NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Civics Chapter 3 - Electoral Politics
Q1. Which of the following statements about the reasons for conducting elections are false?
(a) Elections enable people to judge the performance of the government.
(b) People select the representative of their choice in an election.
(c) Elections enable people to evaluate the performance of the judiciary.
(d) People can indicate which policies they prefer.
Ans: Statement (c).
This statement is incorrect because the judiciary works separately from elections. Elections let people choose their representatives and check how well the government is working. They also show what policies the elected leaders will follow. However, elections cannot judge how well the courts are doing.
Q2. Which of these is not a good reason to say that Indian elections are democratic?
(a) India has the largest number of voters in the world.
(b) India’s Election Commission is very powerful.
(c) In India, everyone above the age of 18 has a right to vote.
(d) In India, the losing parties accept the electoral verdict.
Ans: Statement (a).
Having the largest number of voters does not necessarily indicate that elections are democratic, whereas the other options reflect key aspects of a functioning democracy.
Q3. Match the following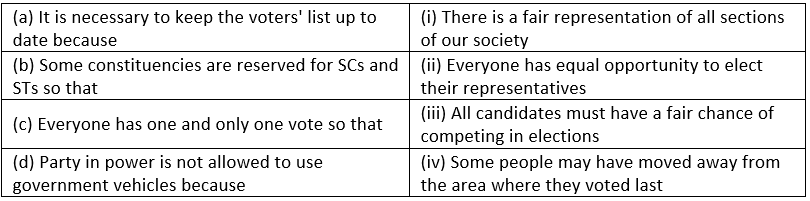
Ans: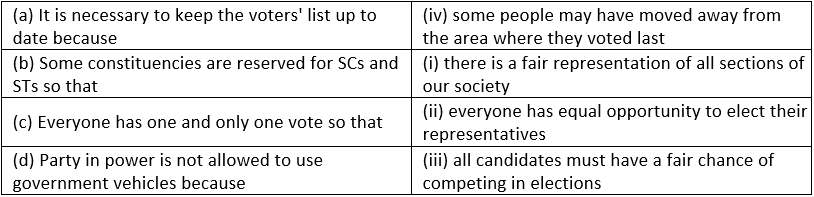
Q4. List all the different election-related activities mentioned in the chapter and arrange them in a time sequence, beginning with the first activity and ending with the last. Some of these activities are given below: releasing election manifestos; counting of votes; making of voters’ list; election campaign; declaration of election results; casting of votes; ordering of re-poll; announcing election schedule; filing nomination.
Ans: Election-related activities:
(i) Announcing the election schedule
(ii) Filing nominations
(iii) Making of voters’ list
(iv) Releasing election manifesto
(v) Election campaign
(vi) Casting of votes
(vii) Counting of votes
(viii) Declaration of election results
(ix) Ordering of re-poll
Q5. Surekha is an officer in-charge of ensuring free and fair elections in an assembly constituency in a state. Describe what should she focus on for each of the following stages of election:
(a) Election Campaign
(b) Polling Day
(c) Counting Day
Ans:
(a) Election Campaign
- For this, Surekha will have to focus on seeing that the candidates do not bribe or threaten the voters; appeal to them in the name of caste or religion; use government resources for the election campaign, do not spend excessive amounts of money in terms of expenditure or use a place of worship for campaigning.
- In addition to this, she will have to see that ministers do not use government vehicles for their campaigns and that they do not make major policy decisions after the elections are announced.
(b) Polling Day
- For this, Surekha will have to cross-check the voters' list and check their Voter IDs. She will also need to ensure that incidents of rigging and booth capturing do not take place.
(c) Counting Day
- For this, Surekha will have to see that the polling agents are present to ensure that counting is done properly.
Q6. The table below gives the proportion of different communities among the candidates who won elections to the US Congress. Compare these to the proportion of these communities in the population of the US. Based on this, would you suggest a system of reservations in the US Congress? If yes, why and for which communities? If no, why not?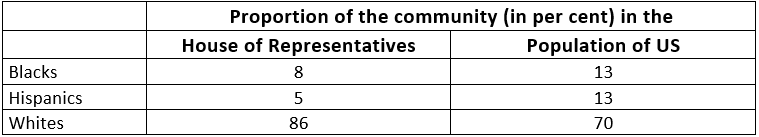
Ans:
Based on the table, a reservation for the Hispanic and Blacks community is a good idea. This is to make their representation in proportion to the percentage of their population, which is currently less for both the classes. On the other hand, Whites do not need any reservation because they have more seats (86% in the House of Representatives) compared to their population (70%).
Q7. Can we draw the following conclusions from the information given in this chapter? Give two facts to support your position for each of these.
(a) Election Commission of India does not have enough powers to conduct free and fair elections in the country.
(b) There is a high level of popular participation in the elections in our country.
(c) It is very easy for the party in power to win an election.
(d) Many reforms are needed to make our elections completely free and fair.
Ans:
(a) This is an incorrect conclusion.
- The Election Commission of India is powerful enough to conduct free and fair elections. It implements the code of conduct and punishes any candidate or party that violates it.
- While on election duty, government officials work under the EC and not the government.
(b) This is a correct conclusion.
- The facts support that voter turnout has increased over the past years.
- At the same time, election-related activities in the last few years have seen larger participation by the people.
(c) This is an incorrect conclusion.
- The ruling parties routinely lose elections.
- Candidates who are known to spend a lot of money often lose elections.
(d) This is a correct conclusion.
- Reforms are needed because candidates and parties with a lot of money enjoy an unfair advantage.
- Also, some candidates have criminal connections which they use to terrorise the voters and other candidates.
Q8. Chinappa was convicted for torturing his wife for dowry. Satbir was held guilty of practicing untouchability. The court did not allow either of them to contest elections. Does this decision go against the principles of democratic elections?
Ans: This decision does not go against the principles of democratic elections as both Chinappa and Satbir are criminals. Hence, they should be prevented from holding positions in the central or state assemblies.
Q9. Here are some reports of electoral malpractices from different parts of the world. Is there anything that these countries can learn from India to improve their elections? What would you suggest in each case?
(a) During an election in Nigeria, the officer in charge of counting votes deliberately increased the votes of one candidate and declared him elected. The court later found out that more than five lakh votes cast for one candidate were counted in favour of another.
(b) Just before elections in Fiji, a pamphlet was distributed warning voters that a vote for former Prime Minister, Mahendra Chaudhry will lead to bloodshed. This was a threat to voters of Indian origin.
(c) In the US, each state has its own method of voting, its own procedure of counting and its own authority for conducting elections. Authorities in the state of Florida took many controversial decisions that favoured Mr Bush in the presidential elections in 2000. But no one could change those decisions.
Ans:
(a) In this case, representatives of each candidate should be present to make sure that the votes are counted in a fair way.
(b) The election commission should set up an enquiry into the case and debar the candidate or party involved in distributing such pamphlets.
(c) There should be a single election commission that should be free from political influence and should be responsible for conducting elections throughout the country.
Q10. Here are some reports of malpractices in the Indian elections. Identify what the problem in each case is. What should be done to correct the situation?
(a) Following the announcement of elections, the minister promised to provide financial aid to reopen the closed sugar mill.
(b) Opposition parties alleged that their statements and campaign was not given due attention in Doordarshan and All India Radio.
(c) An inquiry by the Election Commission showed that electoral rolls of a state contain the name of 20 lakh fake voters.
(d) The hoodlums of a political party were moving with guns, physically preventing supporters of other political parties to meet the voters and attacking meetings of other parties.
Ans:
(a)
- By promising financial aid to the sugar mill, the minister announced a policy decision.
- This is not right since policy decisions cannot be made after the elections are announced. The minister should not be allowed to contest the elections.
(b)
- By not giving the opposition party’s statements and campaign due attention in Doordarshan and All India Radio, the government gained an unfair advantage over the opposition.
- To counter this, the opposition should be given sufficient time on the national media.
(c)
- The presence of fake voters means that the elections were rigged by the authorities who prepared the electoral rolls.
- The election commission should supervise the preparation of fresh electoral rolls.
(d) By using hoodlums, the political party is terrorising its rivals. The election commission should order the arrest of the hoodlums and bar the party from the elections.
Q11. Ramesh was not in class when this chapter was being taught. He came the next day and repeated what he had heard from his father. Can you tell Ramesh what is wrong with these statements?
(a) Women always vote the way men tell them to. So what is the point of giving them the right to vote?
(b) Party politics creates tension in society. Elections should be decided by consensus, not by competition.
(c) Only graduates should be allowed to stand as candidates for elections.
Ans:
(a)
- The statement is wrong because the policy of secret ballot ensures that an individual can vote for whoever he/she wants.
- Women are fully capable of making decisions on their own and selecting the candidate they like.
(b)
- It is true that party politics creates tension in society, but it is wrong to say that elections should be decided by consensus.
- Competition in politics works out for the good of the people as politicians compete with each other in fulfilling their promises.
- They might not be honest, but they know that they need to work to be elected. Thus, even their selfish actions benefit people.
(c) Educational qualification is not required to understand the people’s needs and to represent their interests. Thus, it is not necessary for politicians to be graduates.
|
53 videos|437 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Civics Chapter 3 - Electoral Politics
| 1. What is electoral politics and why is it important in a democracy? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of elections held in India? |  |
| 3. How does the Election Commission of India ensure free and fair elections? |  |
| 4. What role do political parties play in electoral politics? |  |
| 5. What are the challenges faced in electoral politics in India? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|













