NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics Chapter 2 - People as Resource
Q1. What do you understand by ‘people as a resource’?
Ans:
People as a Resource:
- The term 'People as a resource' refers to how the population can be an asset rather than a liability.
- When equipped with knowledge, skills, and technology, people can effectively utilize nature to create valuable resources.
Role in Production Factors:
- Production of goods and services necessitates the presence of four factors: land, labor, physical capital, and human capital.
- Human capital, comprising knowledge and enterprise, integrates the other three factors to generate output.
- Thus, investments in education, training, and healthcare transform the population into an asset rather than a burden.
Q2. How is human resource different from other resources like land and physical capital
Ans: Human resources is different in the following ways:
- Land and other resources are fixed, limited and specified, whereas human resources can be nurtured through education and health.
- Human resources can change other resources, whereas others can not change or affect a human resource.
- Human resources can make use of land and physical capital, whereas land and physical capital can not become useful on their own.
Q3. What is the role of education in human capital formation?
Ans: The role of education in human capital formation is as follows:
Economic Asset: Education transforms individuals into valuable assets for the economy rather than burdens.
Enhanced Opportunities: Education helps people take advantage of job opportunities, which increases the country's income and promotes a variety of cultures. It also makes the government work better and more efficiently.
Increased Productivity: Educated individuals are more productive, delivering higher quality and quantity of output.
Health Benefits: Education promotes awareness of health and hygiene practices, leading to better overall health outcomes for the population.
Q4. What is the role of health in human capital formation?
Ans: The role of health in human capital formation is as follows:
- Improved Immunity: Good health strengthens the immune system, reducing the likelihood of illness and absenteeism.
- Increased Productivity: Healthier individuals demonstrate higher productivity and efficiency in their work tasks.
- Economic Growth: Improved healthcare results in a healthier population, enhancing human capital and overall productivity, which fuels economic growth.
- Quality of Life: Good health improves quality of life by enabling individuals to perform tasks efficiently, earn more, and make greater contributions to society.
Q5. What part does health play in the individual’s working life?
Ans: Health plays a very important role in human capital formation in the following ways:
- Improved Work Focus: Good health allows individuals to concentrate better on tasks, make decisions confidently, and complete work more quickly and accurately.
- Increased Work Capacity: Healthy individuals can work for longer periods without succumbing to illness or fatigue, enabling them to accomplish more tasks effectively.
- Reduced Absenteeism: Being healthy reduces the frequency of sickness, resulting in fewer missed days at work and greater reliability in attendance.
- Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity: Healthier individuals exhibit higher efficiency and productivity compared to those who are unhealthy, contributing positively to their work outcomes and overall performance.
Q6. What are the various activities undertaken in the primary sector, secondary sector and tertiary sector?
Ans: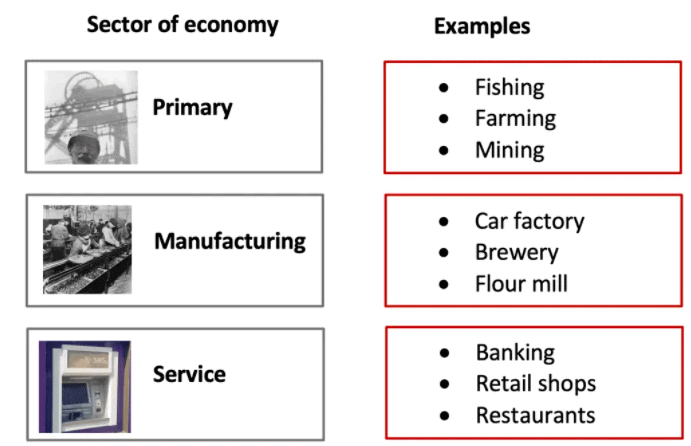
Primary Sector
- Comprises activities related to the extraction and production of natural resources.
- Agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, fishing, poultry farming, mining, and quarrying are the activities undertaken in this sector.
Secondary Sector
- Comprises activities related to the processing of natural resources.
- Manufacturing is included in this sector.
Tertiary Sector
- Comprises activities that provide support to the primary and secondary sectors through various services.
- Trade, transport, communication, banking, education, health, tourism, insurance, etc., are examples of tertiary activities.
Q7. What is the difference between economic activities and non-economic activities?
Ans: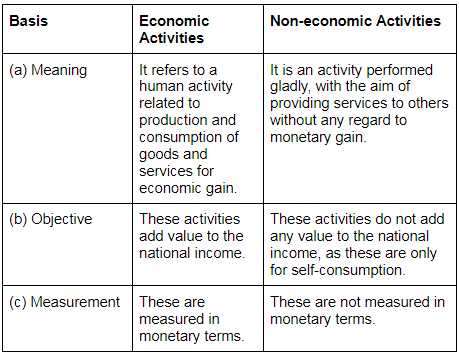
Q8. Why are women employed in low-paid work?
Ans:
- Gender Prejudices and Stereotypes: Gender biases, like the idea that women are not as good at physical work as men, continue to create unfairness in the workplace. These stereotypes hurt women and lead to lower pay.
- Earnings Based on Education and Skill: Women's earnings, like those of men, depend on their level of education and skills. Many women have less access to education and skill development, which results in lower wages compared to men.
- Job Insecurity and Benefits: Women frequently work in jobs without job security or benefits like maternity leave and childcare support. Balancing household responsibilities further impacts their ability to work full-time and earn equally with men.
Q9. How will you explain the term unemployment?
Ans: Unemployment is a situation in which people who are able and willing to work at the same wages cannot find jobs. An individual is termed as unemployed if he or she is part of the workforce of a country and is capable and willing to work for payment but is unable to do so.
Q10. What is the difference between disguised unemployment and seasonal unemployment?
Ans: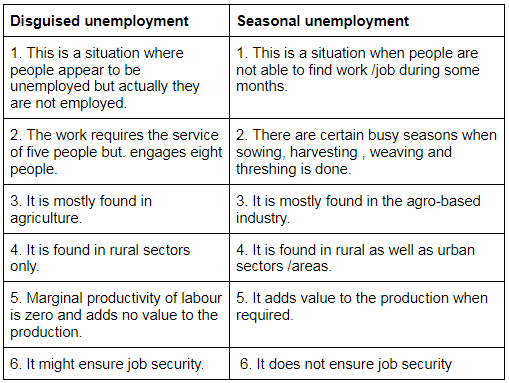
Q11. Why is educated unemployed, a peculiar problem in India?
Ans:
- Educated unemployment is becoming increasingly prevalent in India.
- Despite having qualifications such as matriculation, graduation, and even post-graduation, many young people struggle to find employment.
- The Indian education system allows individuals over 18 years old to enter the workforce without ensuring they possess the necessary skills demanded by employers.
- Consequently, a significant number of educated individuals lack essential skills and face unemployment.
- It is crucial for individuals to not only obtain academic degrees but also acquire practical skills that align with the requirements of the job market to secure employment opportunities.
Q12. In which field do you think India can build the maximum employment opportunity?
Ans:
- The employment sector in India is categorized into three main types: the primary sector, secondary sector, and tertiary sector.
- Agriculture constitutes the primary sector and employs a substantial portion of the population.
- Disguised unemployment is prevalent in the agricultural sector, where more people are employed than necessary for efficient operations.
- The secondary sector includes manufacturing industries, which have the capacity to absorb a significant number of workers.
- Expansion of industries within the secondary sector offers potential for generating employment opportunities on a large scale in India.
Hence, the manufacturing sector, a secondary activity, is the one where the maximum part of the population can be given employment due to the increase in the number of industries.
Q13. Can you suggest some measures in the education system to mitigate the problem of the educated unemployed?
Ans: Some measures that can be taken in the education system to mitigate the problem of educated unemployed are as follows:
- Promote Vocational Education: Encourage vocational education to ensure individuals are well-prepared for jobs, reducing difficulties in finding employment.
- Enhance Use of Information Technology: Increase the integration of information technology in education delivery to enhance learning outcomes and prepare students for modern work environments.
- Job-Oriented Education: Make education more job-oriented to align with industry needs and improve employability prospects for students.
- Expand Opportunities in Tertiary Sector: Create more employment opportunities in the tertiary sector to accommodate the growing number of educated individuals seeking jobs.
- Career-Oriented Secondary Education: Introduce career-oriented education at the secondary level to equip students with practical skills relevant to the current job market demands.
Q14. Can you imagine some village that initially had no job opportunities but later came up with many?
Ans: Rampur was a small village that initially depended on agriculture, which was also dependent on rainfall. Then electricity reached the village, and people could irrigate their fields and could grow 2 to 3 crops in a year and get work. Some people set up small-scale industries that could be run by electricity and provided employment to people. A school was established, and now the population started to become educated and as a result, they could seek employment in and outside the village. The village became prosperous and soon had better health, education, transport and job facilities.
Q15. Which capital would you consider the best - land, labour, physical capital, and human capital? Why?
Ans:
- Human capital is highly valued because unlike other resources, humans possess the ability to effectively utilize and leverage natural and physical resources for productive outcomes.
- Efficient use of human capital has not only made these nations prosperous but also positioned them as leaders in technology and industry, driving continuous economic advancement and development.
For Example:
- Countries like Japan have demonstrated that investing in human capital, particularly through education and health initiatives, can drive development even in the absence of natural resources.
- Despite lacking natural resources, these countries have become developed and wealthy by importing needed resources and maximizing their efficient use through advancements in technology and productivity.
- Emphasis on education and health has enhanced the skills and capabilities of their populations, enabling them to innovate and contribute significantly to economic growth.
|
52 videos|437 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics Chapter 2 - People as Resource
| 1. What is the concept of 'People as Resource'? |  |
| 2. How does education contribute to the development of human resources? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of human resources? |  |
| 4. Why is health considered an important aspect of human resource development? |  |
| 5. How can governments promote the development of human resources? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|


















