NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science - Periodic Classification of Elements
In-Text Questions
Page No: 81
Ques 1. Did Dobereiner's triads also exist in the columns of Newlands' Octaves? Compare and find out.
Ans: Yes, Dobereiner's triads also exist in the columns of Newlands' Octaves. One such column is Li, K, Na.
Newlands’ octaves:
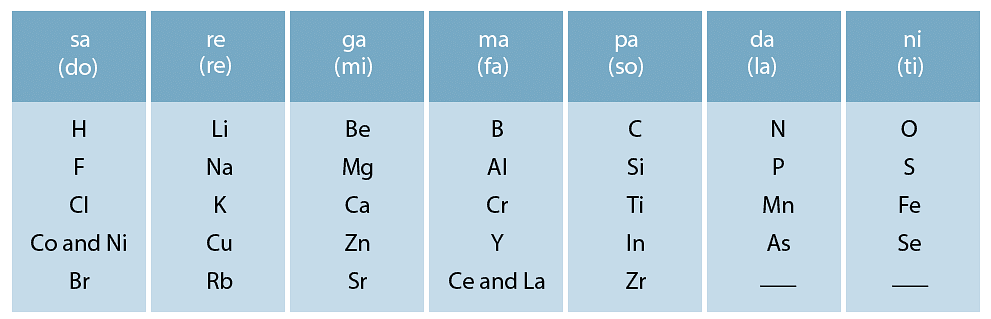
Ques 2. What were the limitations of Dobereiner's classification?
Ans: Limitation of Dobereiner's classification:
(i) He could only classify three triads from the elements discovered at that time.
(ii) Many chemically similar elements like nitrogen, phosphorus and arsenic could not prove the validity of Dobereiner’s theory of triads.
(iii) Many elements having different chemical properties like carbon, nitrogen and oxygen could not verify his theory of triads.
Ques 3. What were the limitations of Newlands' Law of Octaves?
Ans: Limitations of Newlands' law of octaves:
- It was not applicable throughout the arrangements. It was applicable up to calcium only. The properties of the elements listed after calcium showed no resemblance to the properties of the elements above them.
- Those elements which were discovered after Newlands' octaves did not follow the law of octaves.
- The position of cobalt and nickel in the group of the elements (F, Cl) of different properties could not be explained.
- Placing of iron far away from cobalt and nickel, which have similar properties as iron, could also not be explained.
Page No: 85
Ques 1. Use Mendeleev's Periodic Table to predict the formulae for the oxides of the following elements:
K, C, Al, Si, Ba.
Ans: Oxygen is a member of group VI A in Mendeleev’s periodic table. Its valency is 2. Similarly, the valencies of all the elements listed can be predicted from their respective groups. This will help in writing the formulae of their oxides.
(i) Potassium (K) is a member of group IA. Its valency is 1. Therefore, the formula of its oxide is K2O.
(ii) Carbon (C) is a member of group IV A. Its valency is 4. Therefore, the formula of its oxide is C2O4 or CO2.
(iii) Aluminium (Al) belongs to group III A and its valency is 3. The formula of its oxide is Al2O3.
(iv) Silicon (Si) is present in group IV A after carbon. Its valency is also 4. The formula of its oxide is Si2O4 or SiO2.
(v) Barium (Ba) belongs to group II A and the valency of the element is 2. The formula of its oxide of the element is Ba2O2 or BaO.
Ques 2. Besides gallium, which other elements have since been discovered that were left by Mendeleev in his Periodic Table? (any two)
Ans: Scandium and germanium are the elements that are left by Mendeleev in his Periodic Table since its discovery.
Ques 3. What were the criteria used by Mendeleev in creating his Periodic Table?
Ans: Mendeleev’s periodic table was based on the observation that the properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic masses. This means that if elements are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic masses, then their properties get repeated after regular intervals.
Ques 4. Why do you think the noble gases are placed in a separate group?
Ans: Noble gases are inert elements. Their properties are different from all other elements. Therefore, the noble gases are placed in a separate group.
Page No: 90
Ques 1. How could the Modern Periodic Table remove various anomalies of Mendeleev's Periodic Table?
Ans: Various anomalies of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table removed as follows in the Modern Periodic Table:
- Elements are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic number in Modern Periodic Table, thus there was no need for keeping more than one element in one slot.
- In Modern Periodic Table, there was no problem of the place of isotopes, as isotopes have same atomic mass with different atomic numbers.
- Elements having same valence electron are kept in same group.
- Elements having same number of shells were put under the same period.
- Position of hydrogen became clarified in as it is kept in the group with the elements of same valence electrons.
Ques 2. Name two elements you would expect to show chemical reactions similar to magnesium. What is the basis for your choice?
Ans: Calcium (Ca) and Strontium (Sr) are expected to show chemical reactions similar to magnesium (Mg). This is because the number of valence electrons (2) is the same in all these three elements and since chemical properties are due to valence electrons, they show the same chemical reactions.
Ques 3. Name
(a) three elements that have a single electron in their outermost shells.
(b) two elements that have two electrons in their outermost shells.
(c) three elements with filled outermost shells.
Ans:
(a) Lithium (Li), sodium (Na), and potassium (K) have a single electron in their outermost shells.
(b) Magnesium (Mg) and calcium (Ca) have two electrons in their outermost shells.
(c) Neon (Ne), argon (Ar), and xenon (Xe) have filled outermost shells.
Ques 4. (a) Lithium, sodium, potassium are all metals that react with water to liberate hydrogen gas. Is there any similarity in the atoms of these elements?
(b) Helium is an unreactive gas and neon is a gas of extremely low reactivity. What, if anything, do their atoms have in common?
Ans:
(a) Yes. The atoms of all the three elements lithium, sodium, and potassium have one electron in their outermost shells.
(b) Both helium (He) and neon (Ne) have filled outermost shells. Helium has a duplet in its K shell, while neon has an octet in its L shell.
Ques 5. In the Modern Periodic Table, which are the metals among the first ten elements?
Ans: Among the first ten elements, lithium (Li) and beryllium (Be) are metals.
Ques 6. By considering their position in the Periodic Table, which one of the following elements would you expect to have maximum metallic characteristic?
Ans: Among the elements listed in the question. Be and Ga are expected to be most metallic. Out of Be and Ga, Ga is bigger in size and hence has a greater tendency to lose electrons than Be. Therefore, Ga is more metallic than Be.
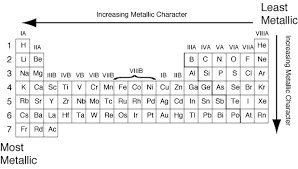
Fig: Maximum Metallic
Exercise
Page No: 91
Ques 1. Which of the following statements is not a correct statement about the trends when going from left to right across the periods of Periodic Table.
(a) The elements become less metallic in nature.
(b) The number of valence electrons increases.
(c) The atoms lose their electrons more easily.
(d) The oxides become more acidic.
Ans:
(c) The atoms lose their electrons more easily.
(On moving from left to right across the periods of the periodic table, the non-metallic character increases. Hence, the tendency to lose electrons decreases.)
Ques 2. Element X forms a chloride with the formula XCl2, which is solid with a high melting point. X would most likely be in the same group of the Periodic Table as
(a) Na
(b) Mg
(c) Al
(d) Si
Ans:
(b) X would most likely be in the same group of the Periodic Table as magnesium (Mg).
Ques 3. Which element has
(a) two shells, both of which are completely filled with electrons?
(b) electronic configuration 2, 8, 2?
(c) a total of three shells, with four electrons in its valence shell?
(d) a total of two shells, with three electrons in its valence shell?
(e) twice as many electrons in its second shell as in its first shell?
Ans:
(a) Neon has two shells, both of which are completely filled with electrons (2 electrons in K shell and 8 electrons in L shell).
(b) Magnesium has the electronic configuration 2, 8, 2.
(c) Silicon has a total of three shells, with four electrons in its valence shell (2 electrons in K shell, 8 electrons in L shell and 4 electrons in M shell).
(d) Boron has a total of two shells, with three electrons in its valence shell (2 electrons in K shell and 3 electrons in L shell).
(e) Carbon has twice as many electrons in its second shell as in its first shell (2 electrons in K shell and 4 electrons in L shell).
Ques 4. (a) What property do all elements in the same column of the Periodic Table as boron have in common?
(b) What property do all elements in the same column of the Periodic Table as fluorine have in common?
Ans:
(a) All the elements in the same column as boron have the same number of valence electrons (3). Hence, they all have valency equal to 3.
(b) All the elements in the same column as fluorine have the same number of valence electrons (7). Hence, they all have valency equal to 1.
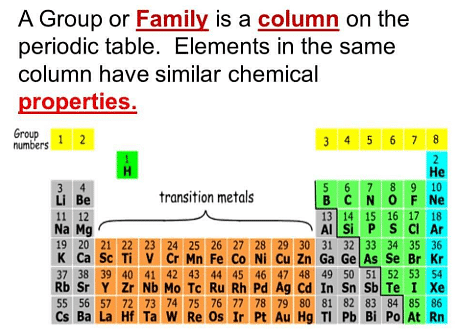
Fig: Periodic Table
Ques 5. An atom has electronic configuration 2, 8, 7.
(a) What is the atomic number of this element?
(b) To which of the following elements would it be chemically similar? (Atomic numbers are given in parentheses.)
N(7) F(9) P(15) Ar(18)
Ans:
(a) The atomic number of this element is 17.
(b) It would be chemically similar to F(9) with configuration as 2, 7.
Page No: 92
Ques 6. The position of three elements A, B and C in the Periodic Table are shown below -

(a) State whether A is a metal or non-metal.
(b) State whether C is more reactive or less reactive than A.
(c) Will C be larger or smaller in size than B?
(d) Which type of ion, cation or anion, will be formed by element A?
Ans:
(a) A is a non-metal.
(b) C is less reactive than A, as reactivity decreases down the group in halogens.
(c) C will be smaller in size than B as moving across a period, the nuclear charge increases and therefore, electrons come closer to the nucleus.
(d) A will form an anion as it accepts an electron to complete its octet.
Ques 7. Nitrogen (atomic number 7) and phosphorus (atomic number 15) belong to group 15 of the Periodic Table. Write the electronic configuration of these two elements. Which of these will be more electronegative? Why?
Ans:
Nitrogen (7): 2, 5
Phosphorus (15): 2, 8, 5
Nitrogen is more electronegative than phosphorus. On moving down a group, the number of shells increases. Therefore, the valence electrons move away from the nucleus and the effective nuclear charge decreases. This causes the decrease in the tendency to attract electrons and hence electronegativity decreases.
Fig: Electron Configuration chart
Since electronegativity decreases with moving from top to bottom in a group, thus Nitrogen will be more electronegative.
Ques 8. How does the electronic configuration of an atom relate to its position in the Modern Periodic Table?
Ans:
In the modern periodic table, atoms with similar electronic configurations are placed in the same column. In a group, the number of valence electrons remains the same.
Elements across a period show an increase in the number of valence electrons.
Ques 9. In the Modern Periodic Table, calcium (atomic number 20) is surrounded by elements with atomic numbers 12, 19, 21, and 38. Which of these have physical and chemical properties resembling calcium?
Ans:
The element with atomic number 12 has same chemical properties as that of calcium. This is because both of them have same number of valence electrons (2).
Fig: Modern Periodic Table
Ques 10. Compare and contrast the arrangement of elements in Mendeleev's periodic Table and the Modern Periodic Table.
Ans:
|
150 videos|391 docs|243 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science - Periodic Classification of Elements
| 1. What is the periodic classification of elements? |  |
| 2. How are elements arranged in the periodic table? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the periodic classification of elements? |  |
| 4. What are the characteristics of metals, non-metals, and metalloids in the periodic table? |  |
| 5. How does the periodic table help in understanding chemical reactions and bonding? |  |
|
150 videos|391 docs|243 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for BPSC (Bihar) exam
|

|


















