NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 - Heredity and Evolution
Page No. 129
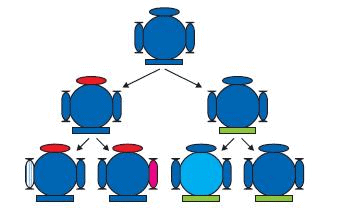
Q1: If a trait A exists in 10% of a population of an asexually reproducing species and a trait B exists in 60% of the same population, which trait is likely to have arisen earlier?
Ans.
- In asexual reproduction, the reproducing cells produce a copy of their DNA through some chemical reactions.
- However, this copying of DNA is not accurate and therefore, the newly formed DNA has some variations.

- It can be easily observed in the above figure that in asexual reproduction, very few variations are allowed.
- Therefore, if a trait is present in only 10% of the population, it is more likely that the trait has arisen recently.
- Hence, it can be concluded that trait B that exists in 60% of the same population has arisen earlier than trait A.
Q2: How does the creation of variations in a species promote survival?
Ans.
- Sometimes for a species, the environmental conditions change so drastically that their survival becomes difficult.
Example: If the temperature of water increases suddenly, most of the bacteria living in that water would die. Only few variants resistant to heat would be able to survive. If these variants were not there, then the entire species of bacteria would have been destroyed. - Thus, these variants help in the survival of the species.
- However, not all variations are useful.
- Therefore, these are not necessarily beneficial for the individual organisms.
Page No. 133
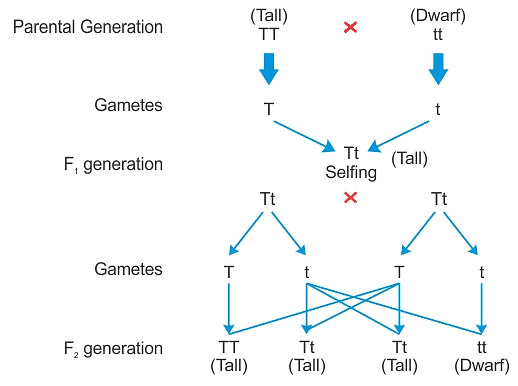
Q1: How do Mendel’s experiments show that traits may be dominant or recessive?
Ans.
- Mendel selected true breeding tall (TT) and dwarf (tt) pea plants. Then, he crossed these two plants.
- The seeds formed after fertilization were grown and these plants that were formed represent the first filial or F1 generation.
- All the F1 plants obtained were tall.
- Then, Mendel self-pollinated the F1 plants and observed that all plants obtained in the F2 generation were not tall.
- Instead, one-fourth of the F2 plants were short.

- From this experiment, Mendel concluded that the F1 tall plants were not true-breeding.
- They were carrying traits of both short height and tall height. They appeared tall only because the tall trait is dominant over the dwarf trait.
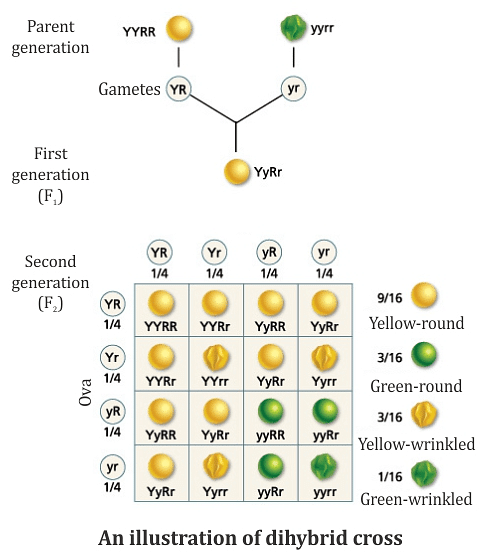
Q2: How do Mendel’s experiments show that traits are inherited independently?
Ans.
- Mendel crossed pea plants having round green seeds (RRyy) with pea plants having wrinkled yellow seeds (rrYY).
- Since the F1 plants are formed after crossing pea plants having green round seeds and pea plants having yellow wrinkled seeds, F1 generation will have both these characters in them.
- However, as we know that yellow seed colour and round seeds are dominant characters, therefore, the F1 plants will have yellow round seeds.
- Then this F1 progeny was self-pollinated and the F2 progeny was found to have yellow round seeds, green round seeds, yellow wrinkled seeds, and green wrinkled seeds in the ratio of 9:3:3:1.

- In the above cross, more than two factors are involved, and these are independently inherited.
Q3: A man with blood group A marries a woman with blood group O and their daughter has blood group O. Is this information enough to tell you which of the traits − blood group A or O − is dominant? Why or why not?
Ans.
- No. This information is not sufficient to determine which of the traits − blood group A or O − is dominant.
- This is because we do not know about the blood group of all the progeny.
- Blood group A can be genotypically AA or AO. Hence, the information is incomplete to draw any such conclusion.
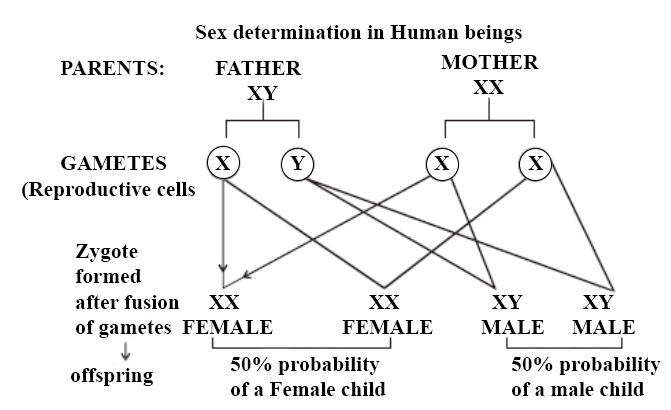
Q4: How is the sex of the child determined in human beings?
Ans.
- In human beings, the females have two X chromosomes and the males have one X and one Y chromosome.
- Therefore, the females are XX and the males are XY.
- The gametes, as we know, receive half of the chromosomes.
- The male gametes have 22 autosomes and either X or Y sex chromosome.
Type of male gametes: 22+X OR 22+ Y. - However, since the females have XX sex chromosomes, their gametes can only have X sex chromosome.
- Type of female gamete: 22+ X

- Thus, the mother provides only X chromosomes. The sex of the baby is determined by the type of male gamete (X or Y) that fuses with the X chromosome of the female.
Exercises
Q1: A Mendelian experiment consisted of breeding tall pea plants bearing violet flowers with short pea plants bearing white flowers. The progeny all bore violet flowers, but almost half of them were short. This suggests that the genetic make-up of the tall parent can be depicted as
(a) TTWW
(b) TTww
(c) TtWW
(d) TtWw
Ans. (c)
Explanation:
- The genetic make-up of the tall parent can be depicted as TtWW
- Since all the progeny bore violet flowers, it means that the tall plant having violet flowers has WW genotype for violet flower colour.
- Since the progeny is both tall and short, the parent plant was not a pure tall plant.
- Its genotype must be Tt.
- Therefore, the cross involved in the given question is

- Therefore, half the progeny is tall, but all of them have violet flowers.
Ans: No. From the given statement, we cannot say with certainty whether light eye colour is dominant or recessive. However, since both children and their parents have light eye colour, the possibility is that light eye colour is a recessive trait. Had the light eye colour been a dominant trait, the homozygous light eyed parents would have only light eyed children but heterozygous light eyed parent might had some recessive dark eyed children (3 : 1 ratio).
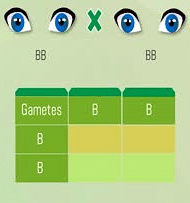
Q3: Outline a project which aims to find the dominant coat colour in dogs?
Ans: Select a homozygous black BB male dog and a homozygous white bb female dog. Crossbreed them and produce offspring F1 generation. If all the offsprings are black we can conclude that black coat colour is dominant over white coat in dogs.
Q4: How is the equal genetic contribution of male and female parents ensured in the progeny?
Ans: The gametes of both the male and the female parent have half the genetic information required for the offspring. Hence, 23 chromosomes are inherited from the father and 23 chromosomes from the mother. Hence, there is an equal contribution of male and females to the offspring.
|
85 videos|437 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 - Heredity and Evolution
| 1. What is heredity and how does it influence traits in living organisms? |  |
| 2. How do dominant and recessive genes affect inheritance patterns? |  |
| 3. Can heredity be influenced by environmental factors? |  |
| 4. How does genetic variation contribute to the diversity of species? |  |
| 5. What are some common genetic disorders that are inherited through heredity? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|