NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues
| Table of contents |

|
| Page No. 61 |

|
| Page No. 65 |

|
| Page No. 69 |

|
| Page No. 70 |

|
| Page No. 71 |

|
Page No. 61
Q1. What is a tissue?
Ans: A group of cells that are similar in structure and/or work together to achieve a particular function forms a tissue.
Q2. What is the utility of tissues in multi-cellular organisms?
Ans:
- Tissues are made up of a group of cells carrying a specialised function. Each specialised function is taken up by a different tissue. Since these cells of a tissue carry out only a particular function, they do it very efficiently.
- The use of tissues in multicellular organisms is to provide structural and mechanical strength.
- Example: In human beings, muscle cells contract or relax to cause movement, nerve cells carry messages, and blood flows to transport gases, food, hormones, waste materials and so on. Likewise, in plants, vascular tissues (xylem, phloem) conduct water and food from one part of the plant to other parts.
- So, multicellular organisms show a division of labour through tissues.
Page No. 65
Q1. Name types of simple tissues.
Ans: Simple permanent tissues are of three types:
(i) Parenchyma
(ii) Collenchyma
(iii) Sclerenchyma
Parenchyma tissue is of further two types:
(i) Aerenchyma
(ii) Chlorenchyma
Q2. Where is apical meristem found?
Ans: Apical meristem is present at the growing tips of stems and roots.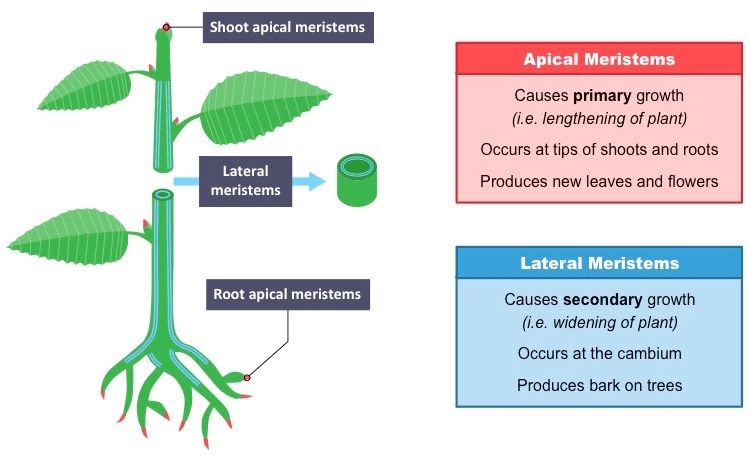
Q3. Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
Ans: Sclerenchyma tissue makes up the husk of coconut. These tissues cause the plant to become stiff and hard. The cells of this tissue are dead and their cell walls are thickened because of the presence of lignin.
Q4. What are the constituents of phloem?
Ans: The constituents of phloem are:
- Sieve tubes
- Companion cells
- Phloem parenchyma
- Phloem fibres
Page No. 69
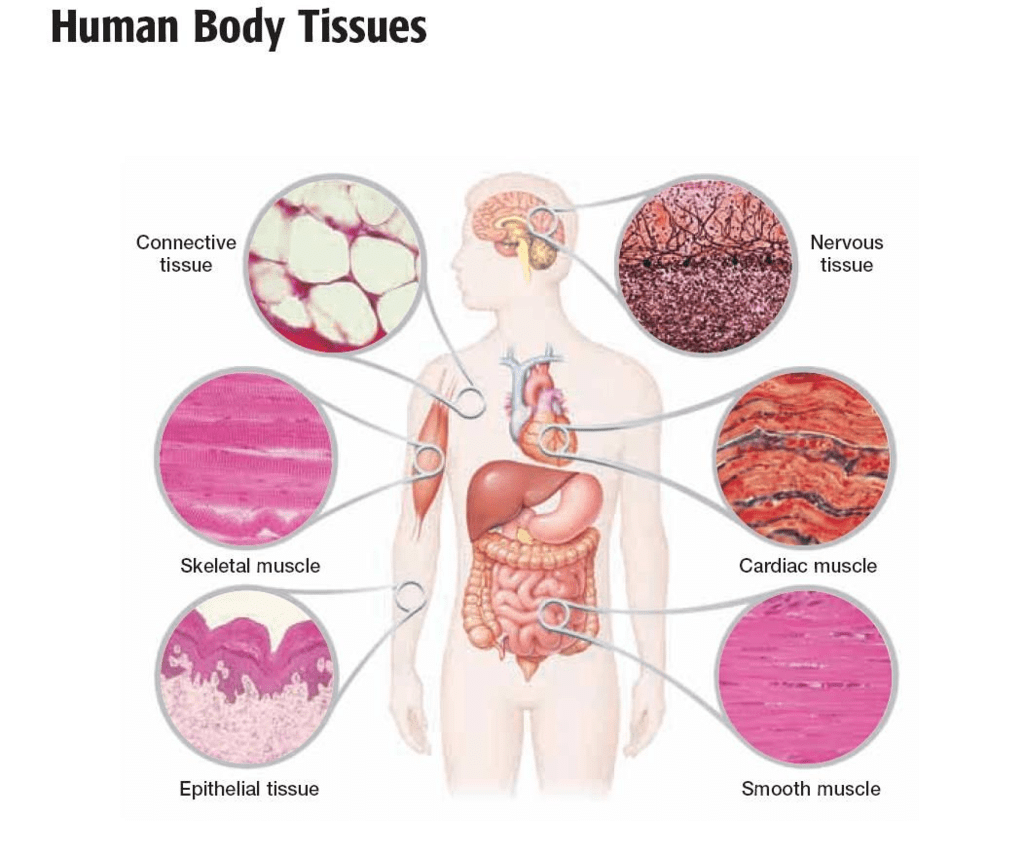
Ans: Two tissues jointly are responsible for the movement of our body, namely:
- Muscular tissue
- Nervous tissue
Q2. What does a neuron look like?
Ans: A neuron consists of a cell body with a nucleus and cytoplasm, from which long thin hair-like parts called dendrites arise. Each neuron has a single long part called the axon.
Q3. Give three features of cardiac muscles.
Ans:
Three features of cardiac muscles are:
(i) Cardiac muscles are involuntary.
(ii) Cardiac muscle cells are cylindrical, branched and uninucleate.
(iii) Cardiac muscles show rhythmic contraction and relaxation.
Q4. What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Ans: Areolar tissue acts as a supportive and packing tissue between organs lying in the body cavity, and also helps in the repair of tissues.
Page No. 70
Ans: A group of cells that are similar in structure and work together to achieve a particular function is called tissue.
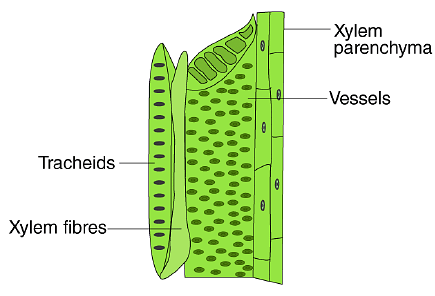
Q2. How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
Ans: Xylem is composed of the following elements:
- Tracheids
- Vessels
- Xylem parenchyma
- Xylem fibres

Q3. How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
Ans: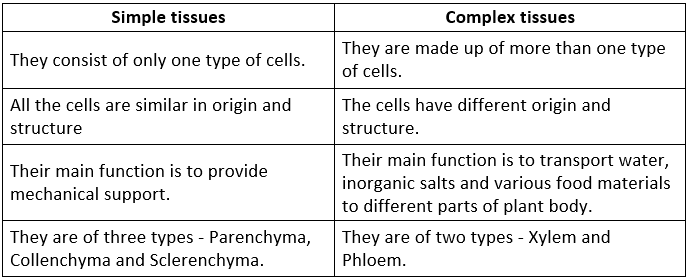
Q4. Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma, on the basis of their cell wall.
Ans: The differences between the cell walls of parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma are: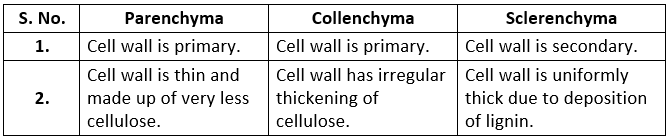
Q5. What are the functions of the stomata?
Ans: The functions of stomata are:
(i) Stomata allow gaseous exchange between the plant and the atmosphere.
(ii) These are sites of transpiration in plants.
Q6. Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle fibres.
Ans: The three types of muscle fibres are:
(i) Striated muscles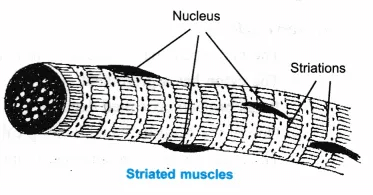 (ii) Smooth muscles (unstriated muscle fibre)
(ii) Smooth muscles (unstriated muscle fibre)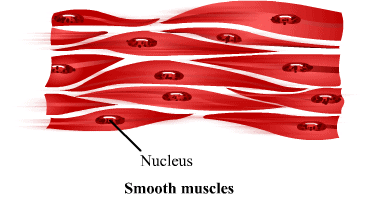 (iii) Cardiac muscles
(iii) Cardiac muscles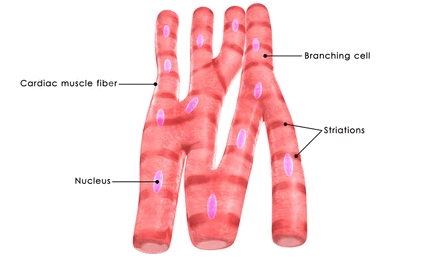
Q7. What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle?
Ans: The cardiac muscles are branched and cylindrical. They are uninucleated and are involuntary in nature. Throughout one’s lifetime, the cardiac muscles bring about the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart.
Q8. Differentiate between striated, unstriated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site/location in the body.
Ans: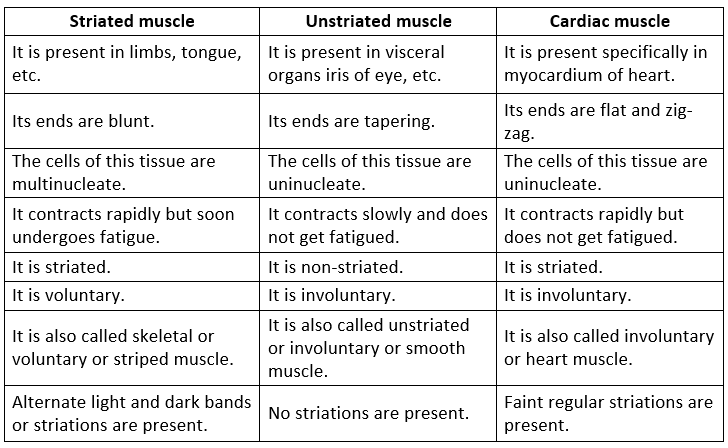
Q9. Draw a labelled diagram of a neuron.
Ans: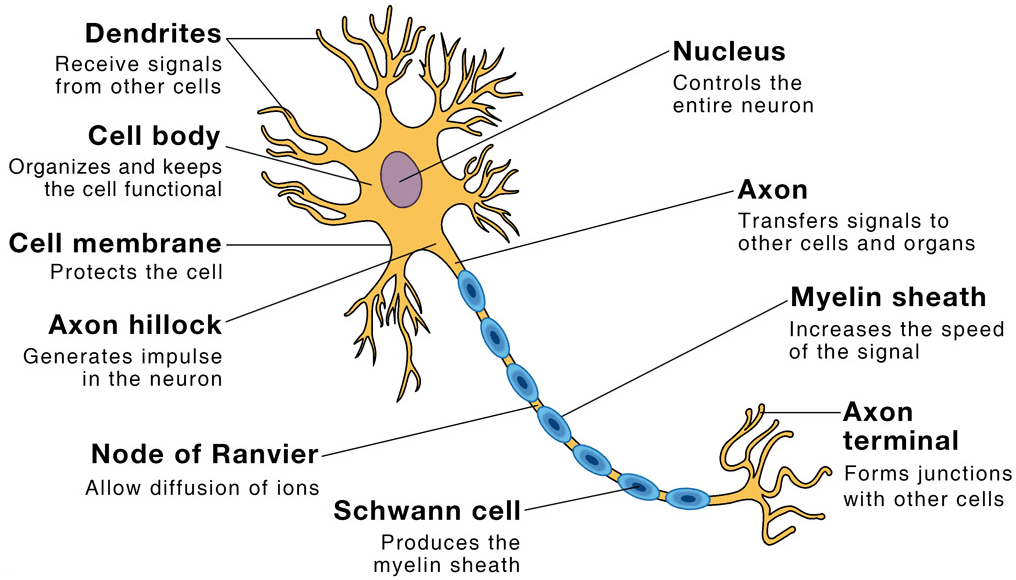
Q10. Name the following:
(a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth.
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans.
(c) Tissue that transports food in plants.
(d) Tissue that stores fat in our body.
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix.
(f) Tissue present in the brain.
Ans:
(a) Simple squamous epithelium
(b) Tendon
(c) Phloem
(d) Adipose tissue
(e) Blood
(f) Nervous tissue
Q11. Identify the type of tissue in the following:
Skin, Bark of Tree, Bone, Lining of Kidney Tubule, Vascular Bundle.
Ans:
Skin: Epithelial tissue (Squamous epithelium)
Bark of Tree: Cork (protective tissue)
Bone: Skeletal tissue (connective tissue)
Lining of Kidney Tubules: Cuboidal epithelial tissue
Vascular Bundle: Complex permanent tissue—xylem and phloem
Page No. 71
Q12. Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
Ans: Parenchyma tissues are found in:
- The pith of stems and roots.
- When parenchyma contains chlorophyll it is called as chlorenchyma, it is found in green leaves.
- Parenchyma found in aquatic plants have large air cavities that enable them to float and are hence called aerenchyma.
Q13. What is the role of the epidermis in plants?
Ans: Role of the epidermis in plants:
(i) It acts as a protective tissue, covering the plant body.
(ii) It protects the plant from excessive heat or cold and from the attack of parasitic fungi and bacteria.
(iii) It allows the exchange of gases and transpiration through stomata.
(iv) The cuticle of the epidermis checks the excessive evaporation of water.
Q14. How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
Ans: The cork cells are dead and do not have any intercellular spaces. The cell walls of the cork cells are coated with suberin (a waxy substance). Suberin makes these cells impermeable to water and gases, or in simpler words, it makes them waterproof and blocks gases from passing through. Thus, it protects underlying tissues from desiccation (loss of water from the plant body), infection and physical damage.
Q15. Complete the table:
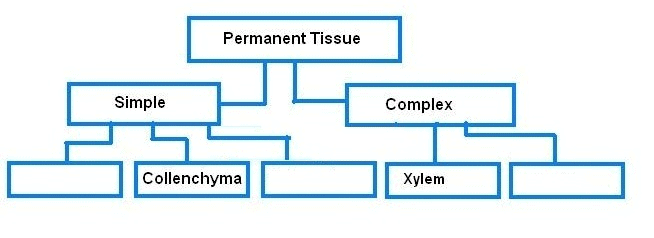 Ans:
Ans:
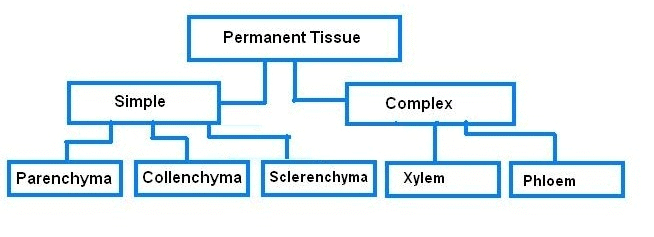
|
87 videos|369 docs|67 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues
| 1. What are the main types of plant tissues and their functions? |  |
| 2. How do animal tissues differ from plant tissues? |  |
| 3. What is the role of xylem in plants? |  |
| 4. What are the characteristics of muscular tissues in animals? |  |
| 5. Why is the study of tissues important in biology? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|