Dual Nature of Radiation & Matter - 2 NCERT Solutions | Physics for Airmen Group X - Airforce X Y / Indian Navy SSR PDF Download
Ques 11.19:
What is the de Broglie wavelength of a nitrogen molecule in air at 300 K? Assume that the molecule is moving with the root-mean square speed of molecules at this temperature. (Atomic mass of nitrogen = 14.0076 u)
Ans: Temperature of the nitrogen molecule, T = 300 K
Atomic mass of nitrogen = 14.0076 u
Hence, mass of the nitrogen molecule, m = 2 × 14.0076 = 28.0152 u
But 1 u = 1.66 × 10−27 kg
∴m = 28.0152 ×1.66 × 10−27 kg
Planck’s constant, h = 6.63 × 10−34 Js
Boltzmann constant, k = 1.38 × 10−23 J K−1
We have the expression that relates mean kinetic energy  of the nitrogen molecule with the root mean square speed
of the nitrogen molecule with the root mean square speed  as:
as:
Hence, the de Broglie wavelength of the nitrogen molecule is given as:

Therefore, the de Broglie wavelength of the nitrogen molecule is 0.028 nm.
Ques 11.20:
(a) Estimate the speed with which electrons emitted from a heated emitter of an evacuated tube impinge on the collector maintained at a potential difference of 500 V with respect to the emitter. Ignore the small initial speeds of the electrons. The specific charge of the electron, i.e., its e/m is given to be 1.76 × 1011 C kg−1.
(b) Use the same formula you employ in (a) to obtain electron speed for an collector potential of 10 MV. Do you see what is wrong? In what way is the formula to be modified?
Ans: (a)Potential difference across the evacuated tube, V = 500 V
Specific charge of an electron, e/m = 1.76 × 1011 C kg−1
The speed of each emitted electron is given by the relation for kinetic energy as:

Therefore, the speed of each emitted electron is 
(b) Potential of the anode, V = 10 MV = 10 × 106 V
The speed of each electron is given as:

This result is wrong because nothing can move faster than light. In the above formula, the expression (mv2/2) for energy can only be used in the non-relativistic limit, i.e., for v << c.
For very high speed problems, relativistic equations must be considered for solving them. In the relativistic limit, the total energy is given as:
E = mc2
Where,
m = Relativistic mass
m0 = Mass of the particle at rest
Kinetic energy is given as:
K = mc2 − m0c2
Ques 11.21:
(a) A monoenergetic electron beam with electron speed of 5.20 × 106 m s−1 is subject to a magnetic field of 1.30 × 10−4 T normal to the beam velocity. What is the radius of the circle traced by the beam, given e/m for electron equals 1.76 × 1011 C kg−1.
(b) Is the formula you employ in (a) valid for calculating radius of the path of a 20 MeV electron beam? If not, in what way is it modified?
[Note: Exercises 11.20(b) and 11.21(b) take you to relativistic mechanics which is beyond the scope of this book. They have been inserted here simply to emphasise the point that the formulas you use in part (a) of the exercises are not valid at very high speeds or energies. See answers at the end to know what ‘very high speed or energy’ means.]
Ans: (a)Speed of an electron, v = 5.20 × 106 m/s
Magnetic field experienced by the electron, B = 1.30 × 10−4 T
Specific charge of an electron, e/m = 1.76 × 1011 C kg−1
Where,
e = Charge on the electron = 1.6 × 10−19 C
m = Mass of the electron = 9.1 × 10−31 kg−1
The force exerted on the electron is given as:

θ = Angle between the magnetic field and the beam velocity
The magnetic field is normal to the direction of beam.

The beam traces a circular path of radius, r. It is the magnetic field, due to its bending nature, that provides the centripetal force  for the beam.
for the beam.
Hence, equation (1) reduces to:

Therefore, the radius of the circular path is 22.7 cm.
(b) Energy of the electron beam, E = 20 MeV
The energy of the electron is given as:

This result is incorrect because nothing can move faster than light. In the above formula, the expression (mv2/2) for energy can only be used in the non-relativistic limit, i.e., for v << c
When very high speeds are concerned, the relativistic domain comes into consideration.
In the relativistic domain, mass is given as:

Where,
m0 = Mass of the particle at rest
Hence, the radius of the circular path is given as:

Ques 11.22:
An electron gun with its collector at a potential of 100 V fires out electrons in a spherical bulb containing hydrogen gas at low pressure (∼10−2 mm of Hg). A magnetic field of 2.83 × 10−4 T curves the path of the electrons in a circular orbit of radius 12.0 cm. (The path can be viewed because the gas ions in the path focus the beam by attracting electrons, and emitting light by electron capture; this method is known as the ‘fine beam tube’ method. Determine e/m from the data.
Ans: Potential of an anode, V = 100 V
Magnetic field experienced by the electrons, B = 2.83 × 10−4 T
Radius of the circular orbit r = 12.0 cm = 12.0 × 10−2 m
Mass of each electron = m
Charge on each electron = e
Velocity of each electron = v
The energy of each electron is equal to its kinetic energy, i.e.,
It is the magnetic field, due to its bending nature, that provides the centripetal force  for the beam. Hence, we can write:
for the beam. Hence, we can write:
Centripetal force = Magnetic force

Putting the value of v in equation (1), we get:

Therefore, the specific charge ratio (e/m) is 
Ques 11.23:
(a) An X-ray tube produces a continuous spectrum of radiation with its short wavelength end at 0.45 Å. What is the maximum energy of a photon in the radiation?
(b) From your answer to (a), guess what order of accelerating voltage (for electrons) is required in such a tube?
Ans: (a) Wavelength produced by an X-ray tube, 
Planck’s constant, h = 6.626 × 10−34 Js
Speed of light, c = 3 × 108 m/s
The maximum energy of a photon is given as:

Therefore, the maximum energy of an X-ray photon is 27.6 keV.
(b) Accelerating voltage provides energy to the electrons for producing X-rays. To get an X-ray of 27.6 keV, the incident electrons must possess at least 27.6 keV of kinetic electric energy. Hence, an accelerating voltage of the order of 30 keV is required for producing X-rays.
Ques 11.24:
In an accelerator experiment on high-energy collisions of electrons with positrons, a certain event is interpreted as annihilation of an electron-positron pair of total energy 10.2 BeV into two γ-rays of equal energy. What is the wavelength associated with each γ-ray? (1BeV = 109 eV)
Ans: Total energy of two γ-rays:
E = 10. 2 BeV
= 10.2 × 109 eV
= 10.2 × 109 × 1.6 × 10−10 J
Hence, the energy of each γ-ray:
Planck’s constant, 
Speed of light, 
Energy is related to wavelength as:

Therefore, the wavelength associated with each γ-ray is 
Ques 11.25:
Estimating the following two numbers should be interesting. The first number will tell you why radio engineers do not need to worry much about photons! The second number tells you why our eye can never ‘count photons’, even in barely detectable light.
(a) The number of photons emitted per second by a Medium wave transmitter of 10 kW power, emitting radiowaves of wavelength 500 m.
(b) The number of photons entering the pupil of our eye per second corresponding to the minimum intensity of white light that we humans can perceive (∼10−10 W m−2). Take the area of the pupil to be about 0.4 cm2, and the average frequency of white light to be about 6 × 1014 Hz.
Ans: (a) Power of the medium wave transmitter, P = 10 kW = 104 W = 104 J/s
Hence, energy emitted by the transmitter per second, E = 104
Wavelength of the radio wave, λ = 500 m
The energy of the wave is given as:

Where,
h = Planck’s constant = 6.6 × 10−34 Js
c = Speed of light = 3 × 108 m/s

Let n be the number of photons emitted by the transmitter.
∴ nE1 = E

The energy (E1) of a radio photon is very less, but the number of photons (n) emitted per second in a radio wave is very large.
The existence of a minimum quantum of energy can be ignored and the total energy of a radio wave can be treated as being continuous.
(b) Intensity of light perceived by the human eye, I = 10−10 W m−2
Area of a pupil, A = 0.4 cm2 = 0.4 × 10−4 m2
Frequency of white light, ν= 6 × 1014 Hz
The energy emitted by a photon is given as:
E = hν
Where,
h = Planck’s constant = 6.6 × 10−34 Js
∴E = 6.6 × 10−34 × 6 × 1014
= 3.96 × 10−19 J
Let n be the total number of photons falling per second, per unit area of the pupil.
The total energy per unit for n falling photons is given as:
E = n × 3.96 × 10−19 J s−1 m−2
The energy per unit area per second is the intensity of light.
∴E = I
n × 3.96 × 10−19 = 10−10
= 2.52 × 108 m2 s−1
The total number of photons entering the pupil per second is given as:
nA = n × A
= 2.52 × 108 × 0.4 × 10−4
= 1.008 × 104 s−1
This number is not as large as the one found in problem (a), but it is large enough for the human eye to never see the individual photons.
Ques 11.26:
Ultraviolet light of wavelength 2271 Å from a 100 W mercury source irradiates a photo-cell made of molybdenum metal. If the stopping potential is −1.3 V, estimate the work function of the metal. How would the photo-cell respond to a high intensity (∼105 W m−2) red light of wavelength 6328 Å produced by a He-Ne laser?
Ans: Wavelength of ultraviolet light, λ = 2271 Å = 2271 × 10−10 m
Stopping potential of the metal, V0 = 1.3 V
Planck’s constant, h = 6.6 × 10−34 J
Charge on an electron, e = 1.6 × 10−19 C
Work function of the metal = 
Frequency of light = ν
We have the photo-energy relation from the photoelectric effect as:
= hν − eV0

Let ν0 be the threshold frequency of the metal.


Wavelength of red light, = 6328 × 10−10 m
∴ Frequency of red light, 


Since ν0> νr, the photocell will not respond to the red light produced by the laser.
Ques 11.27:
Monochromatic radiation of wavelength 640.2 nm (1nm = 10−9 m) from a neon lamp irradiates photosensitive material made of caesium on tungsten. The stopping voltage is measured to be 0.54 V. The source is replaced by an iron source and its 427.2 nm line irradiates the same photo-cell. Predict the new stopping voltage.
Ans: Wavelength of the monochromatic radiation, λ = 640.2 nm
= 640.2 × 10−9 m
Stopping potential of the neon lamp, V0 = 0.54 V
Charge on an electron, e = 1.6 × 10−19 C
Planck’s constant, h = 6.6 × 10−34 Js
Let φo be the work function and ν be the frequency of emitted light.
We have the photo-energy relation from the photoelectric effect as:
eV0 = hν − φo

Wavelength of the radiation emitted from an iron source, λ' = 427.2 nm
= 427.2 × 10−9 m
Let V'0 be the new stopping potential. Hence, photo-energy is given as:

Hence, the new stopping potential is 1.50 eV.
Ques 11.28:
A mercury lamp is a convenient source for studying frequency dependence of photoelectric emission, since it gives a number of spectral lines ranging from the UV to the red end of the visible spectrum. In our experiment with rubidium photo-cell, the following lines from a mercury source were used:
λ1 = 3650 Å, λ2= 4047 Å, λ3= 4358 Å, λ4= 5461 Å, λ5= 6907 Å,
The stopping voltages, respectively, were measured to be:
V01 = 1.28 V, V02 = 0.95 V, V03 = 0.74 V, V04 = 0.16 V, V05 = 0 V
Determine the value of Planck’s constant h, the threshold frequency and work function for the material.
[Note: You will notice that to get h from the data, you will need to know e (which you can take to be 1.6 × 10−19 C). Experiments of this kind on Na, Li, K, etc. were performed by Millikan, who, using his own value of e (from the oil-drop experiment) confirmed Einstein’s photoelectric equation and at the same time gave an independent estimate of the value of h.]
Ans: Einstein’s photoelectric equation is given as:
eV0 = hν− φo

Where,
V0 = Stopping potential
h = Planck’s constant
e = Charge on an electron
ν = Frequency of radiation
φo = Work function of a material
It can be concluded from equation (1) that potential V0 is directly proportional to frequency ν.
Frequency is also given by the relation:

This relation can be used to obtain the frequencies of the various lines of the given wavelengths.

The given quantities can be listed in tabular form as:
Frequency x 1014 Hz | 8.219 | 7.412 | 6.884 | 5.493 | 4.343 |
Stopping potential V0 | 1.28 | 0.95 | 0.74 | 0.16 | 0 |
The following figure shows a graph between V and V0.

It can be observed that the obtained curve is a straight line. It intersects the ν-axis at 5 × 1014 Hz, which is the threshold frequency (ν0) of the material. Point D corresponds to a frequency less than the threshold frequency. Hence, there is no photoelectric emission for the λ5 line, and therefore, no stopping voltage is required to stop the current.
Slope of the straight line = 
From equation (1), the slope  can be written as:
can be written as:

The work function of the metal is given as:
φo = hν0
= 6.573 × 10−34 × 5 × 1014
= 3.286 × 10−19 J

= 2.054 eV
Ques 11.29:
The work function for the following metals is given:
Na: 2.75 eV; K: 2.30 eV; Mo: 4.17 eV; Ni: 5.15 eV. Which of these metals will not give photoelectric emission for a radiation of wavelength 3300 Å from a He-Cd laser placed 1 m away from the photocell? What happens if the laser is brought nearer and placed 50 cm away?
Ans: Mo and Ni will not show photoelectric emission in both cases
Wavelength for a radiation, λ = 3300 Å = 3300 × 10−10 m
Speed of light, c = 3 × 108 m/s
Planck’s constant, h = 6.6 × 10−34 Js
The energy of incident radiation is given as:
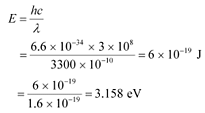
It can be observed that the energy of the incident radiation is greater than the work function of Na and K only. It is less for Mo and Ni. Hence, Mo and Ni will not show photoelectric emission.
If the source of light is brought near the photocells and placed 50 cm away from them, then the intensity of radiation will increase. This does not affect the energy of the radiation. Hence, the result will be the same as before. However, the photoelectrons emitted from Na and K will increase in proportion to intensity.
Ques 11.30:
Light of intensity 10−5 W m−2 falls on a sodium photo-cell of surface area 2 cm2. Assuming that the top 5 layers of sodium absorb the incident energy, estimate time required for photoelectric emission in the wave-picture of radiation. The work function for the metal is given to be about 2 eV. What is the implication of your answer?
Ans: Intensity of incident light, I = 10−5 W m−2
Surface area of a sodium photocell, A = 2 cm2 = 2 × 10−4 m2
Incident power of the light, P = I × A
= 10−5 × 2 × 10−4
= 2 × 10−9 W
Work function of the metal, φo = 2 eV
= 2 × 1.6 × 10−19
= 3.2 × 10−19 J
Number of layers of sodium that absorbs the incident energy, n = 5
We know that the effective atomic area of a sodium atom, Ae is 10−20 m2.
Hence, the number of conduction electrons in n layers is given as:
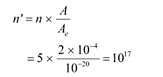
The incident power is uniformly absorbed by all the electrons continuously. Hence, the amount of energy absorbed per second per electron is:
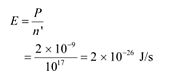
Time required for photoelectric emission:
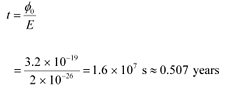
The time required for the photoelectric emission is nearly half a year, which is not practical. Hence, the wave picture is in disagreement with the given experiment.
Ques 11.31:
Crystal diffraction experiments can be performed using X-rays, or electrons accelerated through appropriate voltage. Which probe has greater energy? (For quantitative comparison, take the wavelength of the probe equal to 1 Å, which is of the order of inter-atomic spacing in the lattice) (me= 9.11 × 10−31 kg).
Ans: An X-ray probe has a greater energy than an electron probe for the same wavelength.
Wavelength of light emitted from the probe, λ = 1 Å = 10−10 m
Mass of an electron, me = 9.11 × 10−31 kg
Planck’s constant, h = 6.6 × 10−34 Js
Charge on an electron, e = 1.6 × 10−19 C
The kinetic energy of the electron is given as:
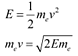
Where,
v = Velocity of the electron
mev = Momentum (p) of the electron
According to the de Broglie principle, the de Broglie wavelength is given as:
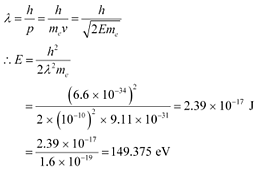
Energy of a photon, 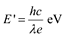
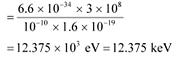
Hence, a photon has a greater energy than an electron for the same wavelength.
Ques 11.32:
(a) Obtain the de Broglie wavelength of a neutron of kinetic energy 150 eV. As you have seen in Exercise 11.31, an electron beam of this energy is suitable for crystal diffraction experiments. Would a neutron beam of the same energy be equally suitable? Explain. (mn= 1.675 × 10−27 kg)
(b) Obtain the de Broglie wavelength associated with thermal neutrons at room temperature (27 ºC). Hence explain why a fast neutron beam needs to be thermalised with the environment before it can be used for neutron diffraction experiments.
Ans: (a) De Broglie wavelength = ; neutron is not suitable for the diffraction experiment
; neutron is not suitable for the diffraction experiment
Kinetic energy of the neutron, K = 150 eV
= 150 × 1.6 × 10−19
= 2.4 × 10−17 J
Mass of a neutron, mn = 1.675 × 10−27 kg
The kinetic energy of the neutron is given by the relation:

Where,
v = Velocity of the neutron
mnv = Momentum of the neutron
De-Broglie wavelength of the neutron is given as:
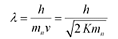
It i$ clear that wavelength is inversely proportional to the square root of mass. Hence, wavelength decreases with increase in mass and vice versa.

It is given in the previous problem that the inter-atomic spacing of a crystal is about 1 Å, i.e., 10−10 m. Hence, the inter-atomic spacing is about a hundred times greater. Hence, a neutron beam of energy
150 eV is not suitable for diffraction experiments.
(b) De Broglie wavelength = 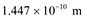
Room temperature, T = 27°C = 27 + 273 = 300 K
The average kinetic energy of the neutron is given as:


Where,
k = Boltzmann constant = 1.38 × 10−23 J mol−1 K−1
The wavelength of the neutron is given as:
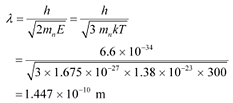
This wavelength is comparable to the inter-atomic spacing of a crystal. Hence, the high-energy neutron beam should first be thermalised, before using it for diffraction.
Ques 11.33:
An electron microscope uses electrons accelerated by a voltage of 50 kV. Determine the de Broglie wavelength associated with the electrons. If other factors (such as numerical aperture, etc.) are taken to be roughly the same, how does the resolving power of an electron microscope compare with that of an optical microscope which uses yellow light?
Ans: Electrons are accelerated by a voltage, V = 50 kV = 50 × 103 V
Charge on an electron, e = 1.6 × 10−19 C
Mass of an electron, me = 9.11 × 10−31 kg
Wavelength of yellow light = 5.9 × 10−7 m
The kinetic energy of the electron is given as:
E = eV
= 1.6 × 10−19 × 50 × 103
= 8 × 10−15 J
De Broglie wavelength is given by the relation:
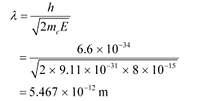
This wavelength is nearly 105 times less than the wavelength of yellow light.
The resolving power of a microscope is inversely proportional to the wavelength of light used. Thus, the resolving power of an electron microscope is nearly 105 times that of an optical microscope.
Ques 11.34:
The wavelength of a probe is roughly a measure of the size of a structure that it can probe in some detail. The quark structure of protons and neutrons appears at the minute length-scale of 10−15 m or less. This structure was first probed in early 1970’s using high energy electron beams produced by a linear accelerator at Stanford, USA. Guess what might have been the order of energy of these electron beams. (Rest mass energy of electron = 0.511 MeV.)
Ans: Wavelength of a proton or a neutron, λ ≈ 10−15 m
Rest mass energy of an electron:
m0c2 = 0.511 MeV
= 0.511 × 106 × 1.6 × 10−19
= 0.8176 × 10−13 J
Planck’s constant, h = 6.6 × 10−34 Js
Speed of light, c = 3 × 108 m/s
The momentum of a proton or a neutron is given as:

The relativistic relation for energy (E) is given as:


Thus, the electron energy emitted from the accelerator at Stanford, USA might be of the order of 1.24 BeV.
Ques 11.35:
Find the typical de Broglie wavelength associated with a He atom in helium gas at room temperature (27 ºC) and 1 atm pressure; and compare it with the mean separation between two atoms under these conditions.
Ans: De Broglie wavelength associated with He atom = 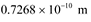
Room temperature, T = 27°C = 27 273 = 300 K
Atmospheric pressure, P = 1 atm = 1.01 × 105 Pa
Atomic weight of a He atom = 4
Avogadro’s number, NA = 6.023 × 1023
Boltzmann constant, k = 1.38 × 10−23 J mol−1 K−1
Average energy of a gas at temperature T,is given as:
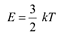
De Broglie wavelength is given by the relation:
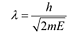
Where,
m = Mass of a He atom
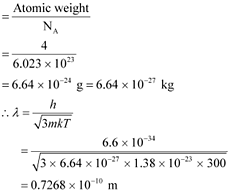
We have the ideal gas formula:
PV = RT
PV = kNT

Where,
V = Volume of the gas
N = Number of moles of the gas
Mean separation between two atoms of the gas is given by the relation:
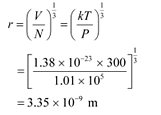

Hence, the mean separation between the atoms is much greater than the de Broglie wavelength.
Ques 11.36:
Compute the typical de Broglie wavelength of an electron in a metal at 27 ºC and compare it with the mean separation between two electrons in a metal which is given to be about 2 × 10−10 m.
[Note: Exercises 11.35 and 11.36 reveal that while the wave-packets associated with gaseous molecules under ordinary conditions are non-overlapping, the electron wave-packets in a metal strongly overlap with one another. This suggests that whereas molecules in an ordinary gas can be distinguished apart, electrons in a metal cannot be distinguished apart from one another. This indistinguishibility has many fundamental implications which you will explore in more advanced Physics courses.]
Ans: Temperature, T = 27°C = 27 273 = 300 K
Mean separation between two electrons, r = 2 × 10−10 m
De Broglie wavelength of an electron is given as:

Where,
h = Planck’s constant = 6.6 × 10−34 Js
m = Mass of an electron = 9.11 × 10−31 kg
k = Boltzmann constant = 1.38 × 10−23 J mol−1 K−1
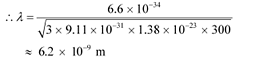
Hence, the de Broglie wavelength is much greater than the given inter-electron separation.
Ques 11.37:
Answer the following questions:
(a) Quarks inside protons and neutrons are thought to carry fractional charges [( 2/3)e ; (−1/3)e]. Why do they not show up in Millikan’s oil-drop experiment?
(b) What is so special about the combination e/m? Why do we not simply talk of e and m separately?
(c) Why should gases be insulators at ordinary pressures and start conducting at very low pressures?
(d) Every metal has a definite work function. Why do all photoelectrons not come out with the same energy if incident radiation is monochromatic? Why is there an energy distribution of photoelectrons?
(e) The energy and momentum of an electron are related to the frequency and wavelength of the associated matter wave by the relations:
E = hν, p = 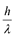
But while the value of λ is physically significant, the value of ν (and therefore, the value of the phase speed νλ) has no physical significance. Why?
Ans: (a) Quarks inside protons and neutrons carry fractional charges. This is because nuclear force increases extremely if they are pulled apart. Therefore, fractional charges may exist in nature; observable charges are still the integral multiple of an electrical charge.
(b) The basic relations for electric field and magnetic field are
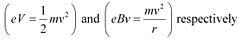
These relations include e (electric charge), v (velocity), m (mass), V (potential), r (radius), and B (magnetic field). These relations give the value of velocity of an electron as 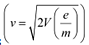 and
and 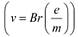
It can be observed from these relations that the dynamics of an electron is determined not by e and m separately, but by the ratio e/m.
(c) At atmospheric pressure, the ions of gases have no chance of reaching their respective electrons because of collision and recombination with other gas molecules. Hence, gases are insulators at atmospheric pressure. At low pressures, ions have a chance of reaching their respective electrodes and constitute a current. Hence, they conduct electricity at these pressures.
(d) The work function of a metal is the minimum energy required for a conduction electron to get out of the metal surface. All the electrons in an atom do not have the same energy level. When a ray having some photon energy is incident on a metal surface, the electrons come out from different levels with different energies. Hence, these emitted electrons show different energy distributions.
(e) The absolute value of energy of a particle is arbitrary within the additive constant. Hence, wavelength (λ) is significant, but the frequency (ν) associated with an electron has no direct physical significance.
Therefore, the product νλ(phase speed)has no physical significance.
Group speed is given as:

This quantity has a physical meaning.
|
199 videos|422 docs|281 tests
|
FAQs on Dual Nature of Radiation & Matter - 2 NCERT Solutions - Physics for Airmen Group X - Airforce X Y / Indian Navy SSR
| 1. What is the dual nature of radiation and matter? |  |
| 2. What is the photoelectric effect? |  |
| 3. How does the intensity of light affect the photoelectric effect? |  |
| 4. What are the main features of the experimental setup used to study the photoelectric effect? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the photoelectric effect? |  |


















