NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 - Lines and Angles
Exercise 6.1
Q1. In the following figure, lines AB and CD intersect at O. If ∠AOC +∠BOE = 70° and ∠BOD = 40°, find ∠BOE and reflex ∠COE.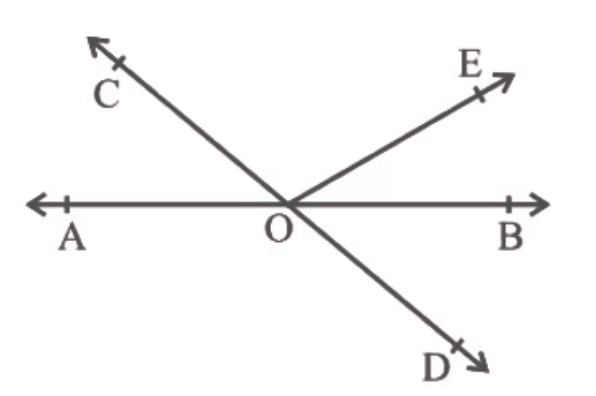
Ans:
AB is a straight line, OC and OE are rays from O.
We know that a straight line covers 180°
⇒ ∠AOC + ∠COE + ∠BOE = 180°
By clubbing ∠AOC and ∠BOE together we can rewrite the above equation as
⇒ (∠AOC + ∠BOE) + ∠COE = 180°
Putting ∠AOC + ∠BOE = 70°
⇒ 70° + ∠COE = 180°
⇒ ∠COE = 180° - 70°
⇒∠COE = 110°
Hence reflex ∠COE = 360° - 110°
reflex ∠COE = 250°
Similarly, CD is a straight line, OB and OE are rays from O.
We know that a straight line covers 180°
⇒ ∠BOD + ∠COE + ∠BOE = 180°
⇒ 40° + 110° + ∠BOE = 180°
⇒ ∠BOE = 180° - (40° + 110°)
⇒ ∠BOE = 180° - 150°
⇒ ∠BOE = 30°
Hence ∠BOE = 30° and reflex ∠COE = 250°
Q2. In the following figure, lines XY and MN intersect at O. If ∠POY = 90° and a : b = 2 : 3, find c.
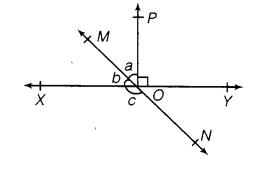
Ans: We know that the sum of linear pair is always 180°.
So,
POY +a +b = 180°
Putting the value of POY = 90° (as given in the question) we get,
a+b = 90°
Now, it is given that a : b = 2 : 3 so,
Let a be 2x and b be 3x
∴ 2x+3x = 90°
Solving this we get
5x = 90°
So, x = 18°
∴ a = 2×18° = 36°
Similarly, b can be calculated and the value will be
b = 3×18° = 54°
From the diagram, b+c also forms a straight angle so,
b+c = 180°
c+54° = 180°
∴ c = 126°
Q3. In the following figure, ∠PQR = ∠PRQ, then prove that ∠PQS = ∠PRT.
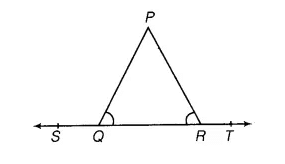
Ans:
ST is a straight line, QP is a line segment from Q in ST to any point P.
∠PQS + ∠PQR = 180° (linear pair)
⇒ ∠PQR = 180° - ∠PQS ......(1)
Similarly
∠PRT + ∠PRQ = 180° (linear pair)
⇒ ∠PRQ = 180° - ∠PRT ......(2)
Now, ∠PQR = ∠PRQ (as given in the question)
Therefore, on equating equations (1) and (2), we get
180° - ∠PQS = 180° - ∠PRT
⇒ ∠PQS = ∠PRT
Hence proved
Q4. In the following figure, if x + y = w + z, then prove that AOB is a line.
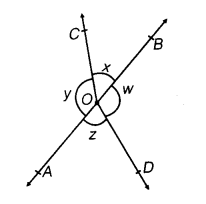
Ans: For proving AOB is a straight line, we will have to prove x+y is a linear pair
i.e. x+y = 180°
We know that the angles around a point are 360° so,
x + y + w + z = 360°
In the question, it is given that,
x+y = w+z
So, (x+y)+(x+y) = 360°
2(x+y) = 360°
∴ (x+y) = 180° (Hence proved).
Q5. In the adjoining figure, POQ is a line. Ray OR is perpendicular to line PQ. OS is another ray lying between rays OP and OR. Prove that ∠ROS = ½ (∠QOS – ∠POS).
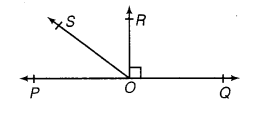
Ans:
Since OR ⊥ PQ
Therefore,
∠POR = 90°
∠POS + ∠ROS = 90°
⇒ ∠ROS = 90° - ∠POS … (1)
Similarly,
∠QOR = 90° (Since OR ⊥ PQ)
∴ ∠QOS - ∠ROS = 90°
⇒ ∠ROS = ∠QOS - 90° … (2)
Adding equations (1) and (2), 90° gets cancelled out
⇒ 2∠ROS = ∠QOS - ∠POS
Which can easily be written as
⇒ ∠ROS = ½ (∠QOS - ∠POS)
Hence proved
Q6. It is given that ∠XYZ = 64° and XY is produced to point P. Draw a figure from the given information. If ray YQ bisects ∠ZYP, find ∠XYQ and reflex ∠QYP.
Ans:
 Here, XP is a straight line.
Here, XP is a straight line.
It is given that line YQ bisects ∠ZYP.
Hence, ∠QYP = ∠ZYQ
It can easily be understood that PX is a line, YQ and YZ being rays standing on it.
∠XYZ + ∠ZYQ + ∠QYP = 180°
From above relation ∠QYP = ∠ZYQ we can write
64° + 2∠QYP = 180°
⇒ 2∠QYP = 180° – 64°
⇒ ∠QYP = 58°
Therefore ∠ZYQ = 58°
Also Reflex ∠QYP = 302°
Now we can write ∠XYQ as below
∠XYQ = ∠XYZ + ∠ZYQ
64° + 58° = 122°
Therefore we found ∠XYQ = 122° and so the Reflex ∠QYP = 302°
Exercise 6.2
Q1. In the following Figure, if AB || CD, CD || EF and y : z = 3 : 7, find x.
Ans:
It is given that AB || CD and CD || EF
∴ AB || CD || EF (Lines parallel to other fixed line are parallel to each other)
It can easily be understood that
x = z (since alternate interior angles are equal) … (1)
It is given that y : z = 3 : 7
Let y = 3a and z = 7a
Also, x + y = 180° (Co-interior angles together sum up to 180°)
z + y = 180°
It can further written as shown
7a + 3a = 180°
⇒ 10a = 180°
⇒ a = 18°
From equation one ∠z = ∠x
∠z = ∠x = 7 × a
∴ x = 7 × 18°
∴ x = 126°
Q2. In the following figure, if AB || CD, EF ⊥ CD and ∠GED = 126°, find ∠AGE, ∠GEF and ∠FGE.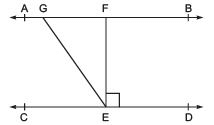 Ans: We are given that,
Ans: We are given that,
AB || CD and EF ⊥ CD and
∠GED = 126°
Which can be written as
⇒ ∠GEF + ∠FED = 126°
⇒ ∠GEF + 90° = 126°
Hence, we can obtain ∠GEF as shown below
⇒ ∠GEF = 126° - 90°
⇒ ∠GEF = 36°
∠AGE = ∠GED = 126° (∠AGE and ∠GED are alternate interior angles)
But
∠AGE + ∠FGE = 180° (because these form a linear pair)
⇒ 126° + ∠FGE = 180°
⇒ ∠FGE = 180° - 126°
⇒ ∠FGE = 54°
Hence, we found ∠AGE = 126°, ∠GEF = 36°, ∠FGE = 54°
Q3. In the following figure, if PQ || ST, ∠PQR = 110° and ∠RST = 130°, find ∠QRS.
[Hint : Draw a line parallel to ST through point R.]
Ans: 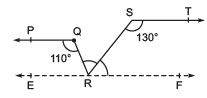 In this question we will have some construction of our own, we draw a line XY parallel to ST and so parallel to PQ passing through point R.
In this question we will have some construction of our own, we draw a line XY parallel to ST and so parallel to PQ passing through point R.
∠PQR + ∠QRX = 180° (Co-interior angles on the same side of transversal QR together sum up to 180°)
∴ 110° + ∠QRX = 180°
⇒ ∠QRX = 70°
Also,
∠RST + ∠SRY = 180° (sum of Co-interior angles on the same side of transversal SR equals 180°)
⇒ ∠SRY = 180° - 130°
⇒ ∠SRY = 50°
Now from the construction XY is a straight line. RQ and RS are rays from it.
∠RX + ∠QRS + ∠SRY = 180°
⇒ 70° + ∠QRS + 50° = 180°
Hence we found that
∠QRS = 60°
Q4. In the following figure, if AB || CD, ∠ APQ = 50° and ∠ PRD = 127°, find x and y.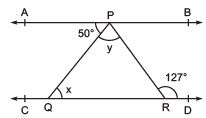 Ans: From the diagram,
Ans: From the diagram,
∠APQ = ∠PQR (Alternate interior angles)
Now, putting the value of ∠APQ = 50° and ∠PQR = x, we get
x = 50°
Also,
∠APR = ∠PRD (Alternate interior angles)
Or, ∠APR = 127° (As it is given that ∠PRD = 127°)
We know that
∠APR = ∠APQ+∠QPR
Now, putting values of ∠QPR = y and ∠APR = 127°, we get
127° = 50°+ y
Or, y = 77°
Thus, the values of x and y are calculated as:
x = 50° and y = 77°
Q5. In the following figure, PQ and RS are two mirrors placed parallel to each other. An incident ray AB strikes the mirror PQ at B, the reflected ray moves along the path BC and strikes the mirror RS at C and again reflects back along CD. Prove that AB || CD.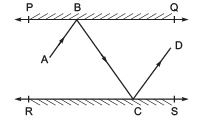
Ans: First, draw two lines, BE and CF, such that BE ⊥ PQ and CF ⊥ RS.
Now, since PQ || RS,
So, BE || CF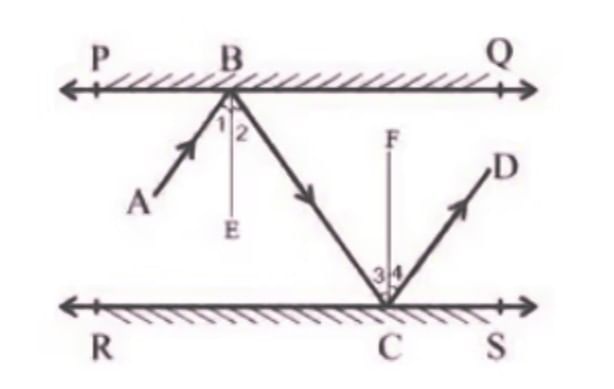
We know that,
Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection (By the law of reflection)
So,
∠1 = ∠2 and
∠3 = ∠4
We also know that alternate interior angles are equal. Here, BE ⊥ CF and the transversal line BC cuts them at B and C
So, ∠2 = ∠3 (As they are alternate interior angles)
Now, ∠1 +∠2 = ∠3 +∠4
Or, ∠ABC = ∠DCB
So, AB || CD (alternate interior angles are equal)
|
40 videos|471 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 - Lines and Angles
| 1. What are lines and angles? |  |
| 2. How do you classify angles based on their measures? |  |
| 3. What is the relationship between parallel lines and transversals? |  |
| 4. How can we determine if two lines are perpendicular? |  |
| 5. What is the sum of the angles in a triangle? |  |

















