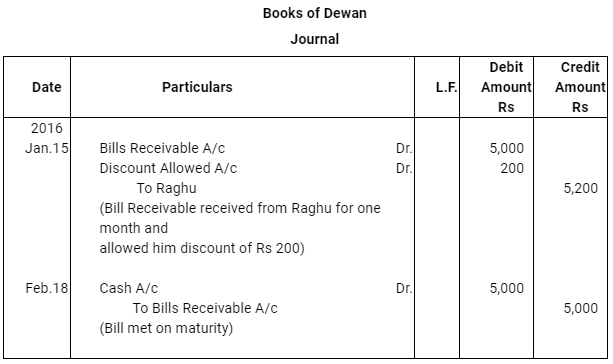
Note: In this question, there is no information regarding honour of the first bill of Rs 5,000. Therefore, it has been assumed that the first bill has been met on maturity.
Page No 336:
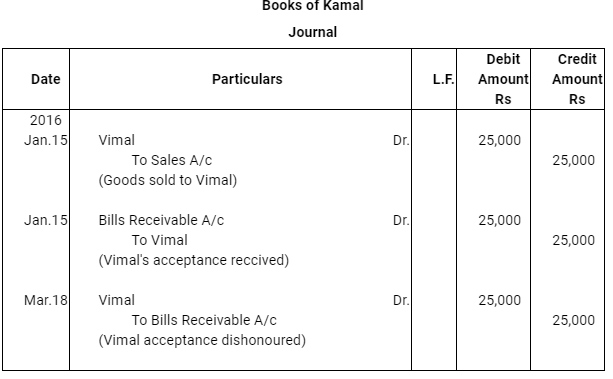
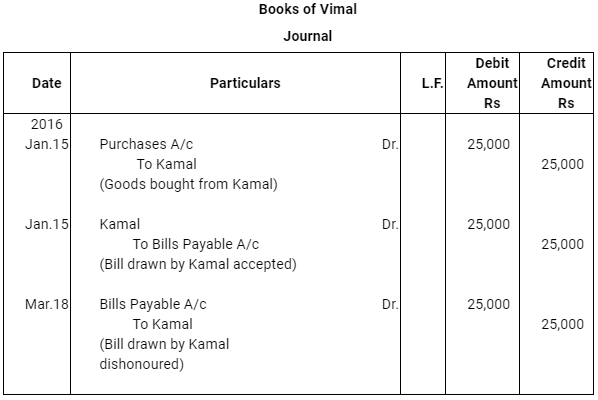
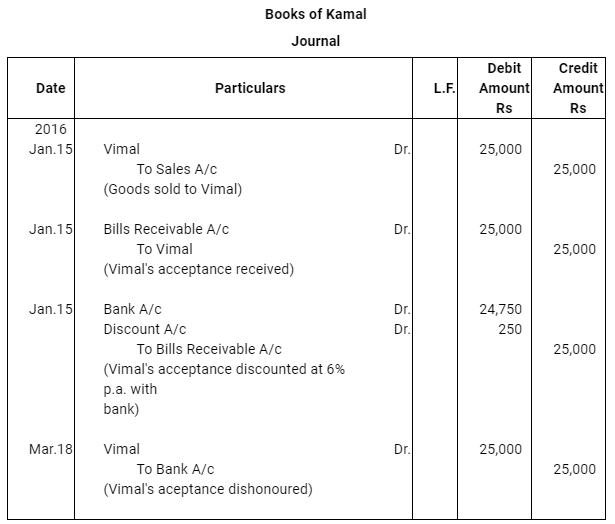
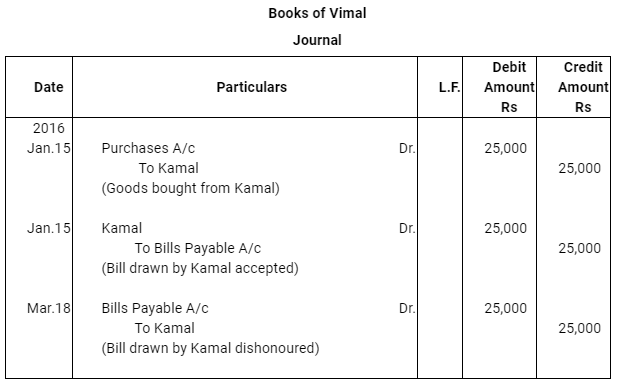
Q13 : Vimal purchased goods Rs 25,000 from Kamal on Jan 15, 2016 and accepted a bill of exchange drawn upon him by Kamal payable after two months. On the date of the maturity the bill was duly presented for payment. Vimal dishonoured the bill. record the necessary journal entries in the books of Kamal and Vimal when.
- The bill was retained by Kamal till the date of its maturity.
- The bill was immediately discounted by Kamal with his bank @ 6% p.a.
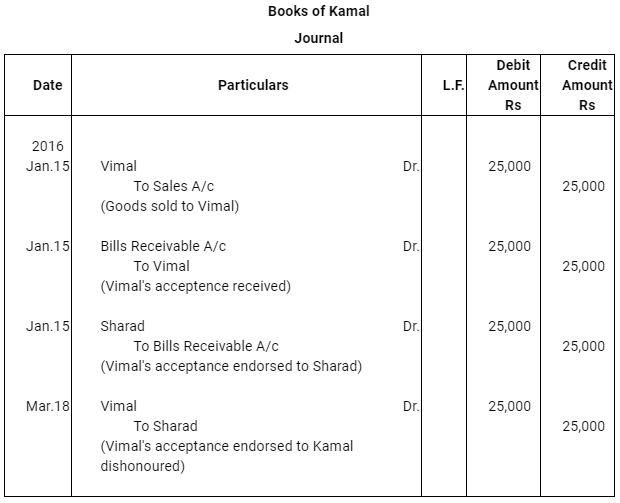
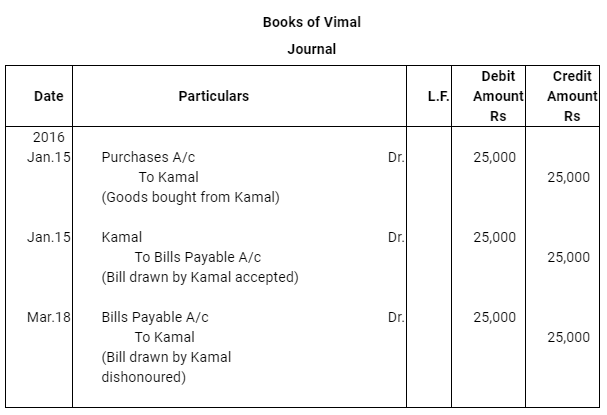
- The bill was endorsed by Kamal in favour of his creditor Sharad.
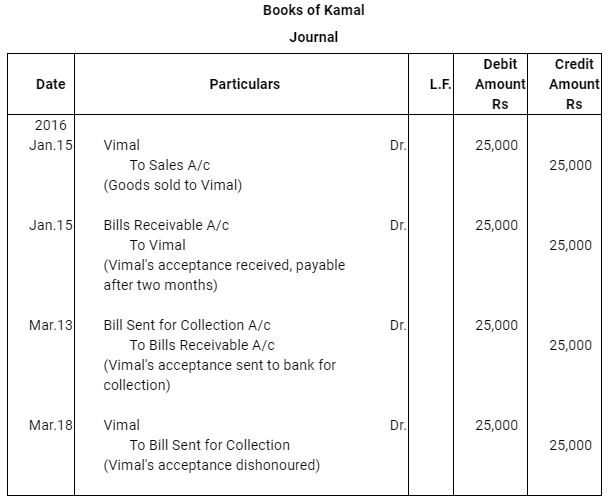
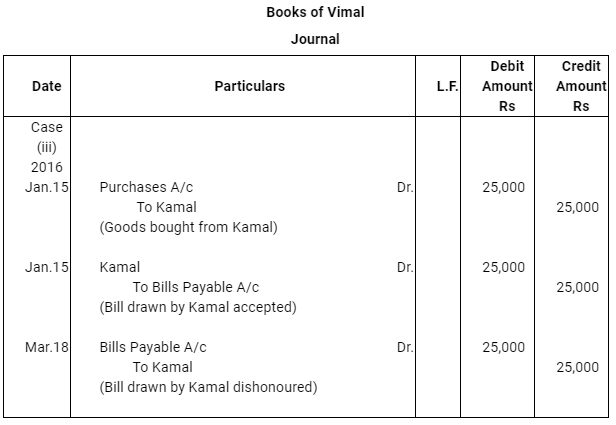
- Five days before its maturity the bill was sent by Kamal to his bank for collection.
Answer :
Case (i) : The bill was retained by Kamal till the date of its maturity
Case (ii) : The bill was immediately discounted by Kamal with his bank @ 6% p.a.
Case (iii) : The bill was endorsed by Kamal in favour of his creditor Sharad
Case (iv) : Five days before its maturity the bill was sent by Kamal to his bank for collection
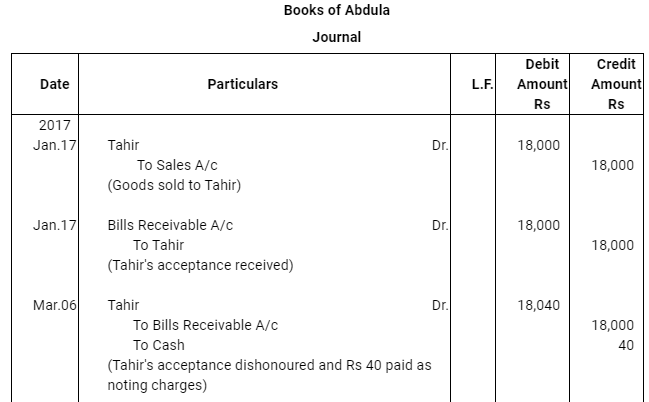
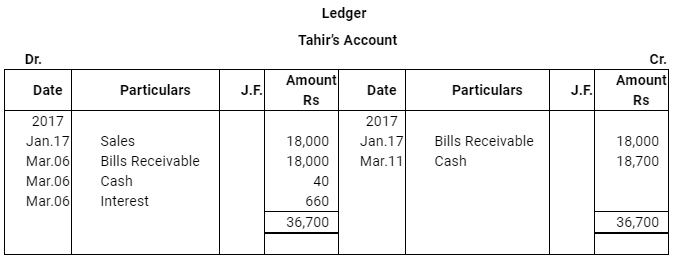
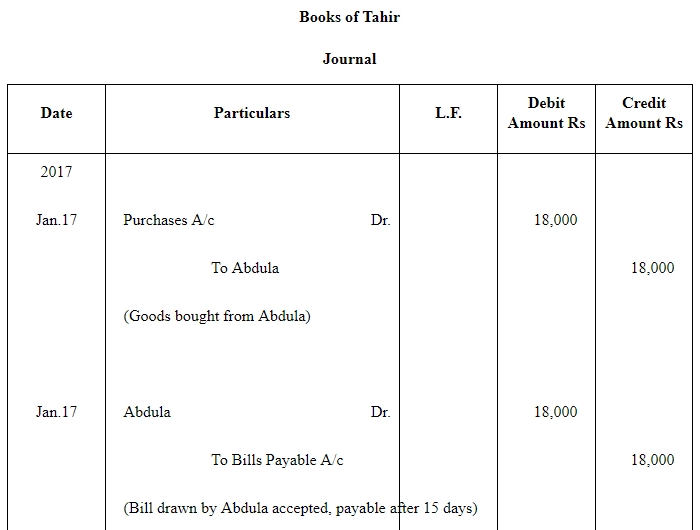
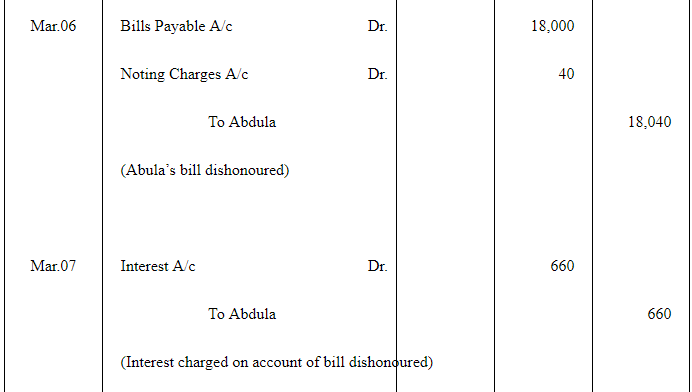
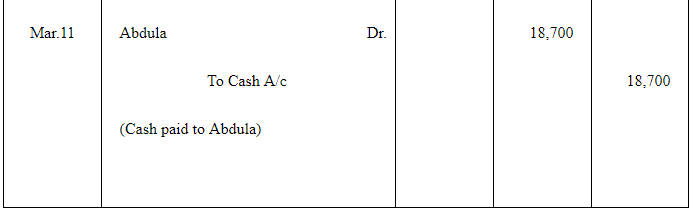
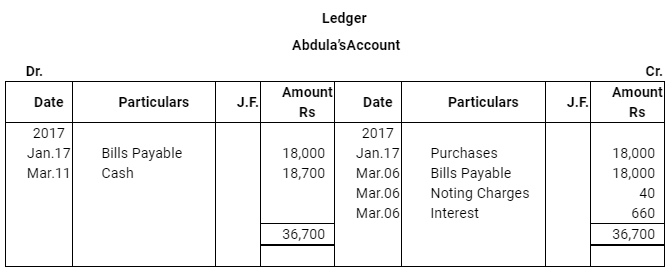
Q14 :Abdula sold goods to Tahir on Jan 17, 2017 for Rs 18,000. He drew a bill of exchange for the same amount on Tahir for 45 days. On the same date Tahir accepted the bill and returned it to Abdulla. On the due date Abdulla presented the bill to Tahir which was dishonoured. Abdulla paid Rs 40 as noting charges. Five days after the dishonour of his acceptance Tahir settled his debt by making a payment of Rs 18,700 including interest and noting charges. Record the necessary journal entries in the books of Abdulla and Tahir. Also prepare Tahir's account in the books of Abdulla and Abdulla's account in the books of Tahir.
Answer :

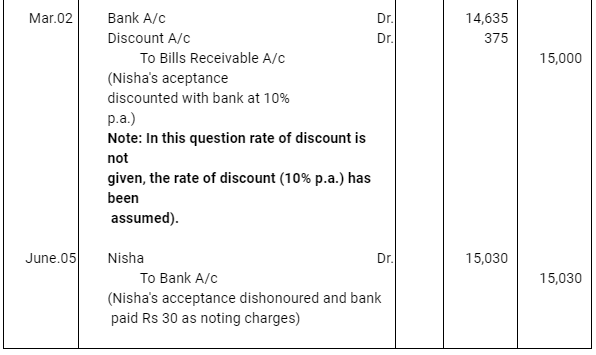
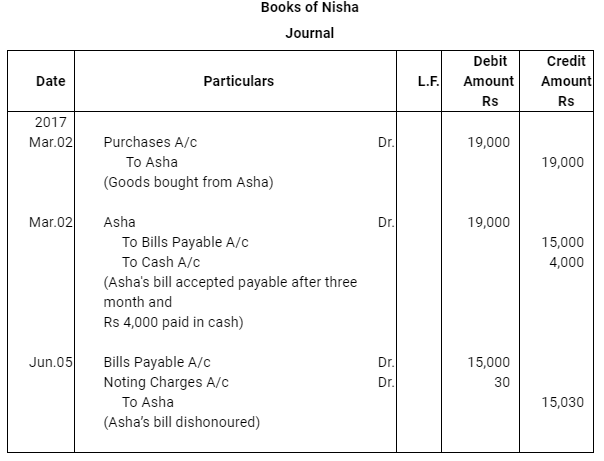
Question 15: Asha sold goods worth Rs 19,000 to Nisha on March 02, 2017. Rs 4,000 were paid by Nisha immediately and for the balance she accepted a bill of exchange drawn upon her by Asha payable after three months. Asha discounted the bill immediately with her bank. On the due date Nisha dishonoured the bill and the bank paid Rs 30 as noting charges. Record the necessary journal entries in the books of Asha and Nisha.
ANSWER: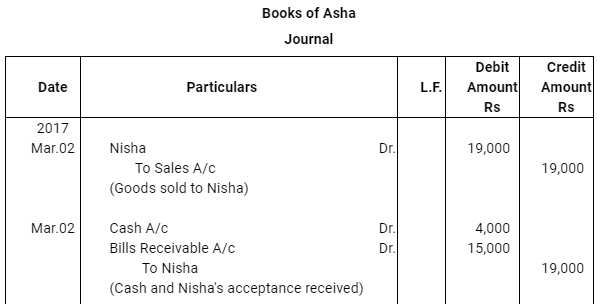
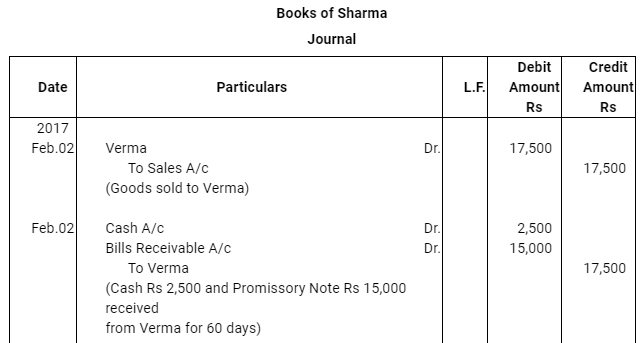
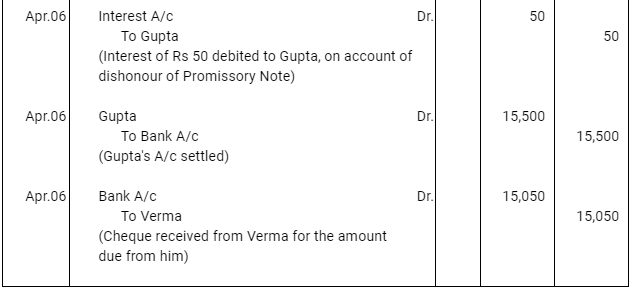
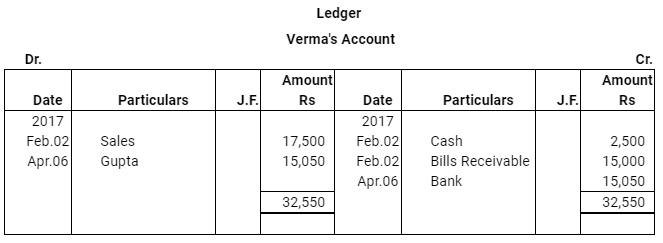
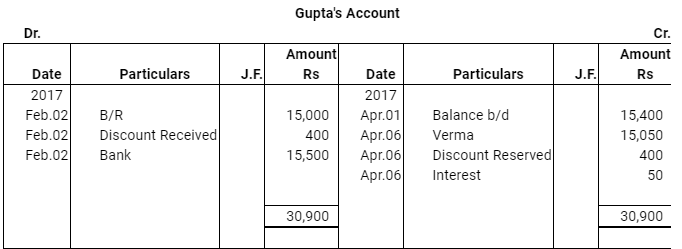
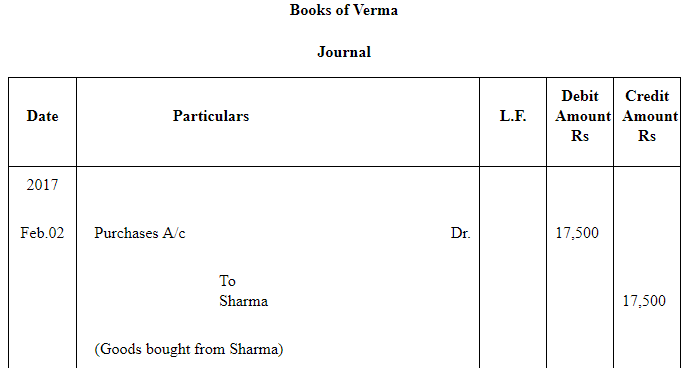
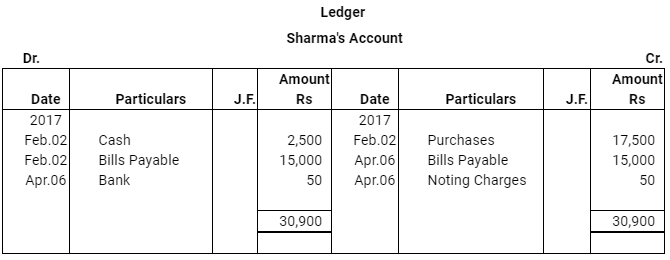
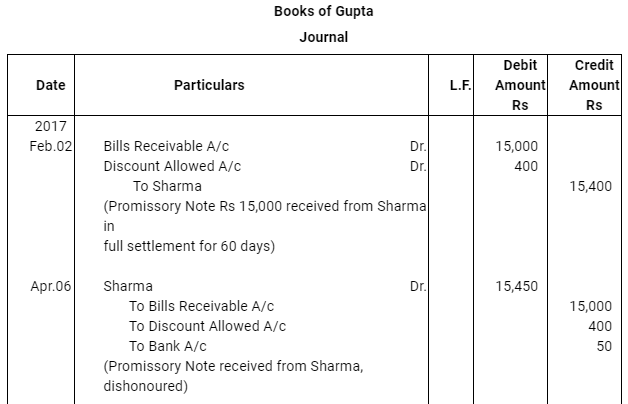
Question 16: On Feb. 02, 2017, Verma purchased from Sharma goods for Rs 17,500. Verma paid Rs 2,500 immediately and for the balance gave a promissory note to Sharma payable after 60 days. Sharma immediately endorsed the promissory note in favour of his creditor.
Gupta for the full settlement of a debt of Rs 15,400. On the due date of the bill Gupta presented the bill to Verma which the latter dishonoured and Gupta paid Rs 5,000 noting charges. On the same date Gupta informed Sharma about the dishonour of the bill. Sharma settled his debt to Gupta by cheque for Rs 15,500 which includes noting charges and interest. Verma settled Sharma.s claim by cheque for the same amount. Record the necessary journal entries is the books of Sharma, Gupta and Verma for the above transaction and prepare Verma.s and Gupta.s accounts in the books of Sharma. Sharma.s account in the books of Verma. And also Sharma.s account in the books of Gupta.
ANSWER:




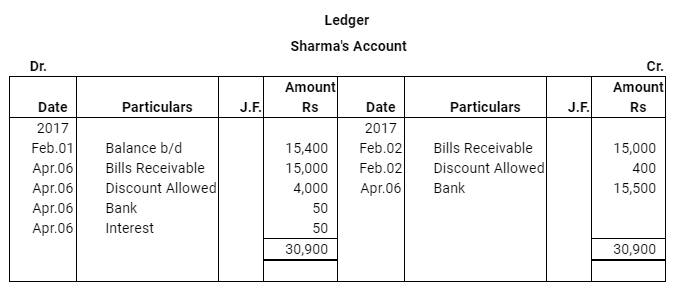
Question 17: Lilly sold goods to Mathew on 1.3.2017 for Rs 12,000 and drew upon Mathew a bill of exchange for the same amount payable after two months. Lilly immediately discounted the bill with her bank at 9% p.a. The maturity date of the bill was a non business day (holiday), therefore, Lilly had to present the bill as per the provisions of the Indian Instruments Act.1881. The bill was dishonoured by Mathew and Lilly paid Rs 45 as noting charges. Mathew settled the claim of Lilly five days after the dishonour of the bill by a cheque, which includes interest @ 12% for the term of the bill. Journalise the above transactions in the books of Lilly and Mathew and prepare Mathew’s account in the books of Lilly and Lilly’s account in the books of Mathew.
ANSWER:
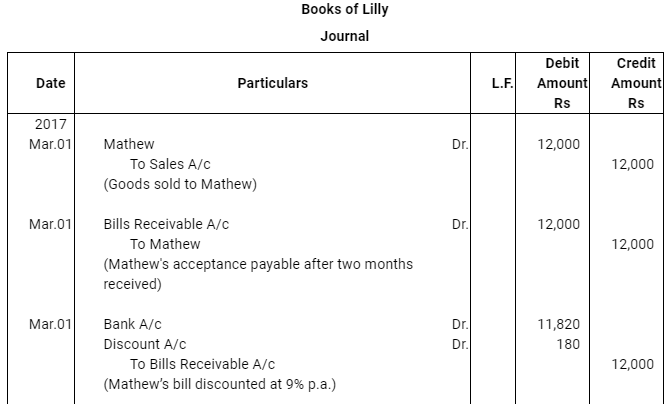

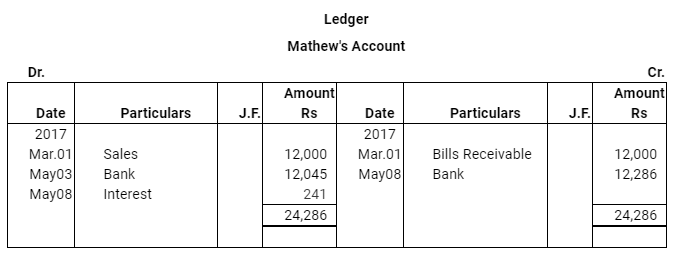
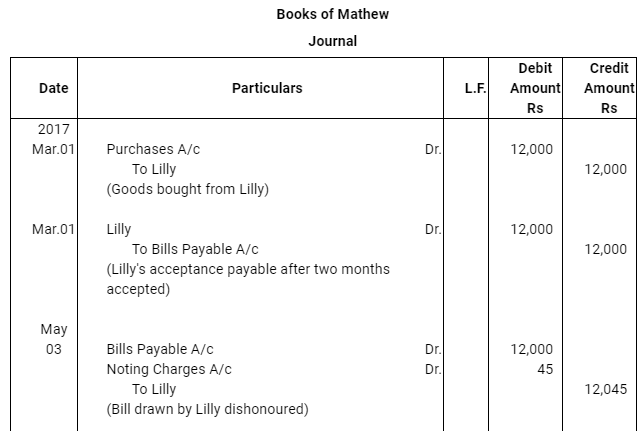

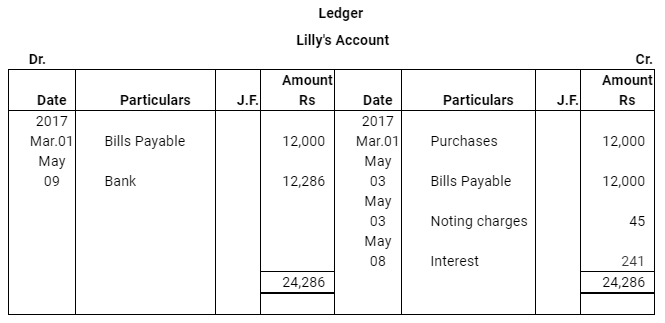
Note: In this question, there is a contradiction. As per the discounting rule–Bank is regarded as the holder of the bill. It is the bank who presents the bill for payment and also pays the noting charges on behalf of the drawer (Lilly). However, as per the question, Lilly, who is presenting, discounting the bill and also paying the noting charges. Thus, in the solution, we have assumed that it is bank and not Lilly who presents, discounts and pays the noting charges in case of dishonour of bill.
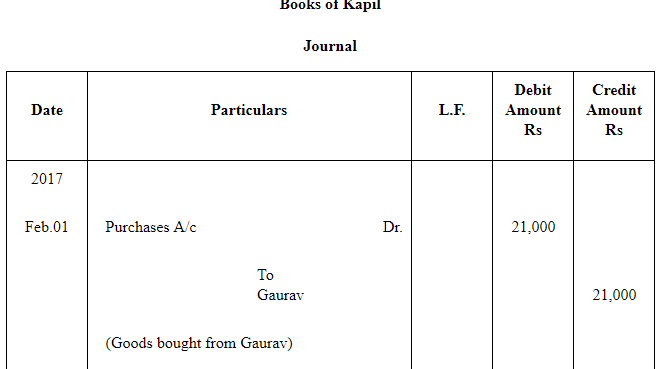
Question 18: Kapil purchased goods for Rs 21,000 from Gaurav on 1.2.2017 and accepted a bill of exchange drawn by Gaurav for the same amount. The bill was payable after one month. On 25.2.2017 Gaurav sent the bill to his bank for collection. The bill was duly presented by the bank. Kapil dishonoured the bill and the bank paid Rs 100 as noting charges. Record the necessary journal entries for the above transactions in the books of Kapil and Gourav.
ANSWER: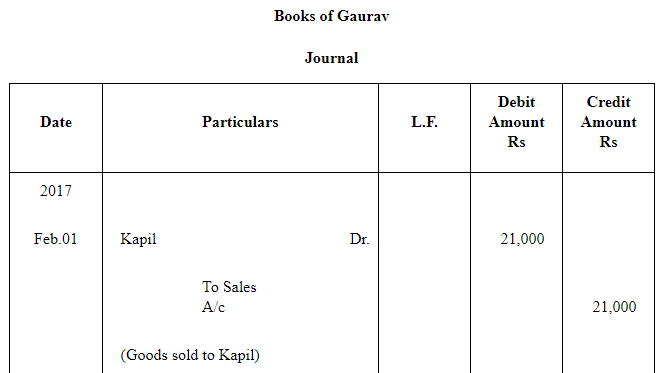



|
65 videos|230 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solution (Part - 3) - Bills of Exchange - Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What is a bill of exchange? |  |
| 2. What are the essential features of a bill of exchange? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between a bill of exchange and a promissory note? |  |
| 4. What are the advantages of using bills of exchange in business transactions? |  |
| 5. How are bills of exchange honored in case of non-payment? |  |

















