NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 - Physical Features of India
Q1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below.
(i) A landmass bounded by the sea on three sides is referred to as
(a) Coast
(b) Island
(c) Peninsula
(d) None of the above
Ans: (c) Peninsula
Peninsulas are typically surrounded by water on three sides, with the fourth side connected to a larger landmass. They can vary in size and shape. Some famous examples of peninsulas include the Iberian Peninsula (Spain and Portugal), the Italian Peninsula, and the Malay Peninsula.
 A Peninsula
A Peninsula
(ii) Mountain ranges in the eastern part of India forming its boundary with Myanmar are collectively called
(a) Himachal
(b) Uttarakhand
(c) Purvachal
(d) None of the above
Ans: (c) Purvachal
Purvachal is home to several mountain ranges, including the Patkai, Naga Hills, and Manipur Hills. These mountain ranges play a significant role in shaping the topography of the region and act as a natural boundary between India and Myanmar.
(iii) The western coastal strip, south of Goa is referred to as
(a) Coromandel
(b) Konkan
(c) Kannad
(d) Northern Circar
Ans: (c) Kannad
The Konkan region is located in the states of Maharashtra, Goa, and Karnataka. It is known for its beautiful beaches, lush greenery, and rich cultural heritage. The region is famous for its seafood, coconut-based cuisine, and traditional music and dance forms.
(iv) The highest peak in the Eastern Ghats is
(a) Anai Mudi
(b) Kanchenjunga
(c) Mahendragiri
(d) Khasi
Ans: (c) Mahendragiri
Mahendragiri is located in the Paralakhemundi region of the Gajapati district in Odisha, India. It stands at an elevation of approximately 1,501 meters (4,925 feet) above sea level.
Q2. Answer the following questions briefly.
(i) What is the bhabar?
Ans: Bhabar is a narrow belt containing pebbles instead of silt along the banks of the upper Himalayan rivers from the Indus River to the Teesta River.
(ii) Name the three major divisions of the Himalayas from north to south.
Ans:
(a) The Greater Himalayas or Himadri (Inner Himalayas)
(b) Himachal or Lesser Himalayas (Middle Himalayas)
(c) The Shiwaliks (Outer Himalayas)
(iii) Which plateau lies between the Aravali and the Vindhyan ranges?
Ans: The Malwa plateau lies between the Aravali and the Vindhyan ranges.
(iv) Name the island group of India having coral origin.
Ans: Lakshadweep islands are the island group having coral origin.
Q3. Distinguish between:
(i) Bhangar and Khadar
Ans: 
(ii) The Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats
Ans: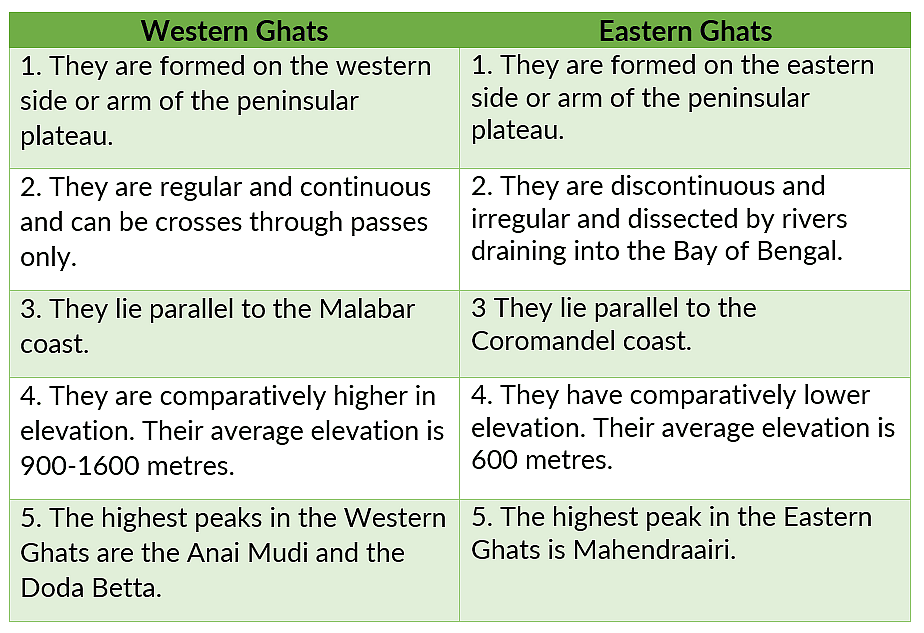
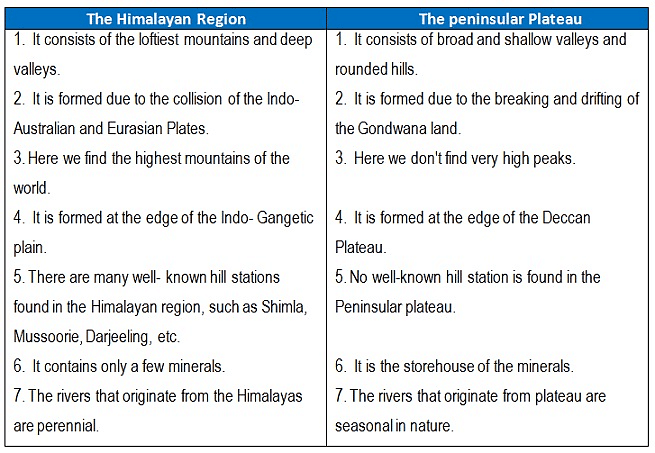
Q4. Which are the major physiographic divisions of India? Contrast the relief of the Himalayan region with that of the Peninsular plateau.
Ans:
The major physiographic divisions of India are:
(i) The Himalayan Mountains
(ii) The Northern Plains
(iii) The Peninsular Plateau
(iv) The Indian Desert
(v) The Coastal Plains
(vi) The Islands
Q5. Give an account of the Northern Plains of India.
Ans:
- The Northern Plains have been formed from the alluvium that the mountain rivers deposited here.
- It led to the soil turning fertile on the surface for growing a rich harvest of various crops. This also resulted in the development of the Indus River Valley Civilisation.
- The rich soil was further aided by a favourable climate and constant water supply from the rivers. Between the mouths of the Indus and the Ganga-Brahmaputra, the North Indian Plain covers a distance of 3200 km.
- The North Indian Plains have the Indus River system in the west and the Ganga- Brahmaputra river system in the east.
- The first includes Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas, and Satluj. The Indus flows into the Arabian Sea.
- The second includes Ganga, its tributaries, and the Brahmaputra, which combine as Meghna as they drain into the Bay of Bengal.
- They form the world’s largest and fastest-growing delta.
- The difference in relief has led the North Indian Plains to be divided into four zones:
(i) Bhabhar
(ii) Tarai
(iii) Bangar
(iv) Khadar
Q6. Write short notes on the following.
(i) The Indian Desert
Ans:
- The Indian desert lies to the west of the Aravali hills. It is an uneven sandy plain covered with sand dunes.
- Barchans (crescent-shaped sand dunes) cover a larger part of the desert. Near the Indo-Pakistan border, longitudinal sand dunes are more common.
- It has an arid climate with scarce vegetation and rainfall below 150 mm per year.
- Rivers/streams appear only during the rainy season and soon afterwards disappear in the sand. They do not have enough water to reach the sea. River Luni is the only large river in this area.

(ii) The Central Highlands
Ans:
- Central Highlands is the Part of the Peninsular plateau, north of the Narmada River. These highlands are made up of hard igneous and metamorphic rocks.
- It is bordered by the Aravali range to the northwest. The Central Highlands include the Malwa Plateau to the west and the Chotanagpur Plateau to the east.
- The Central Highlands are wider in the west and become narrow eastwards. The eastward extension of the Malwa plateau is locally called Bundelkhand and Baghelkhand. The Damodar River, a southern tributary of the Ganga River, drains the Chotanagpur plateau in the east.
(iii) The Island groups of India
Ans: India has two groups of islands, namely:
- Lakshadweep Islands
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands group
Lakshadweep Islands
- These island groups are located in the Arabian Sea, west of the Malabar coast of Kerala.
- These islands are of coral origin formed by the deposition of dead remains.
- The total area of the islands is 32 sq km. In Lakshadweep, the administrative headquarters is in Kavaratti Island.
- They have a wide diversity of flora and fauna.
Andaman and Nicobar Island
- These islands are located in the Bay of Bengal and are the raised portion of the submerged mountain ranges projecting out of the seawater.
- Large in size and are more numerous. Some of them are of volcanic origin.
Example: Barren Island is the only active volcano. - These islands are of strategic importance as it lies very close to south-east Asia.
- The capital city is Port Blair.
Map-Based Question
Q1. On an outline map of India show the following.
(a) Mountain and hill ranges — the Karakoram, the Zaskar, the Patkai Bum, the Jaintia, the Vindhya range, the Aravali and the Cardamom hills.
(b) Peaks— K2, Kanchenjunga, Nanga Parbat and Anai Mudi.
(c) Plateaus— Chotanagpur and Malwa
(d) The Indian Desert, Western Ghats, Lakshadweep Islands.
Ans: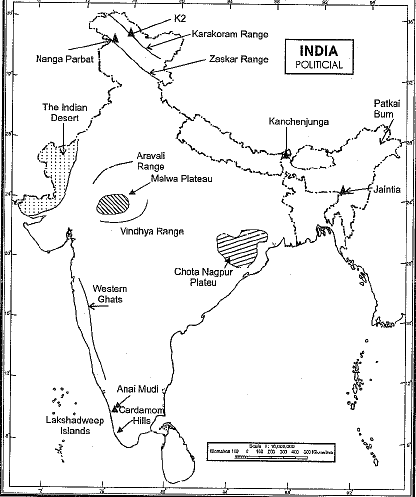
|
53 videos|437 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 - Physical Features of India
| 1. भारत की भौगोलिक विशेषताओं में मुख्य तत्व कौन-कौन से हैं ? |  |
| 2. भारत के प्रमुख नदियाँ कौन सी हैं और उनकी विशेषताएँ क्या हैं ? |  |
| 3. भारत के जलवायु के प्रकार क्या हैं ? |  |
| 4. भारत के प्रमुख पठारों का नाम बताइए ? |  |
| 5. भारत की भौगोलिक विशेषताओं का मानव जीवन पर क्या प्रभाव पड़ता है ? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|


















